Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Aose, Shinichi
JAEA-Research 2006-082, 56 Pages, 2006/12
The shredder type mechanical crusher was developed for using in a hot cell in Chemical Processing Facility, and the first crush experiment with this crusher was carried out at July 2004 using the simulated core fuel pin. This experiment showed that the crushed fragments could not be grinded efficiency because screen blade vibrated up and down during the operation. Additionally, the strength of screen blade block was insufficient to crush the sheared fuel pieces stably. Therefore, about 70% of fuel was recovered in maximum. Based on the results of the first experiment, screen blade was fixed up mainly and the second experiment was carried out with improved apparatus at September 2005. In this experiment, about 96% of fuel could be recovered in maximum because screen blade was stable during the operation.
 concentration feed solution and scrubbing solution
concentration feed solution and scrubbing solutionNakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Miyachi, Shigehiko; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Koyama, Tomozo; Aose, Shinichi
JAEA-Research 2006-030, 43 Pages, 2006/06
Concerning the advanced aqueous reprocessing system, the simplified solvent extraction process for U, Pu and Np co-recovery has been investigated. We carried out the counter-current experiment, which aimed for Np oxidation and extraction by high [HNO ] condition. For preventing Np leakage to the raffinate, feed solution and scrubbing solution with high [HNO
] condition. For preventing Np leakage to the raffinate, feed solution and scrubbing solution with high [HNO ] were used, which would bring high [HNO
] were used, which would bring high [HNO ] in the extraction section and efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. In addition, high [HNO
] in the extraction section and efficient Np oxidation and extraction in this section. In addition, high [HNO ] in the feed solution could help the pre-oxidation of Np to extractable Np(VI). In the steady state, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under about 1%. The stage efficiencies for these elements were estimated by fitting the concentration profiles calculated by MIXSET-X into the experimental results. The stage efficiency of U, Pu and Np were evaluated 100%, 100% and 98.5% in the extraction section and 95%, 90% and 89% in the stripping section respectively.
] in the feed solution could help the pre-oxidation of Np to extractable Np(VI). In the steady state, the Np leakage to the raffinate could be kept under about 1%. The stage efficiencies for these elements were estimated by fitting the concentration profiles calculated by MIXSET-X into the experimental results. The stage efficiency of U, Pu and Np were evaluated 100%, 100% and 98.5% in the extraction section and 95%, 90% and 89% in the stripping section respectively.
Toya, Yuichi; Washiya, Tadahiro; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
In this study, the prospect of the applicability of the YAG laser to the disassembly device was obtained by confirming the transmission efficiency of the optical fiber under the radiation environment and the cutting performance to the fuel assembly, and a structural concept of a new disassembly device adopted the YAG laser system was constructed.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Ogino, Hideki; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has been developing centrifugal contactors which are compact and high performance for solvent extraction process in industrial reprocessing plant. Centrifugal contactor has some advantages which are more compact, smaller holdup volume and higher separation performance than conventional contactor such as mixer-settler or pulse column and contributes to economic advantage and reduction of solvent waste. In addition, the compact contactor is easy to manage the critical safety, and the operation ratio for fuel treatment can be improved because of short start-up and shut-down time. Since 1985, JNC stared the development of centrifugal contactor and then fundamental design was established for engineering scale hot test plant (RETF). The life time was evaluated by the result of endurance test, and system performance of multi-stages contactor on engineering scale was demonstrated. [1] In addition, several types of advanced contactors have been developing. This paper introduces the development of centrifugal contactor in JNC
Koizumi, Kenji; Washiya, Tadahiro; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2005/10
JNC has been developing the mechanical decladding system for FBR oxide fuel. The mechanical decladding system is consists of the fuel pin crushing step(mechanical crusher), the hull separation step(magnetic separator) and the hull rinsing step(melting separator). The system mock-up test device is fabricated, and the system performance tests are carried out with simulated oxide fuel pins. As the results, the basic performance of each device and system performance were confirmed. The longevity of the crushing blades of mechanical crusher is one year or more and practical use. The majority of wrapping wire can be separated by the vibration classifier. High fuel purity and a high fuel separation efficiency are obtained by the multi-stage magnetic separator. An efficient fuel recovery is possible according to the CCLM technology. In the future, the positive proof data that uses the spent fuel will be obtained, and the design for the remote maintenance will be verified.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Higuchi, Hidetoshi; Sano, Yuichi; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13), P. 330, 2005/05
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has been developing the crystallization technology for the advanced aqueous reprocessing plant to realize the FBR fuel cycle. The crystallization process is applied in front of the extraction process for removing large amount of uranium and reducing the throughput of extraction process. The crystallization process requires high concentrated dissolution ( 500g-HM/L) to mitigate the cooling conditions. The powdered fuel dissolution is a promising technology to obtain the high concentrated dissolution. Hot experiments of the powdered fuel dissolution were carried out at CPF to verify the dissolution speed and characteristics. As result, the speed is ten times faster than conventional sheared fuel. For the powdered fuel dissolution, particle handling is a key issue to prevent piling up of the fuel particles on the dissolver bottom and elutriation rate to the off gas system. In this paper, functional requirements and subjects for the powdered fuel dissolution were discussed. And an innovative dissolver design based on the cylindrical stirring type dissolver was proposed for reliable continuous dissolver system with the powdered fuel. Some engineering scale test and computer code evaluations were carried out to verify the dynamic performance of simulated fuel particles and water in the dissolver design.
