Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Kira, Hiroshi; Oi, Motoki; Maekawa, Fujio; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Ino, Takashi*; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 340, p.012037_1 - 012037_7, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.66(Physics, Condensed Matter)At the Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC, an experiment of detecting a neutron polarizing ability caused by a neutron-nuclear (n-N) spin correlation term at a resonant peak of  Xe is planned. The Xe gas having a high polarization under low magnetic field and room temperature by a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) technique is expected to become a suitable target for verification of the neutron optical theorem (NOPT). We evaluated measurable quantities based on the NOPT, developed a polarized Xe gas system, and carried out a feasibility test of our apparatus. This paper reports on the present status of the experiment.
Xe is planned. The Xe gas having a high polarization under low magnetic field and room temperature by a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) technique is expected to become a suitable target for verification of the neutron optical theorem (NOPT). We evaluated measurable quantities based on the NOPT, developed a polarized Xe gas system, and carried out a feasibility test of our apparatus. This paper reports on the present status of the experiment.
 He neutron spin filters on the small-angle neutron scattering spectrometer SANS-J-II
He neutron spin filters on the small-angle neutron scattering spectrometer SANS-J-IISakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Noda, Yohei; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 294(1), p.012017_1 - 012017_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.75(Physics, Applied) He neutron spin filter in Japan
He neutron spin filter in JapanKira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Chang, L.-J.; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Arimoto, Yasushi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 294, p.012014_1 - 012014_5, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:94.40(Physics, Applied) He neutron spin filter cells
He neutron spin filter cellsSakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Suzuya, Kentaro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 294(1), p.012004_1 - 012004_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.75(Physics, Applied) He neutron spin filters
He neutron spin filtersSakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Suzuya, Kentaro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 406(12), p.2443 - 2447, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.82(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Endo, Yasuo; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 406(12), p.2433 - 2435, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.04(Physics, Condensed Matter) He neutron spin filters
He neutron spin filtersSakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Suzuya, Kentaro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 406(12), p.2443 - 2447, 2011/06
 He neutron spin filter cells
He neutron spin filter cellsSakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Suzuya, Kentaro; Arai, Masatoshi; Takeda, Masayasu; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 634(1, Suppl.), p.S122 - S125, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
Nuclear Physics Review, 26(Suppl.), p.94 - 99, 2009/07
We constructed MeV- and sub-MeV-photon sources by means of Compton backscattering with a laser light and an electron beam at SPring-8 and KPSI-JAEA. MeV-photon source consists of a continuous-wave optically-pumped far infrared laser and an 8-GeV stored electron beam. Sub-MeV-photon source consists of a Nd:YAG pulse-laser and an 150-MeV electron beam accelerated by a microtron. Both source have been succeeded backscattered photon generation. In this talk, I will present characteristics and future prospects of these photon sources.
 -ray generation from backward Compton scattering at SPring-8
-ray generation from backward Compton scattering at SPring-8Kawase, Keigo; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Okajima, Shigeki*; Shoji, Masazumi*; Suzuki, Shinsuke*; Tamura, Kazuhiro*; Yorita, Tetsuhiko*; Okuma, Haruo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 592(3), p.154 - 161, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)A test experimental line at SPring-8 has been constructed for the generation of backward Compton scattered (BCS)  -ray by head-on collision between an 8 GeV electron beam and a far-infrared (FIR) laser. For the FIR laser, we use a continuous-wave methanol laser optically pumped by a carbon dioxide (
-ray by head-on collision between an 8 GeV electron beam and a far-infrared (FIR) laser. For the FIR laser, we use a continuous-wave methanol laser optically pumped by a carbon dioxide (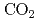 ) laser. The FIR laser output power achieved is 1.6 W at maximum for 118.8
) laser. The FIR laser output power achieved is 1.6 W at maximum for 118.8  m lasing; this value is the highest in the case of this type of laser. As a result of the direct measurement, the generated BCS
m lasing; this value is the highest in the case of this type of laser. As a result of the direct measurement, the generated BCS  -ray flux was found to be about
-ray flux was found to be about 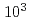 photons/s. This value is consistent with the estimation calculated by taking into account the input laser power and the transmittance of the laser transport system.
photons/s. This value is consistent with the estimation calculated by taking into account the input laser power and the transmittance of the laser transport system.
 He
HeAkimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Nakayama, Shintaro*; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Fushimi, Kenichi*; Hara, Keigo*; Ota, Masahisa*; Shiokawa, Atsuko*; Tanaka, Masayoshi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 67(5), p.051302_1 - 051302_4, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:80.37(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 He neutron spin filters, 3
He neutron spin filters, 3Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Takeda, Masayasu; Wakimoto, Shuichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron scattering is a powerful technique in order to clarify the magnetic structure of materials. The technique is often used in JRR-3 nowadays. However, the available energy has been limited below 100 meV as long as we use the conventional polarizing method. To realize polarized neutron scattering experiments above the energy, the use of  He spin filters is the best solution. In addition, in the new pulsed neutron facility, J-PARC, the neutron source has wide energy spectrum. To polarize all the neutrons, it is desired to use the
He spin filters is the best solution. In addition, in the new pulsed neutron facility, J-PARC, the neutron source has wide energy spectrum. To polarize all the neutrons, it is desired to use the  He spin filters. Taking these backgrounds into account, we are now planning to introduce
He spin filters. Taking these backgrounds into account, we are now planning to introduce  He neutron spin filters to polarized neutron experiments at JRR-3 and J-PARC. In our oral presentation, we report the detailed plan of the experiments and the present status of the preparation.
He neutron spin filters to polarized neutron experiments at JRR-3 and J-PARC. In our oral presentation, we report the detailed plan of the experiments and the present status of the preparation.
 He spin filter technique
He spin filter techniqueSakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oyama, Kenji*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Tsutsumi, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
After the birth of a new neutron scattering facility, MLF at J-PARC, it is desired to establish the most suitable polarizing technique for the facility. In MLF the white neutron beam over the wide energy range is used and the use of  He spin filter technique is the best one. However, the technological level in Japan is far below the world's top level. To realize the polarized neutron scattering experiments using
He spin filter technique is the best one. However, the technological level in Japan is far below the world's top level. To realize the polarized neutron scattering experiments using  He spin filters in MLF, it is necessary to make the experiments at a reactor neutron facility first and to establish the required technique. Therefore, we have performed polarized neutron experiments at HERMES in JRR-3. We used the monochromatized neutron beam with 1.82
He spin filters in MLF, it is necessary to make the experiments at a reactor neutron facility first and to establish the required technique. Therefore, we have performed polarized neutron experiments at HERMES in JRR-3. We used the monochromatized neutron beam with 1.82  . We measured the flipping ratio at the 111 reflection of single-crystalline Cu
. We measured the flipping ratio at the 111 reflection of single-crystalline Cu MnAl and the change was observed. The details of the experimental setup and the results will be reported.
MnAl and the change was observed. The details of the experimental setup and the results will be reported.
 He polarized neutron spin filters and its present status, 2
He polarized neutron spin filters and its present status, 2Kira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 He gas neutron spin filters
He gas neutron spin filtersKira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Ino, Takashi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 He filter technique for condensed-matter physics; Development of spin control devices
He filter technique for condensed-matter physics; Development of spin control devicesTsutsumi, Kenji*; Oyama, Kenji*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Yamaguchi, Yasuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Takeda, Masayasu; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 He neutron spin filter
He neutron spin filterOku, Takayuki; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have been developing an  SEOP polarized
SEOP polarized  He neutron spin filter to apply it to pulsed neutron experiments. The
He neutron spin filter to apply it to pulsed neutron experiments. The  He based neutron polarizer is useful in experiments such as polarized neutron scattering experiments in a wide q-range, inelastic scattering experiment with high energy magnetic and phonon excitation, magnetic field imaging and etc, since it is effective for neutrons in a wide energy range. To introduce the
He based neutron polarizer is useful in experiments such as polarized neutron scattering experiments in a wide q-range, inelastic scattering experiment with high energy magnetic and phonon excitation, magnetic field imaging and etc, since it is effective for neutrons in a wide energy range. To introduce the  SEOP polarized
SEOP polarized  He neutron spin filter into the instruments of the pulsed neutron facility such as J-PARC, it is important to make the system compact and stable, because the system is located inside thick and bulky radiation shields for high energy
He neutron spin filter into the instruments of the pulsed neutron facility such as J-PARC, it is important to make the system compact and stable, because the system is located inside thick and bulky radiation shields for high energy  ray and neutrons. In this study, we have developed a compact laser optics system with a volume holographic grating (VHG) element for the SEOP system. We report the design of our spin filter system and some results of the
ray and neutrons. In this study, we have developed a compact laser optics system with a volume holographic grating (VHG) element for the SEOP system. We report the design of our spin filter system and some results of the  He polarizing experiments in this paper.
He polarizing experiments in this paper.
 He
HeChang, L.-J.; Oku, Takayuki; Kira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Takeda, Masayasu; et al.
no journal, ,
Oku, Takayuki; Kira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Sakai, Kenji; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shinohara, Takenao; Koizumi, Satoshi; Takata, Shinichi; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
no journal, ,
Material and Life science experimental facility (MLF) of J-PARC center have started user program in which experiments using pulsed neutron beam are available from December 2008. The source power of the pulsed spallation neutron source JSNS is gradually increasing and now reached 120 KW, where its final goal is 1 MW. With increasing the neutron source power, the number of user programs is also increasing. In this situation, a 5-years project, which aims at higher efficient utilization of neutrons in neutron scattering research, have started since 2008 in Japan. Six Japanese institutes join this project, and neutron optical devices including  He spin filters, neutron imaging device and neutron scattering method are being developed. In this paper, we report the current status of optical devices development and application and future perspective in Japan.
He spin filters, neutron imaging device and neutron scattering method are being developed. In this paper, we report the current status of optical devices development and application and future perspective in Japan.
 He neutron spin filters, 2
He neutron spin filters, 2Kira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Arimoto, Yasushi*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English