Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with high kinetic energy
with high kinetic energyTakahashi, Shin*; Aruga, Tetsuya*; Teraoka, Yuden
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, A, 136(7), p.462 - 463, 2016/07
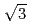

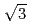 )R30
)R30 surface
surfaceTakahashi, Shin*; Hatta, Shinichiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Aruga, Tetsuya*
Surface Science, 603(1), p.221 - 225, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.31(Chemistry, Physical)An initial oxidation dynamics at 4H-SiC(0001)-(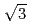

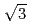 )R30
)R30 surface has been studied using high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic molecular beams. The clean surface was exposed to oxygen molecules with translational energy of 0.5 eV at 300 K. In the initial stage, oxygen molecules are immediately dissociated and atomic oxygens are inserted into Si-Si back bonds to form stable oxide species. At this stage, drastic increase in growth rate of stable oxide species was found by heating molecular beam source to 1400 K. We concluded that the increase of growth rate is mainly caused by molecular vibrational excitation. It suggests that the dissociation barrier is located in the exit channel on potential energy hypersurface. A metastable molecular oxygen species was also found to be adsorbed on a Si-adatom. The adsorption of the metastable species, however, is neither enhanced nor suppressed by molecular vibrational excitation.
surface has been studied using high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic molecular beams. The clean surface was exposed to oxygen molecules with translational energy of 0.5 eV at 300 K. In the initial stage, oxygen molecules are immediately dissociated and atomic oxygens are inserted into Si-Si back bonds to form stable oxide species. At this stage, drastic increase in growth rate of stable oxide species was found by heating molecular beam source to 1400 K. We concluded that the increase of growth rate is mainly caused by molecular vibrational excitation. It suggests that the dissociation barrier is located in the exit channel on potential energy hypersurface. A metastable molecular oxygen species was also found to be adsorbed on a Si-adatom. The adsorption of the metastable species, however, is neither enhanced nor suppressed by molecular vibrational excitation.
 1)-O
1)-OTakahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yosuke*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okuyama, Hiroshi*; Aruga, Tetsuya*
Surface Science, 601(18), p.3809 - 3812, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.63(Chemistry, Physical)Supersonic molecular beam techniques with 0.5-1.0eV and high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation were applied to the dynamics study for oxygen dissociative adsorption on Ru(0001). Increase of adsorption probability and saturation coverage with increasing translational energy suggests a direct dissociation mechanism. We measured uptake curves with and without heating a molecular beam source to verify internal energy effects. We found drastic enhancement of dissociative adsorption. In comparison with rotational and translational cooling during beam expansion, vibrational populations are known to be almost unrelaxed. Then, we concluded that adsorption enhancement was mainly caused by vibrational excitation, indicating that dissociation barrier was located in the exit channel on the potential energy surface. Such vibrational effect was also found on oxygen pre-covered Ru(0001) surface with a 0.5 monolayer corresponding to a p(2 1) structure.
1) structure.
 TiO
TiO
Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Naito, Akira*; Aruga, Takeo; Grismanovs, V.*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1398 - 1403, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:92.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yosuke*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Aruga, Tetsuya*
Chemical Physics Letters, 433(1-3), p.58 - 61, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.75(Chemistry, Physical)Dissociative adsorption of oxygen on Ru(0001) surface was investigated by supersonic molecular beam method combined with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) using synchrotron radiation. We examined effects of the molecular vibrational excitation as well as translational energy on dissociative adsorption of oxygen in the direct adsorption regime. We found an enhancement of dissociative oxygen adsorption on Ru(0001) by molecular vibrational excitation, indicating that potential energy surface has late barrier for this system.
Takahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yosuke*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke*; Aruga, Tetsuya*
KEK Proceedings 2006-3, p.80 - 82, 2006/08
Growth of oxygen adlayer on a Ru(0001) surface with high energy supersonic oxygen molecular beam was studied using high energy resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The Ru 3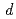
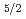 core level was used to monitor the growth of oxygen adlayer in the coverage region from 0.5 to 0.6 monolayer (ML) and the photoelectron spectrum was resolved into bulk and two surface components denoted as S1(2O) and S1(3O), which were first layer Ru atoms bonded to two and three oxygen atoms, respectively. The intensity change of each component as a function of oxygen dosage suggests the possibility of partial island formation on Ru(0001).
core level was used to monitor the growth of oxygen adlayer in the coverage region from 0.5 to 0.6 monolayer (ML) and the photoelectron spectrum was resolved into bulk and two surface components denoted as S1(2O) and S1(3O), which were first layer Ru atoms bonded to two and three oxygen atoms, respectively. The intensity change of each component as a function of oxygen dosage suggests the possibility of partial island formation on Ru(0001).