500g-HM/L) to mitigate the cooling conditions. The powdered fuel dissolution is a promising technology to obtain the high concentrated dissolution. Hot experiments of the powdered fuel dissolution were carried out at CPF to verify the dissolution speed and characteristics. As result, the speed is ten times faster than conventional sheared fuel. For the powdered fuel dissolution, particle handling is a key issue to prevent piling up of the fuel particles on the dissolver bottom and elutriation rate to the off gas system. In this paper, functional requirements and subjects for the powdered fuel dissolution were discussed. And an innovative dissolver design based on the cylindrical stirring type dissolver was proposed for reliable continuous dissolver system with the powdered fuel. Some engineering scale test and computer code evaluations were carried out to verify the dynamic performance of simulated fuel particles and water in the dissolver design.
Okamura, Nobuo; Koizumi, Kenji; Washiya, Tadahiro; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 0 Pages, 2005/05
In Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), a commercial scale electrolyzer, whose capacity is 25tHM/y, is been developing to be used in an oxide electrowinning process, a kind of non-aqueous reprocessing process. It has some significant subjects that must be solved before introduced in a commercial reprocessing plant. It developed in JNC has some innovative characteristics, such as cold crucible induction melting (CCIM), to cope with those subjects. But these characteristics make it difficult to arrange the internal components because of a narrow and deep shape of a crucible. So two kinds of analysis systems with computer were constructed to help a design of the internal constitution. One of them is to evaluate the temperature distribution in the crucible and another is to evaluate the shape of deposits. In this study, the internal constitution in the commercial scale electrolyzer was designed by using them finally.
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Hanada, Keiji; Aose, Shinichi; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Kato, Toshihiro*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(2-4), p.521 - 525, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:77.32(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)None
Yamada, Seiya; Washiya, Tadahiro; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Aose, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(2), p.156 - 166, 2005/00
The application of the fluoride volatility process in the reprocessing of fuel from the fast breeder reactor is regarded as one of the economical methods. Plutonium hexafluoride (PuF6), however, reacting with fluorine (F2) and plutonium dioxide (PuO2) as the raw material, is in an unstable condition and tends to remain as a solid compound in the process after decomposing into plutonium tetrafluoride (PuF4). Suitable conditions should be established for the practical use of this process. One of them is to enhance the stability of PuF6. The behaviour of plutonium fluorination and relevant chemical reactions were investigated by referring to sundry literature and by thermodynamic calculation. It was then compared with recent data from laboratory scale experiments for this paper. Results from the theoretical analysis agreed with experimental observation that PuF6 could be formed stably under a high temperature condition (approx.1000 K) with over supply of figher concentration of F2.
Takata, Takeshi; Koma, Yoshikazu; Sato, Koji; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Ogino, Hideki; Koyama, Tomozo; Aose, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(3), 307 Pages, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:85.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design study of aqueous reprocessing system has been progressed for the feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. Based on the PUREX process,an aqueous reprocessing process with the addition of a uranium crystallization step and
Yamada, Seiya; Washiya, Tadahiro; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Suganuma, Takashi; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-12) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/00
As a part of the feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems, Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has been developing the fuel decladding technology for the dry reprocessing process (oxide electrowinning process) and aqueous reprocessing process. Particularly, in the oxide electrowinning process, the spent fuel should be reduced to powder for quick dissolution in the molten salt at electrolyzer. Heat treatment method such as a voloxidation might not be applicable in the decladding process, because of the high plutonium content as fast reactor fuel. Therefore, JNC proposes new decladding system with innovative mechanical decradding devices. The decladding system consists of fuel crushing stage, hull separation stage and hull rinsing stage. In this paper, the outline of this new decladding system and its innovative devices will be descried.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Koizumi, Kenji; Koichi, Sugai,*; Takashi, Suganuma,; Aose, Shinichi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (25), p.33 - 44, 2004/00
As a part of the feasibility study (FS) on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems, JNC has been developing the fuel decladding technology for the dry reprocessing process (oxide electrowinning process). In this process, the spent fuel should be reduced to powder for quick dissolution in the molten salt at electrolyzer. Therefore, JNC proposes new decladding system with innovative mechanical decradding devices. The decladding system consists of fuel crushing stage, hull separation stage and hull rinsing stage. In the fuel crushing stage, disassembled spent fuel pins are crushed and powdered by mechanical decladding device, then the following stage, the hull and the fuel powder are separated by magnetic separator. Only the fuel powder is fed to the electrolyzer. On the other side, the separated hull is melted by induction heating method, and the small amount of oxide included in the hull fragments is recovered at the hull rinsing stage. The recovered oxide fuel is fed back to the electrolyzer.
