Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Masayuki*; Nishihata, Itsuki*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Ito, Yusuke*; Sugita, Naohiko*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Hirose, Akio*; Sano, Tomokazu*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(7), p.075101_1 - 075101_9, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:66.34(Physics, Applied)Gilbert, M. R.*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Tsuru, Tomohito; 26 of others*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 554, p.153113_1 - 153113_31, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:91.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Modelling will continue to do so until the first generation of fusion power plants come on line and allow long-term behaviour to be observed. In the meantime, the modelling is supported by experiments that attempt to replicate some aspects of the eventual operational conditions. In 2019, a group of leading experts met under the umbrella of the IEA to discuss the current position and ongoing challenges in modelling of fusion materials and how advanced experimental characterisation is aiding model improvement. This review draws from the discussions held during that workshop. Topics covering modelling of irradiation-induced defect production and fundamental properties, gas behaviour, clustering and segregation, defect evolution and interactions are discussed, as well as new and novel multiscale simulation approaches, and the latest efforts to link modelling to experiments through advanced observation and characterisation techniques.
 WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealing
WB-STEM observation of dislocation loop behavior in reactor pressure vessel steel during post-irradiation annealingDu, Y.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Milan, K. J.*; Gerard, R.*; Onuki, Somei*; et al.
Materialia, 12, p.100778_1 - 100778_10, 2020/08
In order to ensure the integrity of the reactor pressure vessel in the long term, it is necessary to understand the effects of irradiation on the materials. In this study, irradiation-induced dislocation loops were observed in neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel specimens during annealing using our newly developed WB-STEM. It was confirmed that the proportion of 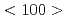 loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two
loops increased with increasing annealing temperature. We also succeeded in observing the phenomenon that two 
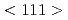 loops collide into a
loops collide into a 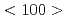 loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.
loop. Moreover, a phenomenon in which dislocation loops decorate dislocations was also observed, and the mechanism was successfully explained by molecular dynamics simulation.
Sano, Tomokazu*; Eimura, Takayuki*; Hirose, Akio*; Kawahito, Yosuke*; Katayama, Seiji*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Masaki, Kiyotaka*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Sano, Yuji*
Metals, 9(11), p.1192_1 - 1192_13, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:61.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The purpose of the present study was to verify the effectiveness of dry laser peening (DryLP), which is the peening technique without a sacrificial overlay under atmospheric conditions using femtosecond laser pulses on the mechanical properties such as hardness, residual stress, and fatigue performance. After DryLP treatment of the laser-welded 2024 aluminum alloy, the softened weld metal recovered to the original hardness of base metal, while residual tensile stress in the weld metal and heat-affected zone changed to compressive stresses. The fatigue life almost doubled at a stress amplitude of 180 MPa and increased by a factor of more than 50 at 120 MPa. As a result, DryLP was found to be more effective for improving the fatigue performance of laser-welded aluminum specimens with welding defects at lower stress amplitudes.
Ono, K.*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Ohashi, Masahiro*; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi; Yoshida, Naoaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 283-287(Part.1), p.210 - 214, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -ray emitters including
-ray emitters including  Cs, 1; Collaborative experiment by the committee on preparation of reference materials for radioactivity analysis of JSAC
Cs, 1; Collaborative experiment by the committee on preparation of reference materials for radioactivity analysis of JSACYonezawa, Chushiro*; Kakita, Kazutoshi*; Takahashi, Takanori*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Maeda, Satoshi; Abe, Takaaki*; Arakawa, Fumihiro*; Kiho, Nobuharu*; Akiyama, Masakazu*; Muramatsu, Isamu*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Kenta*; Du, Y.*; Shimada, Yusuke*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Milan, K. J.*; Gerard, R.*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
no journal, ,
We developed a weak-beam scanning transmission electron microscopy (WB-STEM) by installing a novel beam selector, annular detector, a high-speed CCD camera and imaging filter in a camera chamber of an aberration corrected electron microscope. In-situ observation confirmed that the newly-developed WB-STEM has improved the ability to observe the dynamic behavior of dislocation loops. In addition, we performed a numerical simulation of dislocation loop behavior using molecular dynamics, and confirmed that the experimental results were well explained by the theoretical analysis. Therefore, this WB-STEM is expected to be useful for understanding the embrittlement mechanism of nuclear materials such as reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels.