Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Ikezaki, Kiyomi*; Kawasaki, Tomoyuki; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Akutsu, Atsushi*; Nishikawa, Masaaki*; Fukuda, Shimpei
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerators (AccApp '15), p.255 - 260, 2016/00
Oi, Motoki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Akutsu, Atsushi*; Kawasaki, Tomoyuki; Nishikawa, Masaaki*; Fukuda, Shimpei
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerators (AccApp '15), p.89 - 96, 2016/00
At J-PARC, 3 GeV proton beam with power of 1MW is delivered to the spallation neutron source (JSNS) through beam transport line called 3NBT. At the high power accelerator facilities even a small abnormal event has a possibility to be critical so that the beam control system is crucial. In order to find tiny anomaly, rapid data analysis system is required. We developed control and data analysis system based on the Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS) and Control System Studio (CSS). To carry out beam tuning efficiently, the beam control system based on the Strategic Accelerator Design (SAD) code has been developed. With the several shots of beam and by the one click of operational panel of the screen, required magnet field can be calculated and set automatically. Also we developed automated e-mail system to announce the abnormal event to the experts persons. With these systems, we can reduce both beam tuning time and down time.
Oi, Motoki; Sakai, Kenji; Watanabe, Akihiko; Akutsu, Atsushi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takada, Hiroshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036007_1 - 036007_5, 2015/09
This paper reports on upgrading of the monitor and operation (MO) system for a general control system (GCS) of the Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC. The MLF-GCS consists of programmable logic controllers (PLCs), operator interfaces (OPIs) for integral control and interlock systems, shared servers, and so on. It is controlling various components of the pulsed spallation neutron source such as a mercury target and hydrogen moderators. The MO system is used for monitoring, alarm notification and remote control from the MLF control room. The GCS has been working well as expected, but current MO system which consists of the OPIs and data servers based on iFix has some problems in view of sustainable maintenance because of its poor flexibility of supported OS and software version compatibility. To overcome the problems, we upgraded the MO system to be operated using the framework of EPICS, the OPI of Control System Studio (CSS) and the server software of Postgre SQL. This improves versatility of the MO system, enabling to run on various platforms such as Windows, Linux and Mac OS. At first, we made a prototype MO system, which processed 100 points of data and 5 operation screens and verified that the MO system functions correctly. Then we made full spec MO system which processes the data point of 7000 and operation screens of 130. It was operated in parallel with the current system to evaluate its performance with real data such as data transmission speed from PLCs, control functions from OPI, storage capability of servers and long-term reliability. As results, the new MO system achieved the communication speed of 2 Hz and its operability compatible to the current system. Now, we are operating and debugging it in comparison with the current system during the operating period as a preparation for the system replacement at the end of 2014.
Sakai, Kenji; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Tatsumoto, Hideki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-039, 121 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates the behavior, damage and restoration of a neutron source station of the MLF at the Great East Japan Earthquake and verified the safety design for emergency accidents in the neutron source station. In the MLF, after an occurrence of the Earthquake, strong quakes were detected at the instruments, the external power supply was lost, all of the circulators shut down automatically, and the hydrogen gas was released. The leakages of mercury, hydrogen and radio-activation gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between the shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines by subsidence around the building. But significant damages to the components were not found though the pressure drop of compressed air lines influenced on a target trolley lock system and so on. These results substantiated the validity of the safety design for emergency accidents in the source station, and suggested several points of improvement.
Sakai, Kenji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Takada, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Seki, Masakazu; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-20) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/03
This report investigates behaviors and damages of each component in a neutron target station of the MLF at the J-PARC at the time of the Great East Japan Earthquake (GEJE). At the date of the GEJE, in the MLF, strong quakes were detected at several instruments, an external power supply were lost, all of the circulation systems were shut down automatically, and a hydrogen gas was released as planned. Leakage of activation liquids and gases did not occur. While, the quakes made gaps between shield blocks and ruptured external pipe lines for air and water by subsidence. But significant damages on the components of the target station were not found though a loss of compressed air supply affected lock systems with air cylinders and pneumatic operation values. These results substantiated a validity of safety design on the target station for emergency accidents.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kawase, Keigo*; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Koga, J. K.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(6), p.066401_1 - 066401_3, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.59(Physics, Applied)Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
NIFS-PROC-85, p.30 - 33, 2011/02
The experiment of proton generation is performed for developing the laser-driven ion source. We observe proton signals in the laser-plasma interaction by using a thin-foil target. To get higher energy protons the size of the preformed plasma is reduced by changing the laser contrast level. In the high-contrast laser pulse case the maximum energy of the protons generated at rear side of the target increases.
