Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
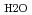 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 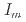 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
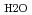 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
Hanamachi, Yuji*; Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
NIMS Bisai Kozo Kaiseki Purattohomu Riyo Hokokusho (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Koike, Ayaka*; Takubo, Yusaku*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Kawakita, Ryohei
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.62 - 64, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
 - and K-montmorillonite
- and K-montmorilloniteKawakita, Ryohei; Saito, Akito*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Sato, Tsutomu*
Applied Clay Science, 231, p.106722_1 - 106722_7, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.27(Chemistry, Physical)Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Anraku, Sohtaro; Walker, C.*; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
Anraku, Sohtaro
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 24(1), p.65 - 68, 2017/06
no abstracts in English
Anraku, Sohtaro; Matsubara, Isamu*; Morimoto, Kazuya*; Sato, Tsutomu*
Nendo Kagaku, 55(2), p.17 - 30, 2017/00
Anionic radionuclides are important for the long-term safety assessment of Japanese transuranic (TRU) waste disposal facilities. Degradation of cementitious materials used to construct the TRU waste disposal facilities, however, can produce a hyperalkaline leachate and so it is necessary to understand the reaction mechanisms that will control the behavior and fate of anionic radionuclides under these hyperalkaline conditions. An excellent natural analogue site to study relevant reaction mechanisms is provided in Oman where hyperalkaline spring waters (pH  11) from serpentinized peridotites discharge into moderately alkaline rivers. Aragonite was found in all secondary mineral samples, with accessory minerals of calcite, layered double hydroxide (LDH) and brucite. LDH was observed at the high Al concentration springs and brucite at the low Al concentration springs. Calcite was only found close to the springs. Distal calcite formation was inhibited due to high Mg concentrations in the river water. The spatial distribution of minerals therefore implicates the importance of the mixing ratio of spring to river water and the relative chemical compositions of the spring and river waters. Supporting mixing model calculations could successfully reproduce the precipitation of aragonite and LDH. The observed decrease in Ca concentration could be explained by aragonite precipitation. pH exerted a strong control on the precipitation of LDH and so too, therefore, on Al concentration. In the mixing water experiments containing up to 40% river water, LDH and brucite were both oversaturated, but brucite was not always identified by XRD. The possible inhibition of brucite by LDH precipitation was an unexpected result.
11) from serpentinized peridotites discharge into moderately alkaline rivers. Aragonite was found in all secondary mineral samples, with accessory minerals of calcite, layered double hydroxide (LDH) and brucite. LDH was observed at the high Al concentration springs and brucite at the low Al concentration springs. Calcite was only found close to the springs. Distal calcite formation was inhibited due to high Mg concentrations in the river water. The spatial distribution of minerals therefore implicates the importance of the mixing ratio of spring to river water and the relative chemical compositions of the spring and river waters. Supporting mixing model calculations could successfully reproduce the precipitation of aragonite and LDH. The observed decrease in Ca concentration could be explained by aragonite precipitation. pH exerted a strong control on the precipitation of LDH and so too, therefore, on Al concentration. In the mixing water experiments containing up to 40% river water, LDH and brucite were both oversaturated, but brucite was not always identified by XRD. The possible inhibition of brucite by LDH precipitation was an unexpected result.
Kawakita, Ryohei*; Saito, Akito*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Sato, Tsutomu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawakita, Ryohei; Anraku, Sohtaro; Hanamachi, Yuji*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
Cement and bentonite materials are to be used in a repository for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes in Japan. Cement will provide structural support to the repository and will be in close contact with bentonite. Understanding the interactions between these two materials is necessary to improve repository design and ensure long-term safety. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is widely used for construction, however, there are concerns that its high pH  13 porewater could cause significant alteration of bentonite. JAEA has therefore developed a High-content Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) to lower the pH of cement porewater. Studies on HFSC and bentonite interactions are, however, limited. In addition, elevated temperatures can be expected in the repository by the combination of radiolytic heating and geothermal gradients. Temperature affects mineral reaction rates and their overall stability, but such thermal effects have not yet been studied in detail in the context of cement and bentonite interactions. Laboratory scale experiments were therefore conducted to investigate the interactions between OPC or HFSC and compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1; dry density = 1.37 Mg/m
13 porewater could cause significant alteration of bentonite. JAEA has therefore developed a High-content Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) to lower the pH of cement porewater. Studies on HFSC and bentonite interactions are, however, limited. In addition, elevated temperatures can be expected in the repository by the combination of radiolytic heating and geothermal gradients. Temperature affects mineral reaction rates and their overall stability, but such thermal effects have not yet been studied in detail in the context of cement and bentonite interactions. Laboratory scale experiments were therefore conducted to investigate the interactions between OPC or HFSC and compacted bentonite (Kunigel V1; dry density = 1.37 Mg/m ) at repository relevant temperatures of 50
) at repository relevant temperatures of 50 C and 80
C and 80 C.
C.
