Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Torikai, Kota*; Kawachi, Naoki; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sato, Takahiro; Nagao, Yuto; Fujimaki, Shu; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(9), p.3638 - 3644, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:100(Engineering, Biomedical)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Nagao, Yuto; Kawachi, Naoki; Sato, Takahiro; Fujimaki, Shu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Torikai, Kota*; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sugai, Hiroyuki*; Sakai, Makoto*; et al.
International Journal of PIXE, 26(1&2), p.61 - 72, 2016/00
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.372 - 378, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1179 - 1181, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.500 - 502, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 715, p.126 - 131, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)An optimum condition for realizing phase bunching in the central region of a cyclotron was quantitatively clarified by a simplified geometric trajectory analysis of charged particles from the first to the second acceleration gap. The phase-bunching performance was evaluated for a general case of a cyclotron. The phase difference of incident particles at the second acceleration gap depends on the combination of four parameters: the acceleration harmonic number 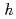 , the span angle
, the span angle 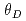 of the dee electrode, the span angle
of the dee electrode, the span angle 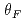 from the first to the second acceleration gap, the ratio
from the first to the second acceleration gap, the ratio 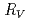 of the peak acceleration voltage between the cyclotron and ion source. Optimum values of
of the peak acceleration voltage between the cyclotron and ion source. Optimum values of 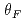 for phase bunching were limited by the relationship between
for phase bunching were limited by the relationship between 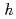 and
and 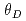 , which is 90
, which is 90 /
/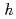 +
+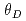 /2
/2 
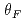
 180
180 /
/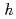 +
+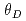 /2, and sin
/2, and sin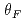
 0. The phase difference with respect to the reference particle at the second acceleration gap is minimized for voltage-ratios between two and four for an initial phase difference within 40 RF degrees. Although the slope of the first acceleration gap contributes to the RF phase at which the particles reach the second acceleration gap, phase bunching was not affected. An orbit simulation of the JAEA AVF cyclotron verifies the evaluation based on geometric analysis.
0. The phase difference with respect to the reference particle at the second acceleration gap is minimized for voltage-ratios between two and four for an initial phase difference within 40 RF degrees. Although the slope of the first acceleration gap contributes to the RF phase at which the particles reach the second acceleration gap, phase bunching was not affected. An orbit simulation of the JAEA AVF cyclotron verifies the evaluation based on geometric analysis.
 -ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton camera
-ray simultaneous imaging by using a Si/CdTe Compton cameraSuzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Torikai, Kota*; Sato, Takahiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; Kawachi, Naoki; Watanabe, Shigeki; et al.
Radiology, 267(3), p.941 - 947, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:65.03(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Nagao, Yuto; Kawachi, Naoki; Fujimaki, Shu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Kokubun, Motohide*; Takeda, Shinichiro*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), 3 Pages, 2013/00
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Torikai, Kota*; Kawachi, Naoki; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sato, Takahiro; Nagao, Yuto; Fujimaki, Shu; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), 2 Pages, 2013/00
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Torikai, Kota*; Kawachi, Naoki; Shimada, Hirofumi*; Sato, Takahiro; Nagao, Yuto; Fujimaki, Shu; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 57(10), p.2843 - 2856, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:79.35(Engineering, Biomedical)Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Kawachi, Naoki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sato, Takahiro; Suzui, Nobuo; Fujimaki, Shu; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Ishikawa, Shinnosuke*; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 145, 2012/01
no abstracts in English
Dobashi, Kunio*; Shimizu, Yasuo*; Matsuzaki, Shinichi*; Nagamine, Takeaki*; Sato, Takahiro; Okubo, Takeru; Yokoyama, Akihito; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 87, 2012/01
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Kawachi, Naoki; Suzui, Nobuo; Fujimaki, Shu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Ishikawa, Shinnosuke*; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 648(Suppl.1), p.S2 - S7, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)We are constructing a three-dimensional imaging system for medical and biological applications. The system will allow simultaneous imaging at high spatial and energy resolutions across a wide energy range, from several tens of keV to a few MeV. In this work, one prototype head module have been developed for a multi-head Si/CdTe Compton camera system. The performance of the prototype was evaluated with a sealed Ba-133 radiation source. The experiments confirmed that the imaging results were consistent with actual source position. In addition to the resolution for the parallel directions to the detector surface, the position resolution was evaluated for the depth direction at a point in near region of the head-module. These position resolutions were well reproduced by Monte Carlo simulation results.