 TiO
TiO irradiated with high energy ions
irradiated with high energy ionsNakazawa, Tetsuya; Grismanovs, V.*; Yamaki, Daiju; Katano, Yoshio*; Aruga, Takeo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.166 - 170, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)Li TiO
TiO samples with high energy oxygen ions were examined by the use of Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Raman spectra of the irradiated samples do not show any evidence of destruction of Li
samples with high energy oxygen ions were examined by the use of Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Raman spectra of the irradiated samples do not show any evidence of destruction of Li TiO
TiO structure. On the other hand, the Bragg peak intensity of XRD is decreased with the increasing the ion fluence. Especially, the intensity of (002) supercell peak is drastically reduced after the irradiation to 1.2E+19 ions/m
structure. On the other hand, the Bragg peak intensity of XRD is decreased with the increasing the ion fluence. Especially, the intensity of (002) supercell peak is drastically reduced after the irradiation to 1.2E+19 ions/m . This result implies that partial site mixing between Li and Ti atoms is induced by the irradiation. The transition to such a disordering is observed also by SEM examination; the grain structure at surface layer is vanished after the irradiation.
. This result implies that partial site mixing between Li and Ti atoms is induced by the irradiation. The transition to such a disordering is observed also by SEM examination; the grain structure at surface layer is vanished after the irradiation.
 O
O
Katano, Yoshio*; Aruga, Takeo; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Yamaki, Daiju; Noda, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 283-287(Part.2), p.942 - 946, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 TiO
TiO ceramics
ceramicsNakazawa, Tetsuya; Grismanovs, V.*; Yamaki, Daiju; Katano, Yoshio*; Aruga, Takeo; Iwamoto, Akira
Proceedings of 2000 International Conference on Ion Implantation Technology (IIT 2000), p.753 - 756, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
 O
O irradiated with triple beam of H, He and heavy ions
irradiated with triple beam of H, He and heavy ionsKatano, Yoshio*; Aruga, Takeo; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Yamaki, Daiju
Proceedings of 2000 International Conference on Ion Implantation Technology (IIT 2000), p.805 - 808, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yoichi*; Aruga, Tetsuya*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke
no journal, ,
Ru(0001) surface was oxidized by supersonic oxygen molecular beams. Chemical bonding states of O and Ru atoms at the surface were analized by photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. First, the Ru(0001) surface was exposed to oxygen gas to be formed oxygen-saturated surface with 0.5 ML. The oxidized Ru surface was irradiated by supersonic oxygen molecular beams. Adsorption characterictics of oxygen molecules were investigated. The translational kinetic energy of oxygen molecular beam was 0.5eV. Differences of oxygen uptake curves were investigated for a nozzle temperature of 300K and 1400K. In the case of 300K, saturated oxygen amount increased up to 0.58ML. The oxygen coverage increased up to 0.61ML in the case of 1400K. The difference was interpreted as a large adsorption probability of vibrationally-excited oxygen molecules.
Takahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yosuke*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Aruga, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
Oxygen adsorption processes at a Ru(0001) surface were investigated in an oxygen coverage region larger than 0.5ML via supersonic oxygen nmolecular beam techniques and high resolution photoemission spectroscopy with synchrotron radiation. It was found that vibrationally-excited oxygen molecules enhanced their adsorption in such a coverage region. This indicates that a trapping-mediated adsorption mechanism via a precursor state is dominant under such experimental conditions.
Takahashi, Shin*; Fujimoto, Yosuke*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Aruga, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Shin*; Aruga, Tetsuya*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Chemical reaction dynamics for oxidation processes of 4H-SiC(0001) surface has been studied by a supersonic molecular beam method and high energy-resolution XPS. Especially, we have focused our attention to effects of vibrationally-excited states for the oxidation processes. All experiments were performed at the surface chemistry experimental station of JAEA BL23SU in the SPring-8. Oxygen uptake curves were obtained by using oxygen molecular beams with different vibrational states, which was changed by selecting nozzle temperature of 300K and 1400K with constant translational energy of 0.5 eV. With increasing nozzle temperature, adsorption probability of oxygen increased widely. And we found that O1s XPS peak was composed of several components. They were deconvoluted by the Doniach-Sunjic function. By plotting these peak intensity against the dose of molecular beam, we have discussed on diffusion processes of oxygen atoms from surface to bulk.
Takahashi, Shin*; Aruga, Tetsuya*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Shin*; Teraoka, Yuden; Aruga, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English