Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Harries, J.; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Homma, Kenji*; Kuniwake, Miki*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Lebech, M.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 44(9), p.095101_1 - 095101_7, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.69(Optics)Obara, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Ryoei*; Yagi, Shuichi*; Toyama, Yuko*; Kutluk, G.*; Osawa, Tetsutaro*; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa; Azuma, Yoshiro*; Nagata, Tetsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(3), p.263 - 271, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A crossed photon-atom beam apparatus has been constructed for absolute measurement of total photoionization cross sections of isolated and neutral metallic atoms. Using this apparatus, measurements on Ba and Eu atoms have been made at their 4d giant resonance regions 110-140 eV and 140-180 eV, respectively. The target atom density was determined using the deposition rate on a quartz crystal sensor and the average velocity of the atoms obtained by a time-of-flight method combined with a pulsed electron gun. The number of photons was determined with use of a double ion chamber. The comparison of the measured cross-section values with previous experimental and theoretical results is reasonable, indicating that the crossed photon-atom beam method is fairly promising technique.
Harries, J.; Kuniwake, Miki*; Homma, Kenji*; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
Long-lived, highly-excited neutral hydrogen atoms are produced near the O 1s edge of the water molecule. This metastable yield has been studied, along with the kinetic energy of the particles. The excited particles also can decay via fluorescence to the ground state, and by lifetime-resolved detection of the fluorescence new information on the dissociation dynamics can be obtained.
Gejo, Tatsuo*; Kuniwake, Miki*; Homma, Kenji*; Harries, J.; Oura, Masaki*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
Exciting an inner-shell electron of a molecule to just-above or just-below its ionisation limit provides a system where the Born-Oppenheimer principle is no longer valid, and a valuable opportunity for studying the interaction of the unstable ion core and a low-energy electron. When the ion core undergoes Auger decay and fragments, the initially excited electron can be recaptured. It is the aim of this research to understand what happens in the case of the water molecule, by (1) detecting excited H atoms produced when the electron is captured by an outgoing proton. (2) detect the Lyman- radiation produced when these excited H atoms decay, and (3) analysing the energy of low-energy Auger electrons emitted when the electron is captured by an O
radiation produced when these excited H atoms decay, and (3) analysing the energy of low-energy Auger electrons emitted when the electron is captured by an O or O
or O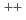 fragment.
fragment.
 fluorescence following O(1s) excitation/ionisation in gas-phase water molecules
fluorescence following O(1s) excitation/ionisation in gas-phase water moleculesHarries, J.; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
In this research we have obtained new information on the photo-dissociation dynamics of the water molecule following O (1s) inner-shell excitation/ionisation. When the O 1s electron is excited neutral excited H atoms can be produced. By investigating which states these H atoms are information can be obtained on the dissociation routes. When the inner-shell O 1s electron is excited/ionises, an unstable H O
O ion core is formed. This is unstable, and Auger decay occurs. The resulting H
ion core is formed. This is unstable, and Auger decay occurs. The resulting H O
O ion core dissociates, and one of the fragments can capture the initially excited electron. When this fragment is H
ion core dissociates, and one of the fragments can capture the initially excited electron. When this fragment is H , a neutral H atom is formed. In this research we use the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation to study the lifetimes of the fluorescing excited states produced.
, a neutral H atom is formed. In this research we use the pulsed nature of synchrotron radiation to study the lifetimes of the fluorescing excited states produced.
 O
OHarries, J.; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Kuniwake, Miki*; Homma, Kenji*; Oura, Masaki*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
Photo-excitation of the O 1s electron in H O can lead to the production of neutral, excited H atoms. Knowledge of the excited state distribution provides information on the dissociation dynamics process. Excitation of the O 1s electron leads to a H
O can lead to the production of neutral, excited H atoms. Knowledge of the excited state distribution provides information on the dissociation dynamics process. Excitation of the O 1s electron leads to a H O
O ion core. Auger decay subsequently leads to H
ion core. Auger decay subsequently leads to H O
O , which dissociates, and one of the fragments can capture the initially excited electron. If this fragment is H
, which dissociates, and one of the fragments can capture the initially excited electron. If this fragment is H , excited neutral H atoms are formed. In this research we use pulsed synchrotron radiation as the excitation source, and detect the UV fluorescence emitted when the excited H atoms decay. Analysis of the decay lifetimes leads to information on the excited state distribution.
, excited neutral H atoms are formed. In this research we use pulsed synchrotron radiation as the excitation source, and detect the UV fluorescence emitted when the excited H atoms decay. Analysis of the decay lifetimes leads to information on the excited state distribution.
Inoue, Naoki*; Nagoshi, Tatsuro*; Yoda, Yumi*; Suzuki, Norihiro*; Harries, J.; Koike, Fumihiro*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
 O; H
O; H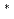 yield and kinetic energy, and ion-H
yield and kinetic energy, and ion-H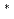 coincidence studies
coincidence studiesHarries, J.; Iseda, Mitsuhiro*; Kuniwake, Miki*; Homma, Kenji*; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
We report here on studies where metastable H atoms and VUV photons are detected following the O 1s excitation of H
atoms and VUV photons are detected following the O 1s excitation of H O. The studies reveal new information not accessible with ion or electron techniques. The studies are performed using pulsed soft X-ray synchrotron radiation at SPring-8's BL27SU. Metastable particles and VUV photons are directly detected using 2 MCP detectors, and the arrival times of the particles are recorded relative both to each other and to the pulses of incoming radiation. The technique allows the separation of VUV and metastable particle yield, and the study of fluorescence lifetimes. The time-resolved detection of Lyman-
O. The studies reveal new information not accessible with ion or electron techniques. The studies are performed using pulsed soft X-ray synchrotron radiation at SPring-8's BL27SU. Metastable particles and VUV photons are directly detected using 2 MCP detectors, and the arrival times of the particles are recorded relative both to each other and to the pulses of incoming radiation. The technique allows the separation of VUV and metastable particle yield, and the study of fluorescence lifetimes. The time-resolved detection of Lyman- radiation allows the determination of the population distribution of excited H atoms.
radiation allows the determination of the population distribution of excited H atoms.
Suzuki, Norihiro*; Nagoshi, Tatsuro*; Yoda, Yumi*; Inoue, Naoki*; Harries, J.; Koike, Fumihiro*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
 O
OHarries, J.; Kuniwake, Miki*; Gejo, Tatsuo*; Homma, Kenji*; Sullivan, J. P.*; Azuma, Yoshiro*
no journal, ,
We report here on studies where metastable H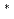 atoms are directly detected following the O 1s inner-shell excitation of the water molecule, revealing new information not accessible with the ion or photon techniques. Metastable H
atoms are directly detected following the O 1s inner-shell excitation of the water molecule, revealing new information not accessible with the ion or photon techniques. Metastable H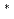 yield differs to partial/total ion yields and H
yield differs to partial/total ion yields and H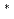 fluorescence yield most strikingly near threshold, where a large peak is observed due to the capture of a Rydberg electron or slow photoelectron by a dissociation H
fluorescence yield most strikingly near threshold, where a large peak is observed due to the capture of a Rydberg electron or slow photoelectron by a dissociation H ion, analogous to a similar observation for N
ion, analogous to a similar observation for N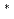 production from N
production from N . The nature of the process is investigated by comparing the kinetic energies of H
. The nature of the process is investigated by comparing the kinetic energies of H and H
and H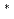 fragments, and also by detecting H
fragments, and also by detecting H in coincidence with H
in coincidence with H , OH
, OH , and O
, and O ions.
ions.