Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 pellets by 28 GHz microwave irradiation
pellets by 28 GHz microwave irradiationAkashi, Masatoshi; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 118, p.1391 - 1394, 2018/06
In this study, CeO pellet sintering by irradiating microwave at a frequency of 28 GHz was carried out to investigate the effect of particle diameter of raw powder on the density of sintered pellet. The highest bulk density is 94.2 %T.D. under the condition of 30 min holding at 1473 K. The bulk density decreases with increasing the particle diameter of used raw powder. On the other hand, all of the apparent density of sintered pellet is more than 93.5 %T.D.. The difference between the bulk density and the apparent density is caused by the difference of open porosity for each sample pellet. It seems that the high density sintered pellets with porous structure are obtained because sample pellet is heated internally and uniformly in microwave sintering.
pellet sintering by irradiating microwave at a frequency of 28 GHz was carried out to investigate the effect of particle diameter of raw powder on the density of sintered pellet. The highest bulk density is 94.2 %T.D. under the condition of 30 min holding at 1473 K. The bulk density decreases with increasing the particle diameter of used raw powder. On the other hand, all of the apparent density of sintered pellet is more than 93.5 %T.D.. The difference between the bulk density and the apparent density is caused by the difference of open porosity for each sample pellet. It seems that the high density sintered pellets with porous structure are obtained because sample pellet is heated internally and uniformly in microwave sintering.
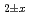
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 487, p.424 - 432, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:75.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential of (U,Pu)O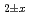 was evaluated based on defect chemistry using an updated experimental data set. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation
was evaluated based on defect chemistry using an updated experimental data set. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation  in (U,Pu)O
in (U,Pu)O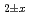 was analyzed, and equilibrium constants of defect formation were determined as functions of Pu content and temperature. Brouwer's diagrams were constructed using the determined equilibrium constants, and a relational equation to determine O/M ratio was derived as functions of O/M ratio, Pu content and temperature. In addition, relationship between oxygen potential and oxygen diffusion coefficients were described.
was analyzed, and equilibrium constants of defect formation were determined as functions of Pu content and temperature. Brouwer's diagrams were constructed using the determined equilibrium constants, and a relational equation to determine O/M ratio was derived as functions of O/M ratio, Pu content and temperature. In addition, relationship between oxygen potential and oxygen diffusion coefficients were described.
 -PuO
-PuO -ZrO
-ZrO pseudo-ternary system
pseudo-ternary systemMorimoto, Kyoichi; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi; Sugata, Hiromasa*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1247 - 1252, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)As a part of decommissioning plan of the damaged reactors at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, some strategies for removing of debris from the reactors are discussed. In these considerations, it is necessary to predict a melt progression during the severe accident based on theoretical evidences. Melting temperature is one of the most important thermal characteristics to analyse a melt progression during the severe accident. In this study, the melting temperatures of specimens of U, Pu and Zr mixed oxide prepared as simulated debris were measured by the thermal arrest technique. From the results of this measurement, the influences of Pu and Zr
and Zr contents on the melting temperature of the simulated debris were evaluated.
contents on the melting temperature of the simulated debris were evaluated.
Kato, Masato; Hirooka, Shun; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Akashi, Masatoshi; Maeda, Koji; Watanabe, Masashi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Proceedings of 19th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2014/08
Uranium and plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel has been developed for Japan sodium-cooled fast reactors. Science based fuel technologies have been developed to analyse behaviours of MOX pellets in the sintering process and irradiation conditions. The technologies can provide appropriate sintering conditions, irradiation behaviour analysis results and so on using mechanistic models which are derived based on theoretical equations to represent various properties.
 and zircaloy-2
and zircaloy-2Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Uchida, Teppei; Akashi, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 437(1-3), p.130 - 134, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.91 - 96, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and zircalloy-2
and zircalloy-2Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Uchida, Teppei; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1444, p.97 - 101, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hidaka, Jusuke*; Makino, Tadashi*; Akashi, Masatoshi*; Shimosaka, Atsuko*; Shirakawa, Yoshiyuki*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
The large-scale particle method supporting the optimized design of die filling of MOX granule in the first process of the formation of pellet's microstructure influencing MOX fuel pellets characteristics has been developed. The optimized granule characteristics and die filling conditions have been cleared using the simulations. The die filling flow behavior obtained by simulations extremely corresponded with that observed from the high speed camera in the various operation conditions, and the reliable die filling simulations of the full-scale examinations have been developed. This simulation can be applicable the MOX pellet fabrication process by varying the WO granule characteristic parameter to MOX.
