Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Arakawa, Masahiko*; Yasui, Minami
Physics and Chemistry of Ice 2010, p.339 - 344, 2011/05
We conducted impact experiments of water ice and measured a post shock temperature of impact crater using an infrared video camera. The surface temperature in a crater showed a peak temperature just after the impact then it cooled down gradually with time. The decay time of maximum temperature might depend on a scale of heated volume in a crater, so we estimated the ratio of thermal energy to projectile kinetic energy. As a result, we found that up to 10% of the projectile kinetic energy was partitioned into the post shock heating of the impact crater.
Shimaki, Yuri*; Arakawa, Masahiko*; Yasui, Minami
Physics and Chemistry of Ice 2010, p.379 - 386, 2011/05
Impact disruption of sintered snowballs was studied to clarify the effect of sintering on impact strength and fragment velocity. Ice and snow projectiles were impacted on sintered snowballs with a porosity of 40%. The sintering duration of snow was changed from 1 hour to 1 month, and the effect of sintering on impact strength and static strength were examined. As a result, it was found that both impact strength and static strength of snow have a power law relationship to a sintering duration with a power law index of about 0.2.
Yasui, Minami; Arakawa, Masahiko*
Physics and Chemistry of Ice 2010, p.387 - 395, 2011/05
We did deformation experiments on ice-silica mixtures to study their flow laws. We found that the mixture became softer as porosity or silica mass content increased. A power law index  and an activation energy
and an activation energy  were found to depend only on silica mass content.
were found to depend only on silica mass content.
Nagamine, Takeaki*; Takada, Hisashi*; Kusakabe, Takahiko*; Nakazato, Kyomi*; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo; Iha, Masahiko*
Biological Trace Element Research, 124(1), p.60 - 69, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.92(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)This study was undertaken to elucidate the intracellular changes of metal elements after the administration of fucoidan extracted from 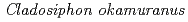 . TRL1215 cells (normal rat liver cell line) were treated with 0, 0.1, or 1.0 mg/mL fucoidan. The cellular distribution of elements was analyzed using in-air micro-PIXE induced X-ray emission. In fucoidan-treated cells, the focal accumulation of Br (BrdU) was correlated spatially with phosphorous-rich region, suggesting that Br was localized within the nucleus. Al distribution provided a spatial association with Br map. These data suggest that fucoidan binding Al us postulated to be transferred into the nucleus.
. TRL1215 cells (normal rat liver cell line) were treated with 0, 0.1, or 1.0 mg/mL fucoidan. The cellular distribution of elements was analyzed using in-air micro-PIXE induced X-ray emission. In fucoidan-treated cells, the focal accumulation of Br (BrdU) was correlated spatially with phosphorous-rich region, suggesting that Br was localized within the nucleus. Al distribution provided a spatial association with Br map. These data suggest that fucoidan binding Al us postulated to be transferred into the nucleus.
Sasa, Narimasa; Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Arakawa, Chuichi*
Nihon Keisan Kogakkai Rombunshu, 7, p.83 - 87, 2005/05
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Machida, Masahiko; Arakawa, Chuichi*
Nihon Keisan Kogakkai Rombunshu, 7, p.243 - 252, 2005/05
no abstracts in English
Sasa, Narimasa; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Arakawa, Chuichi
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu, 8(2), p.757 - 758, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
Sasa, Narimasa; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Arakawa, Chuichi
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu, 7(1), p.171 - 172, 2002/05
Algebraic Multi Grid(AMG) is applied to solve the Ginzburg-Landau equations for Superconductors. The method effectively solves large scale linear algebraic equations. AMG is also applicable for systems with complex boundary condition in contrast with usual Geometrical Multi Grid.
Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Okamoto, Masahiko*; Shin, Masako*; Takeuchi, Aiko*; Hasegawa, Masatoshi*; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo; Nakano, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Masahiko*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Shin, Masako*; Hasegawa, Masatoshi*; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo; Nakano, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Masatoshi*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Shin, Masako*; Okamoto, Masahiko*; Ishiuchi, Shogo*; Asakawa, Isao*; Tamamoto, Tetsuo*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English