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Kato, Toshihiro*; Washiya, Tadahiro; Takashi, Suganuma,; Aose, Shinichi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (23), p.31 - 40, 2004/00
The corrosion resistance of ceramic materials was discussed through thermodynamic calculation and corrosion test. The corrosion test was basically carried out in alkari molten salt under chlorine gas. In addition, the effects of oxygen, carbon and simulated fission products on ceramics corrosion were evaluated in molten salt under chlorine gas. As results, silicon nitrides, mullite and cordierite had a good corrosion resistance in above conditions.
Shiroishi, Masatake*; Aoshima, Shinichi*; Aose, Shinichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
JNC TY8400 2003-007, 43 Pages, 2003/04
None
Washiya, Tadahiro; Koizumi, Kenji; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Energy and Fuel Cycle Systems (GLOBAL 2003) (CD-ROM), 773 Pages, 2003/00
None
Washiya, Tadahiro; Koizumi, Kenji; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Aose, Shinichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Energy and Fuel Cycle Systems (GLOBAL 2003) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2003/00
None
Washiya, Tadahiro; Ogino, Hideki; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Suganuma, T.; Aose, Shinichi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), p.23 - 32, 2003/00
None
; Kato, Toshihiro*; Hanada, Keiji; ; Aose, Shinichi
JNC TN8430 2002-004, 32 Pages, 2002/12
Pyrochemical reprocessing using molten salts (RIAR process) has been recently developed for spent nuclear oxide fuel and discussed in feasibility study. It is required to improve the corrosion resistance of equipments such as electrolyzer because the process is operated in severe corrosion environment. In this study, the corrosion resistance of ceramic materials was discussed through the thermodynamic calculation and corrosion test. The corrosion test was basically carried out in alkali molten salt under chlorine gas condition. And further consideration about the effects of oxygen, carbon and main fission product's chlorides were evaluated in molten salt. The result of thermodynamic calculation shows most of ceramic oxides have good chemical stability on chlorine, oxygen and uranyl chloride, however the standard Gibb's free energies with carbon have negative value. On the other hand, eleven kinds of ceramic materials were examined by corrosion test, then silicon nitride, mullite and cordierite have a good corrosion resistance less than 0.1mm/y. Cracks were not observed on the materials and flexural strength did not reduce remarkably after 480 hours test in molten salt with Cl -O
-O bubbling. In conclusion, these three ceramic materials are most applicable materials for the pyrochemical reprocessing process with chlorine gas condition.
bubbling. In conclusion, these three ceramic materials are most applicable materials for the pyrochemical reprocessing process with chlorine gas condition.
Sano, Yuichi; Aose, Shinichi; ;
PNC TN8410 95-313, 28 Pages, 1995/10
THe coordination properties of the lanthanide (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm and Eu) complexes in lanthanide/TBP (tributylphosphate), lanthanide/CMPO (octyl(phenyl)-N, N-diisobutylcarbamoylmethylphosphine oxide) and lanthanide/CMPO/TBP systems were investigated by the NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) measurements. The numbers of the coordinated CMPO and TBP to the lanthanide ion were estimated about three and two in the lanthanide/CMPO and lanthanide/TBP systems, respectively. It is considered that TBP and CMPO coordinate to the lanthanide (III) ion in the monodentate and the bidentate manners, respectively. In the lanthanide/CMPO/TBP system, 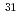 P-NMR spectra suggested that CMPO coordinates to lanthanide(III) ion directly in the bidentate mode, but TBP doesn't exist within the first coordination sphere and coordinates to the lanthanide(III) ion from beyond the first coordination sphere. The activation parameters for the ligand exchange reactions calculated by the CBS (complete bandshape) method suggest that the ligand exchange reactions in the lanthanide (Pr and Eu)/TBP and lanthanide (La, Pr and Sm)/CMPO systems proceed through either the associative (A) mechanism or the dissociative (D) mechanism with an ordering into the second coordination sphere. In the lanthanide (Pr and Sm)/CMPO/TBP systems, it was shown that the CMPO exchange reactions proceed through the mechanism with an ordering into the second coordination sphere, which is caused by TBP in the systems.
P-NMR spectra suggested that CMPO coordinates to lanthanide(III) ion directly in the bidentate mode, but TBP doesn't exist within the first coordination sphere and coordinates to the lanthanide(III) ion from beyond the first coordination sphere. The activation parameters for the ligand exchange reactions calculated by the CBS (complete bandshape) method suggest that the ligand exchange reactions in the lanthanide (Pr and Eu)/TBP and lanthanide (La, Pr and Sm)/CMPO systems proceed through either the associative (A) mechanism or the dissociative (D) mechanism with an ordering into the second coordination sphere. In the lanthanide (Pr and Sm)/CMPO/TBP systems, it was shown that the CMPO exchange reactions proceed through the mechanism with an ordering into the second coordination sphere, which is caused by TBP in the systems.