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Nara, Takayuki; Ishibori, Ikuo; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yokota, Wataru; Nakamura, Yoshiteru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 636(1), p.41 - 47, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)A phase bunching effect has been achieved for the first time using a rising slope of the dee voltage waveform produced at the first acceleration gap between the RF shielding cover of the inflector and the puller in the new central region of the JAEA AVF cyclotron. The feasibility of the phase bunching effect in the central region for a two-dee system with a span angle of 86  in three acceleration harmonic modes was assessed by a simple geometrical analysis of particle trajectories and a three-dimensional beam orbit simulation. The simulation indicated that the initial beam phase width of 40 RF degrees is compressed to 11 RF degrees in the second harmonic mode. A phase width of 1.5 RF degrees FWHM for a 260 MeV
in three acceleration harmonic modes was assessed by a simple geometrical analysis of particle trajectories and a three-dimensional beam orbit simulation. The simulation indicated that the initial beam phase width of 40 RF degrees is compressed to 11 RF degrees in the second harmonic mode. A phase width of 1.5 RF degrees FWHM for a 260 MeV  Ne
Ne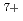 beam accelerated in the second harmonic mode was reduced by the bunching effect, compared with the beam phase width of 7.3 RF degrees FWHM in the same harmonic mode for a 10 MeV H
beam accelerated in the second harmonic mode was reduced by the bunching effect, compared with the beam phase width of 7.3 RF degrees FWHM in the same harmonic mode for a 10 MeV H beam accelerated in the original central region.
beam accelerated in the original central region.
Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Kawachi, Naoki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Suzui, Nobuo; Fujimaki, Shu; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Ishikawa, Shinnosuke*; Kokubun, Motohide*; Watanabe, Shin*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
2010 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record (CD-ROM), p.2004 - 2007, 2010/10
Tanaka, Naritake*; Kimura, Hitoshi*; Faried, A.*; Sakai, Makoto*; Sano, Takaaki*; Inose, Takanori*; Soda, Makoto*; Okada, Koji*; Nakajima, Masanobu*; Miyazaki, Tatsuya*; et al.
Cancer Science, 101(6), p.1487 - 1492, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:31.77(Oncology)We examined the intracellular localization of cisplatin, a key chemotherapeutic agent, in esophageal cancer cell lines and determined their sensitivity to cisplatin using in-air micro-PIXE. Two human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines, TE-2 and TE-13, were examined for their response to cisplatin using MTT assay, flow cytometry and DNA fragmentation assays. Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was also used to evaluate the mRNA expression of multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) in both cell lines. Platinum localizations of intracellular and intranuclear were measured using in-air micro-PIXE. TE-2 cells were more sensitive to cisplatin than TE-13 cells. The results of this study suggest that in-air micro-PIXE could be a useful quantitative method for evaluating the cisplatin sensitivity of individual cells. Finally, we speculate that MRP2 in the cell membrane may play an important role in regulating cisplatin sensitivity of ESCC cells.
Matsuzaki, Shinichi*; Shimizu, Yasuo*; Dobashi, Kunio*; Nagamine, Takeaki*; Sato, Takahiro; Okubo, Takeru; Yokoyama, Akihito; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo*; et al.
International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, 23(1), p.1 - 11, 2010/01
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Ishibori, Ikuo; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yokota, Wataru; Nakamura, Yoshiteru*; Arakawa, Kazuo; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(3), p.033302_1 - 033302_9, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)Single-turn extraction from the JAEA AVF cyclotron with a K number of 110 using a flat-top (FT) acceleration system has been achieved to reduce the energy spread of an ion beam for microbeam formation with energy up to hundreds of MeV and to increase extraction efficiency from the cyclotron. In order to generate an FT waveform voltage using the fifth-harmonic frequency on a dee electrode, an FT resonator was designed using MAFIA code to achieve downsizing and low power consumption. The FT resonator, coupled to the main resonator through a coupling capacitor, covered the full range of the fifth harmonic frequency from 55 to 110 MHz. Various ion beams, accelerated using different acceleration harmonic mode of h = 1 and 2, such as 220 MeV  C
C (h = 2), 260 MeV
(h = 2), 260 MeV  Ne
Ne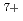 (h = 2), and 45 MeV H
(h = 2), and 45 MeV H (h = 1) were developed by FT acceleration. A clear turn separation of the beam bunches was successfully observed at the extraction region of the large-scale AVF cyclotron with number of revolutions greater than 200. As a result, high extraction efficiency (over 95%) from the cyclotron was achieved. Single-turn extraction was confirmed by counting the number of beam bunches out of the cyclotron for an injected beam pulsed by a beam chopping system in the injection line. The energy spread of the 260 MeV
(h = 1) were developed by FT acceleration. A clear turn separation of the beam bunches was successfully observed at the extraction region of the large-scale AVF cyclotron with number of revolutions greater than 200. As a result, high extraction efficiency (over 95%) from the cyclotron was achieved. Single-turn extraction was confirmed by counting the number of beam bunches out of the cyclotron for an injected beam pulsed by a beam chopping system in the injection line. The energy spread of the 260 MeV  Ne
Ne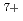 beam was measured using an analyzing magnet and we verified a reduction of the energy spread from
beam was measured using an analyzing magnet and we verified a reduction of the energy spread from  E/E = 0.1% to 0.05% by single-turn extraction.
E/E = 0.1% to 0.05% by single-turn extraction.
Kawachi, Naoki; Watanabe, Shigeki; Sato, Takahiro; Arakawa, Kazuo; Takeda, Shinichiro*; Ishikawa, Shinnosuke*; Aono, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Shin*; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; et al.
2008 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record (CD-ROM), p.1540 - 1543, 2008/10