Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murota, Kento*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Geochemistry, 152, p.105620_1 - 105620_11, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:62.05(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Massey, D.*; Williams, C. D.*; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Aoyagi, Noboru; Ueda, Yuki; Antonio, M. R.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 127(9), p.2052 - 2065, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical) /MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions
/MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutionsFalyouna, O.*; Bensaida, K.*; Maamoun, I.; Ashik, U. P. M.*; Tahara, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Aoyagi, Noboru; Sugihara, Yuji*; Eljamal, O.*
Journal of Cleaner Production, 342, p.130949_1 - 130949_15, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:98.81(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*; Kozai, Naofumi; Sugiura, Yuki; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105178_1 - 105178_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:86.47(Geochemistry & Geophysics)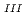 from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphate
from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphateUeda, Yuki; Kikuchi, Kei*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Tanaka, Kazuya; Okamura, Hiroyuki
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(5-6), p.491 - 511, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 ssbauer, infrared, and laser-induced luminescence for classifying rare-earth minerals enriched in iron-rich deposits
ssbauer, infrared, and laser-induced luminescence for classifying rare-earth minerals enriched in iron-rich depositsAoyagi, Noboru; Nguyen, T. T.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Nguyen, T. V.*; Nakada, Masami; Segawa, Yukari; Nguyen, H. T.*; Le, B. T.*
ACS Omega (Internet), 5(13), p.7096 - 7105, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.55(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Oishi, Tomoji*; Kimura, Yu*; Nakajima, Kiyohiko*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Aoyagi, Noboru
Materials Sciences and Applications, 11(3), p.195 - 203, 2020/03
A high-efficiency synthesis method for a latent pigment of red pigment diketo-pyrrolo-pyrrole (Pig. Red 272:272DPP), which is important as a functional organic pigment, was investigated, and the investigation results revealed that irradiation of microwaves (MWs) for several seconds to 272 DPP in NMP (N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) solvent yielded DPP latent pigment (272DPP-BOC) at a high yield of 86.2%. Two kinds of latent-pigment crystals, namely, red and yellow, were obtained by recrystallization, and it was found that the fluorescence-emission properties of the two kinds differ significantly. Single-crystal X-ray structural analysis showed that the difference in the fluorescence-emission properties of the two types is derived from the difference in their crystal structures.
 -CO
-CO ternary complex from brackish potable groundwater; Complex dissociation, transport, and sorption
ternary complex from brackish potable groundwater; Complex dissociation, transport, and sorptionMa, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Collins, R. N.*; Tsarev, S.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kinsela, A. S.*; Jones, A. M.*; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 53(5), p.2739 - 2747, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:89.02(Engineering, Environmental)Aoyagi, Noboru; Palladino, G.*; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Kimura, Takaumi
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.882 - 890, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.18(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The speciation and coordination geometries of M(III)-citrate complexes in aqueous solutions, where M denotes Eu, Tb, Lu, or Cm, are studied using potentiometric titration, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies. Their photophysical properties are also characterized by time-resolved fluorescence spectra. The formation constants of mononuclear, dinuclear, and trinuclear Lu-citrate species were determined by potentiometric titration in 3.00 M NaClO aqueous media. Terminal carboxylic conformation in trinuclear complexes comprised both the five- and six-membered rings at different exchanging rates. Hydration states evaluated for Eu
aqueous media. Terminal carboxylic conformation in trinuclear complexes comprised both the five- and six-membered rings at different exchanging rates. Hydration states evaluated for Eu ions are the chemical formula of [Eu(Cit)
ions are the chemical formula of [Eu(Cit) (H
(H O)
O) ]
] and [Eu
and [Eu (OH)
(OH) (Cit)
(Cit) (H
(H O)
O)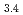 ]
] . These complexes in aqueous solution have geometrical similarity to the crystal structures in the literature. Furthermore, the entity of the hetero-trinuclear complex induces the intramolecular energy transfer from Tb
. These complexes in aqueous solution have geometrical similarity to the crystal structures in the literature. Furthermore, the entity of the hetero-trinuclear complex induces the intramolecular energy transfer from Tb to Eu
to Eu . The incorporation of Cm
. The incorporation of Cm into these homo/hetero-trinuclear citrate complexes proved to be a successful trial to probe the formation of actinide polymer at a trace level.
into these homo/hetero-trinuclear citrate complexes proved to be a successful trial to probe the formation of actinide polymer at a trace level.
Saito, Takumi*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Terashima, Motoki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(4), p.444 - 451, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Humic substances (HSs) are ubiquitous in various environments including deep underground and play an important role in the speciation and mobility of radionuclides. The binding of Eu , a chemical homologue of trivalent actinide ions, to HSs isolated from sedimentary groundwater at -250 m below the surface was studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy combined with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) as a function of pH and salt concentration. PARAFAC modeling reveals the presence of multiple factors that corresponds to different Eu
, a chemical homologue of trivalent actinide ions, to HSs isolated from sedimentary groundwater at -250 m below the surface was studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy combined with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) as a function of pH and salt concentration. PARAFAC modeling reveals the presence of multiple factors that corresponds to different Eu species. These factors resemble those observed for Eu
species. These factors resemble those observed for Eu binding to HSs from surface environments; however, detailed comparison shows that there are some particularities in Eu
binding to HSs from surface environments; however, detailed comparison shows that there are some particularities in Eu binding to the deep groundwater HSs. The distribution coefficients (
binding to the deep groundwater HSs. The distribution coefficients ( ) of Eu
) of Eu binding to the HSs calculated from the PARAFAC modeling exhibits a rather strong salt effect. At 0.01 M NaClO
binding to the HSs calculated from the PARAFAC modeling exhibits a rather strong salt effect. At 0.01 M NaClO the
the  values are relatively large and comparable to those to the surface HSs; they are decreaed at 0.1 M NaClO
values are relatively large and comparable to those to the surface HSs; they are decreaed at 0.1 M NaClO by more than an order of the magnitude. The
by more than an order of the magnitude. The  values are larger for humic acid fraction of the deep underground HSs than fulvic acid over the entire range of pH and salt concentration investigated in this study.
values are larger for humic acid fraction of the deep underground HSs than fulvic acid over the entire range of pH and salt concentration investigated in this study.
Segawa, Yukari; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nakada, Masami; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Tamura, Yukito*; Okamoto, Hisato; Otomo, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-039, 64 Pages, 2017/03
The laboratory building No.1 for the plutonium research program (Bldg. Pu1) was chosen as one of the facilities to decommission by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform in September, 2013. The research groups, users of Bldg. Pu1, were driven by necessity to remove used equipment and transport nuclear fuel to other facilities from Bldg. Pu1. Research Group for Radiochemistry proactively established the Used Equipment Removal Team for the smooth operation of the removal in April, 2015. The team classified six types of work into the nature of the operation, removal of used equipment, disposal of chemicals, stabilization of mercury, stabilization of nuclear fuel, transportation of nuclear fuel and radioisotope, and survey of contamination status inside the glove boxes. These works were completed in December, 2015. This report circumstantially shows six works process, with the exception of the approval of the changes on the usage of nuclear fuel in Bldg. Pu1 to help prospective decommission.
