Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小林 正起*; Anh, L. D.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 金田-高田 真悟*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 芝田 悟朗*; 田中 新*; 田中 雅明*; 大矢 忍*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:47.11(Physics, Applied)A fundamental understanding of the interfacial magnetic properties in ferromagnetic heterostructures is essential for utilizing ferromagnetic materials for spintronic device applications. Here, we investigate the interfacial magnetic and electronic structures of epitaxial single-crystalline LaAlO (LAO)/La
(LAO)/La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO
(LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO (Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn
(Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn 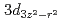 orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the
orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the 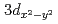 orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
 impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the
impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the  -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb武田 崇仁*; 坂本 祥哉*; 荒木 恒星*; 藤澤 唯太*; Anh, L. D.*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 藤森 淳*; 田中 雅明*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(24), p.245203_1 - 245203_8, 2020/12
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:35.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)(Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration
)Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration  is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3
is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3 states in (Ga
states in (Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb (
)Sb ( = 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2
= 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2 -3
-3 RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3
RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3 impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing
impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing  , which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3
, which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3 partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3
partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3 IB originates from the minority-spin (
IB originates from the minority-spin (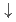 )
)  states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between
states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between 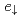 electrons with increasing
electrons with increasing  is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3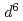 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin  -
- hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:59.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3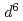 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism坂本 祥哉*; Anh, L. D.*; Hai, P. N.*; 芝田 悟朗*; 竹田 幸治; 小林 正起*; 高橋 文雄*; 小出 常晴*; 田中 雅明*; 藤森 淳*
Physical Review B, 93(3), p.035203_1 - 035203_6, 2016/01
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:62.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to investigate the mechanism of ferromagnetic ordering in the new  -type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a
-type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a  -linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
-linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
 -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As小林 正起*; Anh, L. D.*; Hai, P. N.*; 竹田 幸治; 坂本 祥哉*; 門野 利治*; 岡根 哲夫; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 原田 慈久*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 105(3), p.032403_1 - 032403_4, 2014/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:36.08(Physics, Applied)The electronic and magnetic properties of Fe atoms in the ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be have been studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) at the Fe 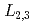 edge. The XAS and XMCD spectra showed simple spectral line shapes similar to Fe metal, but the ratio of the orbital and spin magnetic moments estimated using the XMCD sum rules was significantly larger than that of Fe metal, indicating a significant orbital moment of Fe 3
edge. The XAS and XMCD spectra showed simple spectral line shapes similar to Fe metal, but the ratio of the orbital and spin magnetic moments estimated using the XMCD sum rules was significantly larger than that of Fe metal, indicating a significant orbital moment of Fe 3 electrons in (In,Fe)As:Be. The XMCD intensity as a function of magnetic field indicated hysteretic behavior of the superparamagnetic-like component due to discrete ferromagnetic domains. VC
electrons in (In,Fe)As:Be. The XMCD intensity as a function of magnetic field indicated hysteretic behavior of the superparamagnetic-like component due to discrete ferromagnetic domains. VC