Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (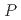
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 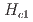 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 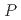 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
Abe, Shinichiro; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Liao, W.*; Kato, Takashi*; Asai, Hiroaki*; Shimbo, Kenichi*; Matsuyama, Hideya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kobayashi, Kazutoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 70(8, Part 1), p.1652 - 1657, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Single event upsets (SEUs) caused by neutrons is a reliability problem for microelectronic devices in the terrestrial environment. Acceleration tests using white neutron beam provide realistic soft error rates (SERs), but only a few facilities can provide white neutron beam in the world. If single-source irradiation applicable to diverse neutron source can be utilized for the evaluation of the SER in the terrestrial environment, it contributes to solve the shortage of beam time. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the SER estimation in the terrestrial environment by any one of these measured data with the SEU cross sections obtained by PHITS simulation. It was found that the SERs estimated by our proposed method are within a factor of 2.7 of that estimated by the Weibull function. We also investigated the effect of simplification which reduce the computational cost in simulation to the SER estimation.
 O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Furukawa, Hazuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(9), p.094707_1 - 094707_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Okuma, Ryutaro*; Kofu, Maiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Avdeev, M.*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.4382_1 - 4382_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences) ions for LaCo
ions for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O
Asai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.014034_1 - 014034_6, 2014/06
We have carried out the neutron scattering measurements for a single crystal of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh
in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh substitution for Co
substitution for Co of LaCoO
of LaCoO . The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4
. The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4 0.2
0.2
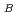 , which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo
, which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O . It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo
. It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh
originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh ions.
ions.
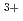 in LaCo
in LaCo Rh
Rh O
O investigated by structural phenomena
investigated by structural phenomenaAsai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kobayashi, Wataru*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Kumai, Reiji*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(11), p.114606_1 - 114606_6, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co
have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O
ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O octahedron of LaCo
octahedron of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh
are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO
substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co
from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co
ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh
ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh ions.
ions.
Mikake, Shinichiro; Yamamoto, Masaru; Ikeda, Koki; Sugihara, Kozo; Takeuchi, Shinji; Hayano, Akira; Sato, Toshinori; Takeda, Shinichi; Ishii, Yoji; Ishida, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2010-026, 146 Pages, 2010/08
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), one of the main facilities in Japan for research and development of the technology for high-level radioactive waste disposal, is under construction in Mizunami City. In planning the construction, it was necessary to get reliable information on the bedrock conditions, specifically the rock mass stability and hydrogeology. Therefore, borehole investigations were conducted before excavations started. The results indicated that large water inflow could be expected during the excavation around the Ventilation Shaft at GL-200m and GL-300m Access/Research Gallery. In order to reduce water inflow, pre-excavation grouting was conducted before excavation of shafts and research tunnels. Grouting is the injection of material such as cement into a rock mass to stabilize and seal the rock. This report describes the knowledge and lessons learned during the planning and conducting of pre-excavation grouting.
Kuji, Masayoshi*; Matsui, Hiroya; Hara, Masato; Minamide, Masashi*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Takeuchi, Shinji; Sato, Toshinori*; Asai, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2008-095, 54 Pages, 2009/01
A large amount of water inflow is frequently generated during the excavation of an underground cavern, such as road and railway tunnels, underground electric facilities etc. The reduction of water inflow is sometimes quite important for the reduction of cost for the water treatment and pumping during the construction of an underground cavern. The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is currently being constructed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. During its excavation, a large amount of water inflow into the shafts has been increasing and affecting the project progress. Therefore, a field experiment of post-excavation grouting around the Ventilation Shaft in a sedimentary formation carried out to confirm the effect of existing grouting technology for sedimentary formations in MIU project. The result shows that the applied methods in this field experiment are effective to prevent water inflow. This report describes the summary of the field experiment and the knowledge obtained through the experiment.
Kuji, Masayoshi*; Asai, Hideaki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hara, Masato
Maeda Kensetsu Gijutsu Kenkyushoho (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory is currently being constructed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. During its excavation, large amount of water inflow into the shafts has been increasing and affecting the project progress. As countermeasures for reducing water inflow, grouting methods are being considered, one is post-excavation grouting for the area already excavated, and another is pre-excavation grouting for the area excavate in future. Therefore, the field experiment for post-excavation grouting was carried out, and the result show that the applied methods in this field experiment is effective to prevent the draining. And pre-excavation grouting has been undertaken and the applicability of several techniques has been evaluated. This report describes the summary of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory and field experiments of post- and pre-excavation grouting method.
Matsui, Hiroya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Asai, Hideaki; Ishii, Yoji; Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Kumada, Koji
no journal, ,
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is a major site for geoscientific research to advance the scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in crystalline rock. Studies on relevant engineering technologies in the MIU consist of research on design and construction technology for very deep underground applications, and engineering technology as a basis of geological disposal. In the Second Phase of the MIU project, engineering studies have focused on research into design and construction technologies for deep underground. The main subjects in the study of very deep underground structures consist of the following: Demonstration of the design methodology, Demonstration of existing and supplementary excavation methods, Demonstration of countermeasures during excavation and Demonstration of safe construction. This poster show the main topics and results of the study until FY2009.
 Es region by Coulomb excitation
Es region by Coulomb excitation  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyYanagihara, Rikuto; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Orlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Hirose, Kentaro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
Asai, Hideaki; Matsui, Hiroya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ito, Hiroaki; Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Ishii, Yoji
no journal, ,
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is currently being constructed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. As part of MIU Project, development of engineering technology for deep underground intended for the crystalline rock is executed. The research to confirm the effectiveness of engineering technology is being executed during its excavation now. It reports on study results up to 300m in depth of engineering technology research and the schedule for the future.
Matsui, Hiroya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Asai, Hideaki; Sugihara, Kozo
no journal, ,
In the construction phase of the MIU project, engineering studies have focused on research into design and construction technologies for deep underground. The main subjects consist of the following: "Demonstration of the design methodology", "Demonstration of existing and supplementary excavation methods", "Demonstration of countermeasures during excavation" and "Demonstration of safe construction". In the FY 2007, identification and evaluation of the subjects for this study were carried out to optimize future research work. Specific studies have been performed as well. Based on these studies, future research focused on the four subject areas has been identified. The design methodology in the surface-based investigation phase was verified to 200 m depth. Evaluation of countermeasures and studies of concepts for the estimation of the influence of high differential water pressures, long-term maintenance and risk management have been proposed with respect to the geological disposal project.
Abe, Shinichiro; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Liao, W.*; Kato, Takashi*; Asai, Hiroaki*; Shimbo, Kenichi*; Matsuyama, Hideya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kobayashi, Kazutoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
no journal, ,
Single event upset (SEU) induced by secondary cosmic-ray neutrons is one of the causes of non-destructive faults (the so-called soft errors) in microelectronics. We have proposed a method to estimate the terrestrial soft error rates (SERs) based on simulation coupled with one-time neutron irradiation testing which can be applied to various kinds of neutron sources. The validity of our method has been investigated for 65-nm bulk SRAMs with the measured data using various neutron sources. This result will be reviewed on the organized session of the 67th Space Sciences and Technology Conference.
Asai, Hideaki; Matsui, Hiroya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Sugihara, Kozo
no journal, ,
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is currently being constructed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. As part of MIU Project, development of engineering technology for deep underground intended for the crystalline rock is executed. The research to confirm the effectiveness of engineering technology is being executed during its excavation now. It reports on the current state of engineering technology research and the schedule for the future.