 N
N anions in the ionic liquid-water distribution of europium(III) chelates
anions in the ionic liquid-water distribution of europium(III) chelatesOkamura, Hiroyuki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Naganawa, Hirochika; Imura, Hisanori*
RSC Advances (Internet), 7(13), p.7610 - 7618, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:56.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The role of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Tf N
N ) anions in the ionic liquid-water distribution systems of the Eu(III) chelates with 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone (Htta) was investigated by the liquid-liquid distribution and time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The effect of the ionic liquids on the distribution constant of Eu(tta)
) anions in the ionic liquid-water distribution systems of the Eu(III) chelates with 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone (Htta) was investigated by the liquid-liquid distribution and time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The effect of the ionic liquids on the distribution constant of Eu(tta) was evaluated by the regular solution theory. The distribution constant of Eu(tta)
was evaluated by the regular solution theory. The distribution constant of Eu(tta) in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C
in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N]) was increased dramatically by the solvation effects of Eu(tta)
N]) was increased dramatically by the solvation effects of Eu(tta) in [C
in [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N]. TRLFS for [Eu(tta)
N]. TRLFS for [Eu(tta) (H
(H O)
O) ] synthesized revealed that the Eu(tta)
] synthesized revealed that the Eu(tta) chelate was almost completely dehydrated in a series of [C
chelate was almost completely dehydrated in a series of [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N]. The Eu(tta)
N]. The Eu(tta) chelate exists as di- or tri-hydrates in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perchlorate ([C
chelate exists as di- or tri-hydrates in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium perchlorate ([C mim][ClO
mim][ClO ]) containing 20 M water, whereas mono-hydrated chelate was formed in [C
]) containing 20 M water, whereas mono-hydrated chelate was formed in [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N, ClO
N, ClO ] in the presence of 0.50 M Tf
] in the presence of 0.50 M Tf N
N and 20 M water. These results show that the coordinated water molecules of [Eu(tta)
and 20 M water. These results show that the coordinated water molecules of [Eu(tta) (H
(H O)
O) ] were replaced by the Tf
] were replaced by the Tf N
N anions. In fact, an anionic adduct, [Eu(tta)
anions. In fact, an anionic adduct, [Eu(tta) (Tf
(Tf N)]
N)] , was observed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in the presence of [C
, was observed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in the presence of [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N].
N].
 on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modeling
on Na-montmorillonite studied by time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy and surface complexation modelingSasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Saito, Takumi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Takagi, Ikuji*; Kimura, Takaumi; Tachi, Yukio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.592 - 601, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influences of pH and the concentrations of Eu and NaNO
and NaNO on the sorption of Eu
on the sorption of Eu to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO
to Na-montmorillonite were investigated through batch sorption measurements and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). The pH had a little effect on the distribution coefficients (Kd) in 0.01 M NaNO , whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO
, whereas the Kd strongly depended on pH at 1 M NaNO . A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu
. A cation exchange model combined with a one-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model was successfully applied to the measured Kd. The TRLFS spectra of Eu sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu
sorbed were processed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), which corresponded to one outer-sphere (factor A) and two inner-sphere (factor B and C) complexes. It turned out that factors A and B correspond to Eu sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH)
sorbed by ion exchange sites and inner-sphere complexation with hydroxyl groups of the edge faces, respectively. Factor C became dominant at relatively high pH and ionic strength and likely correspond to the precipitation of Eu(OH) on the surface.
on the surface.
Saito, Takumi; Terashima, Motoki; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nagao, Seiya*; Fujitake, Nobuhide*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 17(8), p.1386 - 1395, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:32.46(Chemistry, Analytical)The deep groundwater HSs were different from surface HSs, having high aliphaticities, sulfur contents, and small molecular sizes. The amounts of their acidic functional groups were comparable to or slightly larger than those of surface HSs; however, the magnitude of Cu binding to the deep groundwater HSs was smaller. The NICA-Donnan model attributed this to the binding of Cu
binding to the deep groundwater HSs was smaller. The NICA-Donnan model attributed this to the binding of Cu to chemically homogeneous carboxylic-type sites via mono-dentate coordination at relatively low pH. The binding mode tended to shift to multi-dentate coordination with carboxylic-type and probably more heterogeneous alcoholic hydroxide-type groups at higher pH. This study shows the particularity of the deep groundwater HSs in terms of their physicochemical and ion-binding properties, compared with surface HSs.
to chemically homogeneous carboxylic-type sites via mono-dentate coordination at relatively low pH. The binding mode tended to shift to multi-dentate coordination with carboxylic-type and probably more heterogeneous alcoholic hydroxide-type groups at higher pH. This study shows the particularity of the deep groundwater HSs in terms of their physicochemical and ion-binding properties, compared with surface HSs.
V zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(14), p.8487 - 8496, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.81(Engineering, Environmental)The uptake and binding of uranium by a moderately acidophilic fungus, 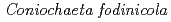 , recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
, recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
 -bis(thiocyanato)aurate(I) complexes in ionic liquids
-bis(thiocyanato)aurate(I) complexes in ionic liquidsAoyagi, Noboru; Shinha, Yusuke*; Ikeda, Atsushi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Brooks, N. R.*; Izuoka, Akira*; Naganawa, Hirochika; Kimura, Takaumi; Binnemans, K.*
Crystal Growth & Design, 15(3), p.1422 - 1429, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The photochemistry of a gold(I) thiocyanate complex has been investigated to determine the coordination structure in both the solid and liquid states. The coordination geometries of the supramolecular complex and the concomitant exciplex have mainly been analyzed by crystallographic analysis and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The Au-S bond distance and Au-Au separation of the compound in the ground state and in the phosphorescent excited state were compared. Upon irradiation with UV light, the excimeric interactions were enhanced, resulting in a contraction of the Au-Au aurophilic distance. A broad luminescence spectrum was observed for the one-dimensional chain suprastructure. The time-resolved luminescence spectra indicated the entity of several oligomeric species in the crude liquid without neutral solvent molecules. In addition, EXAFS spectroscopy exhibited a slight change in the nearest Au-S distance due to the photo-switched transformation. The deformation of the (Au-Au)* exciplexes was not apparently promoted in the liquid state with the asymmetrical imidazoium cations having a non-local charge distribution in the present observation. This is plausibly due to a flexible molecular structure and a property in the liquid state. In conclusion, the photo-excited nature of the pseudo-one dimensional complexes is emerged in controlling bond distances among the supramolecular networks.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1095 - 1098, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.96(Chemistry, Analytical)

Saito, Takumi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kimura, Takaumi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1129 - 1132, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.5(Chemistry, Analytical)Time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS) is a powerful speciation technique for fluorescent metal ions and can be further improved by combining with multi-mode factor analysis such as parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). This study demonstrates the applicability of TRLFS combined with PARAFAC for the speciation of uranyl (UO
 ) in the presence of silicic acid (Si(OH)
) in the presence of silicic acid (Si(OH) ). A series of TRLFS data with varied Si(OH)
). A series of TRLFS data with varied Si(OH) concentration was processed by PARAFAC, resulting in three factors corresponding to free UO
concentration was processed by PARAFAC, resulting in three factors corresponding to free UO
 , UO
, UO SiO(OH)
SiO(OH)
 , and UO
, and UO OH
OH . The stability constant of UO
. The stability constant of UO SiO(OH)
SiO(OH)
 was further optimized, based on the intensity profiles of the factors.
was further optimized, based on the intensity profiles of the factors.
Kozai, Naofumi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Onuki, Toshihiko
Water Research, 68, p.616 - 626, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:60.58(Engineering, Environmental)The radioactive fallout cesium ( Cs) in the sewage sludge ashes (SSAs) produced after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident was tested. Two of tested five SSAs contained
Cs) in the sewage sludge ashes (SSAs) produced after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident was tested. Two of tested five SSAs contained  Cs above the radioactivity criterion for controlled landfill disposal in Japan. The minerals of SSAs are divided into two groups: an HCl-soluble phase mainly composed of phosphates and metal oxides; and silicates. The majority of
Cs above the radioactivity criterion for controlled landfill disposal in Japan. The minerals of SSAs are divided into two groups: an HCl-soluble phase mainly composed of phosphates and metal oxides; and silicates. The majority of  Cs was contained in the HCl-soluble phase. Among the HCl-soluble subphases, Fe-bearing phases, probably iron oxides, were mainly responsible for
Cs was contained in the HCl-soluble phase. Among the HCl-soluble subphases, Fe-bearing phases, probably iron oxides, were mainly responsible for  Cs retention. Pre-pulverizing SSAs and heating them in an aqueous HCl was the most effective method of dissolving the HCl-soluble phase. The radioactivity concentrations of
Cs retention. Pre-pulverizing SSAs and heating them in an aqueous HCl was the most effective method of dissolving the HCl-soluble phase. The radioactivity concentrations of  Cs in all the HCl-treatment residues were below the criterion. This residue was mostly composed of silicates. Static leaching tests of the residue revealed that
Cs in all the HCl-treatment residues were below the criterion. This residue was mostly composed of silicates. Static leaching tests of the residue revealed that  Cs is very stably immobilized in the silicates.
Cs is very stably immobilized in the silicates.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Laser Surface Engineering; Processes and Applications, p.549 - 564, 2015/00