Walker, C.; Anraku, Sohtaro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
no journal, ,
Anraku, Sohtaro; Sato, Hisao*; Walker, C.*; Amano, Yuki; Sakurai, Akitaka; Nakayama, Masashi; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Anraku, Sohtaro; Kawakita, Ryohei; Hanamachi, Yuji*; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
To evaluate the observed alteration of bentonite and secondary mineral formation by OPC or HFSC near the interface, 1D reactive transport models were constructed using the Cement And Bentonite Alteration due to REactive Transport (CABARET) computer modelling code. Supporting calculations for initial hydration of OPC or HFSC were conducted using PHREEQC to generate the initial porewater compositions. JAEA's Thermodynamic DataBase for geochemical reaction was used in all calculations. Modeling of OPC and Kunigel V1 interaction resulted in depletion of Ca in OPC by portlandite dissolution and depletion of Si in Kunigel V1 by chalcedony dissolution leading to C-S-H gel precipitation at the interface, which were confirmed by XRD. Clogging of the interface by the precipitation of C-S-H gel at 80 C, however, limited diffusion and therefore the alteration of Kunigel V1. Coupling between diffusion coefficients and low porosities requires further data and validation to improve the simulation. The temperature dependence of dissolution rates of the C-S-H gel and chalcedony also needs to be confirmed. Modeling of HFSC and Kunigel V1 interaction showed significantly less alteration of the Kunigel V1 from the significantly less alkaline HFSC porewater, which is also consistent with the experiments. Modelled changes in HFSC resulted in an increase in porosity at the interface by the dissolution of C-A-S-H gel and ettringite, and in Kunigel V1 by the slight dissolution of chalcedony. To evaluate the elevated temperature effect in HFSC hydration, it is important to use a C-A-S-H gel model and to confirm the extents of pozzolanic reaction of silica fume and fly ash, which are currently based on measurements at room temperature.
C, however, limited diffusion and therefore the alteration of Kunigel V1. Coupling between diffusion coefficients and low porosities requires further data and validation to improve the simulation. The temperature dependence of dissolution rates of the C-S-H gel and chalcedony also needs to be confirmed. Modeling of HFSC and Kunigel V1 interaction showed significantly less alteration of the Kunigel V1 from the significantly less alkaline HFSC porewater, which is also consistent with the experiments. Modelled changes in HFSC resulted in an increase in porosity at the interface by the dissolution of C-A-S-H gel and ettringite, and in Kunigel V1 by the slight dissolution of chalcedony. To evaluate the elevated temperature effect in HFSC hydration, it is important to use a C-A-S-H gel model and to confirm the extents of pozzolanic reaction of silica fume and fly ash, which are currently based on measurements at room temperature.
 -montmorillonite
-montmorilloniteKawakita, Ryohei*; Saito, Akito*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Sato, Tsutomu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
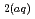 , HSiO
, HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO

Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Oda, Chie; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
Equilibrium constants ( ) describing the formation reactions of SiO
) describing the formation reactions of SiO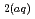 , HSiO
, HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 can be used to derive their thermodynamic properties. However, SiO
can be used to derive their thermodynamic properties. However, SiO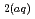 was derived from inaccurate quartz solubility data, HSiO
was derived from inaccurate quartz solubility data, HSiO
 was not extrapolated to zero ionic strength and SiO
was not extrapolated to zero ionic strength and SiO
 is routinely ignored because of its restricted dominance to very high pH
is routinely ignored because of its restricted dominance to very high pH  13 solutions. Using quartz and water data as well known "anchor" points,
13 solutions. Using quartz and water data as well known "anchor" points,  values describing the formation reactions of SiO
values describing the formation reactions of SiO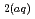 , HSiO
, HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 were revised to derive new thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters. These properties and parameters can be used in the derivation of the thermodynamic properties of other Si bearing aqueous species/complexes and the thermodynamic properties of cementitious, clay, zeolite, and rock forming minerals, and in calculating groundwater compositions relevant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes.
were revised to derive new thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters. These properties and parameters can be used in the derivation of the thermodynamic properties of other Si bearing aqueous species/complexes and the thermodynamic properties of cementitious, clay, zeolite, and rock forming minerals, and in calculating groundwater compositions relevant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes.
Walker, C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
no journal, ,
A thermodynamically credible calcium(-aluminate)-silicate-hydrate (C(-A)-S-H) gel solubility model has to consider a variety of features, including structure, composition, phase boundaries, measured/estimated thermodynamic properties, molar volumes, and, of course, solubility behavior in terms of pH values and Ca, Al and Si concentrations expressed as a function of C(-A)-S-H gel composition, temperature and ionic strength. This study provides an account of the rapidly growing body of data that are concerned with these features and of the more promising approaches that can be used to develop a C(-A)-S-H gel solubility model. JAEA research on the degradation of high content fly ash silica fume cement (HFSC) provides a good working example that highlights the need to develop a C(-A)-S-H gel solubility model.