granule characteristic parameter to MOX.
 and Zircalloy-2, 3; Effect of oxygen chemical potential on phase state
and Zircalloy-2, 3; Effect of oxygen chemical potential on phase stateAkashi, Masatoshi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -cladding simulated debris
-cladding simulated debrisHirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Uchida, Teppei; Akashi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akashi, Masatoshi; Nishina, Masahiro; Kato, Masato; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Shimosaka, Atsuko*; Shirakawa, Yoshiyuki*; Hidaka, Jusuke*
no journal, ,
Akashi, Masatoshi; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi
no journal, ,
Uranium oxide fuels containing Gd O
O had been used to control fuel power in reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant where the severe accident occurred in 2011. JAEA has been evaluating physical properties of the molten fuel debris in the damaged core. However physical properties of the fuel debris containing Gd are not known, hence it is very difficult to select an appropriate debris removal method. Especially, it is important to know the distribution of Gd in the molten fuels for the evaluation of nuclear criticality safety during removal work. In this study, simulated samples of the molten fuel debris, which consisted of ZrO
had been used to control fuel power in reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant where the severe accident occurred in 2011. JAEA has been evaluating physical properties of the molten fuel debris in the damaged core. However physical properties of the fuel debris containing Gd are not known, hence it is very difficult to select an appropriate debris removal method. Especially, it is important to know the distribution of Gd in the molten fuels for the evaluation of nuclear criticality safety during removal work. In this study, simulated samples of the molten fuel debris, which consisted of ZrO , UO
, UO and Gd
and Gd O
O , were prepared and their properties, which are density, crystal structure, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion and melting temperature, were investigated. This study includes results obtained under the research program entrusted to International Research Institute for Nuclear Decommissioning including Japan Atomic Energy Agency by Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) of Japan.
, were prepared and their properties, which are density, crystal structure, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion and melting temperature, were investigated. This study includes results obtained under the research program entrusted to International Research Institute for Nuclear Decommissioning including Japan Atomic Energy Agency by Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) of Japan.
 with iron
with ironAkashi, Masatoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi; Komeno, Akira; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
The influence of Gd on these characteristics is important for the prediction because subassemblies of Gd-bearing uranium oxide fuels were loaded in the some reactor cores of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Additionally, it is important to comprehend the placement of Gd in the debris from the view point of the re-criticality by relocation of the debris during removing the debris. In this study, U, Gd and Zr mixed oxide specimens were fabricated by the conventional powder metallurgy process and these specimens were melted and solidified to prepare simulated corium debris bearing Gd (sim-debris). Melting point and thermal conductivities of sim-debris were measured. X-ray diffraction analysis and electron probe microanalysis were conducted to evaluate the phase states.
Akashi, Masatoshi; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 as simulated corium debris
as simulated corium debrisMorimoto, Kyoichi; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi
no journal, ,
The influence of Gd on characteristics of debris is important for removing the debris from the reactors of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant because subassemblies of nuclear fuels containing Gd O
O were loaded in the some reactor cores. Additionally, it is important to assess the distribution state of Gd from the anxiety of re-criticality caused by the relocation of debris while removing them. In this study, sintered pellets of (U
were loaded in the some reactor cores. Additionally, it is important to assess the distribution state of Gd from the anxiety of re-criticality caused by the relocation of debris while removing them. In this study, sintered pellets of (U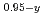 Gd
Gd Zr
Zr )O
)O (y=0,0.5, 2-x=1.989-2.000) were melted and solidified to prepare specimens of simulated corium debris. Phase states and fundamental properties of them were evaluated.
(y=0,0.5, 2-x=1.989-2.000) were melted and solidified to prepare specimens of simulated corium debris. Phase states and fundamental properties of them were evaluated.
Akashi, Masatoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi
no journal, ,
Akashi, Masatoshi; Nishina, Masahiro; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
A die filling experiment was carried out using granulated MOX powder to investigate the condition of MOX granules suitable for constant die filling. It was found that the mean particle diameter and the Hausner ratio gave an indication of the die filling for the granulated MOX powder.
Kitagaki, Toru; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Yano, Kimihiko; Hoshino, Takanori; Okamura, Nobuo; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ogino, Hideki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akashi, Masatoshi; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English