Sugaya, Atsushi; Tanaka, Kenji; Akutsu, Shigeru
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposia 2011 (WM2011) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2011/02
The main component of the liquid wastes is sodium nitrate. Nitrate ion decomposition technology is under development to conserve a circumference environment of a disposal site. To investigate the methods for decomposing nitrate ion, several small-scale trials were performed using reductants and a catalyst in sodium nitrate solutions. It will be reported that the cement based encapsulation trials to immobilize the sodium carbonate based liquid waste, which was performed under non-radioactive condition at both small and full scale to investigate the optimum cement formulation.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nagatomo, Hideo*; et al.
European Physical Journal D, 55(2), p.421 - 425, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.86(Optics)We demonstrate the laser-ion acceleration from a near-critical density plasma, when amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) was used to convert a solid foil target into the lower-density target. In this work, a direct comparison is made by changing the ASE intensity by factor 3 in order to investigate the target density-dependency of the laser-ion acceleration. The beam direction of high-energy component is successfully controlled by modifying the target density. The near-critical density plasma can be a favorable target to control the beam direction to be dependent on its energy.
Sagisaka, Akito; Daido, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.-L.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Frontiers of Optoelectronics in China, 2(3), p.299 - 303, 2009/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy ion, electron, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. We have performed the laser and thin-foil interaction experiments using a high-intensity Ti:sapphire laser. We have observed simultaneous generation of proton beam and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. Simultaneous generation of proton beam and UV harmonics is also observed.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ma, J.-L.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.464 - 467, 2009/09
We measure the UV harmonics from a thin-foil target by changing the laser pulse duration in the high-energy proton generation. The maximum proton energies are around 1 MeV. In the case of the  500 fs, the peaks of UV harmonics up to fourth-order clearly appear. The spectra are broadened and shifted at the pulse durations of
500 fs, the peaks of UV harmonics up to fourth-order clearly appear. The spectra are broadened and shifted at the pulse durations of  100 fs and
100 fs and  30 fs.
30 fs.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi; Kawase, Keigo; Chen, L.-M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1153, p.176 - 181, 2009/07
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Tanoue, Manabu*; Akutsu, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Motomura, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.425 - 430, 2009/06
This paper reviews the temporal contrast and spatial beam quality improvement techniques in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped-pulse amplification (CPA). We describe an optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier that is seeded by a cleaned high-energy pulse. It demonstrates a background amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) level of 10 relative to the peak main femtosecond pulse on the picosecond timescale. We also report a cryogenically-cooled Ti:sapphire final amplifier which generates focused peak intensity in excess of 10
relative to the peak main femtosecond pulse on the picosecond timescale. We also report a cryogenically-cooled Ti:sapphire final amplifier which generates focused peak intensity in excess of 10 W/cm
W/cm at a 10 Hz repetition rate.
at a 10 Hz repetition rate.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Bulanov, S. V.; Bolton, P. R.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 37(6), p.449 - 454, 2009/06
The acceleration of protons driven by a high-intensity laser is comprehensively investigated via control of the target density by using ASE just before the time of the main-laser interaction. Two cases were investigated for which the ASE intensity differed by three orders of magnitude: In the low contrast case the beam centre for higher energy protons is shifted closer to the laser-propagation direction of 45 , while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
, while the center of lower-energy beam remains near the target normal direction. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the characteristic proton acceleration is due to the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 2(6), p.066001_1 - 066001_3, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:50.62(Physics, Applied)Protons with energies up to 3.5 MeV have been generated by a 10 Hz compact laser with an intensity of about 10 W/cm
W/cm , focused on a 7.5 mm thick polyimide target. These protons were used to induce a nuclear reaction of
, focused on a 7.5 mm thick polyimide target. These protons were used to induce a nuclear reaction of  B(p,n)
B(p,n) C. A total activity of 11.1 Bq was created after 60-shot laser irradiation. The possibility of thin layer activation (TLA) using a high-intensity ultra-short pulsed laser is discussed.
C. A total activity of 11.1 Bq was created after 60-shot laser irradiation. The possibility of thin layer activation (TLA) using a high-intensity ultra-short pulsed laser is discussed.
Horiguchi, Kenichi; Sugaya, Atsushi; Saito, Yasuo; Tanaka, Kenji; Akutsu, Shigeru; Hirata, Toshiaki
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), p.9411_1 - 9411_9, 2009/05
The low-level radioactive Waste treatment Facility (LWTF) was constructed at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) and cold test has been carried out since 2006. The waste which is treated in the LWTF is combustible/incombustible solid waste and liquid waste. In the LWTF, The combustible/incombustible solid waste will be incinerated. The liquid waste will be treated by the radio-nuclides removal process subsequently solidified by cement materials. This report describes the essential technologies of the LWTF and results of R&D work for the nitrate-ion decomposition technology for the liquid waste.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Tanoue, Manabu*; Akutsu, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Motomura, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Optics Communications, 282(4), p.625 - 628, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:89.08(Optics)We demonstrate a high-contrast, high-intensity double chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) Ti:sapphire laser system using an optical parametric chirped-pulse (OPCPA) pre- amplifier. By injecting cleaned microjoule seed pulses into the OPCPA, a temporal contrast greater than 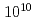 within picosecond times before the main femtosecond pulse is demonstrated with an output pulse energy of 1.7 J and a pulse duration of 30 fs, corresponding to a peak power of 60 TW at a 10 Hz repetition rate. This system uses a cryogenically-cooled Ti:sapphire final amplifier and generates focused peak intensities in excess of
within picosecond times before the main femtosecond pulse is demonstrated with an output pulse energy of 1.7 J and a pulse duration of 30 fs, corresponding to a peak power of 60 TW at a 10 Hz repetition rate. This system uses a cryogenically-cooled Ti:sapphire final amplifier and generates focused peak intensities in excess of 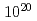 W/
W/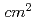 .
.
Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ma, J.*; Sagisaka, Akito; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1872 - 1877, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A dependence of cut-off proton kinetic energy on laser prepulse duration has been observed. ASE pedestal duration is controlled by a fast electro-optic pulse slicer where the risetime is estimated to be 130 ps. We demonstrate a new correlated spectral technique for determining this risetime using a stretched, frequency chirped pulse.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; Akutsu, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Motomura, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2008-007, p.13 - 16, 2008/08
One of the main bottlenecks for the applications of ultrashort and ultrahigh-peak power lasers in high-field physics is a temporal contrast of the pulses. In ultrahigh-peak power lasers, a nanosecond background of the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) is generated at the same time as the femtosecond pulse. This background is mostly generated in the preamplifier (regenerative, multipass amplifier). Even though the contrast level is usually in the range from 10 to 10
to 10 , this level is not sufficiently low at relativistic intensities greater than 10
, this level is not sufficiently low at relativistic intensities greater than 10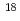 W/cm
W/cm to avoid unwanted pre-plasmas generation. We demonstrated a high-contrast, high-peak power laser with optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA). With the use of OPCPA, contrast is enhanced to better than 7
to avoid unwanted pre-plasmas generation. We demonstrated a high-contrast, high-peak power laser with optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA). With the use of OPCPA, contrast is enhanced to better than 7 10
10 in a few picoseconds before the main pulse, which corresponds to an improvement of three to four orders in magnitude compared with conventional systems.
in a few picoseconds before the main pulse, which corresponds to an improvement of three to four orders in magnitude compared with conventional systems.