Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baron, P.*; Cornet, S. M.*; Collins, E. D.*; DeAngelis, G.*; Del Cul, G.*; Fedorov, Y.*; Glatz, J. P.*; Ignatiev, V.*; Inoue, Tadashi*; Khaperskaya, A.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 117, p.103091_1 - 103091_24, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:94.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The results of an international review of separation processes for spent nuclear fuel (SNF) recycling in future closed fuel cycles with the evaluation of Technology Readiness Level are reported. This study was made by the Expert Group on Fuel Recycling Chemistry (EGFRC) organised by the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). A unique feature of this study was that processes were classified according to a hierarchy of separations aimed at different elements within spent fuel (uranium; uranium-plutonium co-recovery; minor actinides; high heat generating radionuclides) and also the Head-end processes, used to prepare the SNF for chemical separation, were included. Separation processes covered both wet (hydrometallurgical) and dry (pyro-chemical) processes.
de Boissieu, M.*; Francoual, S.*; Minalkovi , M.*; Shibata, Kaoru; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Sidis, Y.*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Wu, D.*; Lograsso, T.*; Regnault, L.-P.*; et al.
, M.*; Shibata, Kaoru; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Sidis, Y.*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Wu, D.*; Lograsso, T.*; Regnault, L.-P.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 6(12), p.977 - 984, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:81.35(Chemistry, Physical)We have carried out inelastic X-ray and neutron scattering experiments on single-grain samples of the Zn-Mg-Sc icosahedral quasicrystal and of the Zn-Sc periodic cubic 1/1 approximant, with the aim of studying the respective influence of the local order and the long-range order (periodic or quasiperiodic) on lattice dynamics. Besides the overall similarities and the existence of a pseudo-gap in the transverse dispersion relation, marked difference are observed, the pseudo-gap being larger and better defined in the approximant than in the quasicrystal. These results are compared with simulations on atomic models and using oscillating pair potentials, and the simulations reproduce in detail the experimental results.
Hoesch, M.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Takenouchi, Tomohiro*; Kawarada, Hiroshi*; Sutter, J. P.*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Nagao, Masanori*; Takano, Yoshihiko*
Physical Review B, 75(14), p.140508_1 - 140508_4, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:77.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We observed phonon dispersions using inelastic X-ray scattering from CVD-grown high quality superconducting ( =4.2 K) boron-doped and non-doped diamonds. By comparing these two, we found almost no change in the acoustic branch along both [111] and [001] directions. On the other hand, strong softening were observed in the optical branch of the boron-doped diamond in both directions: about 2 meV at Brillouin zone boundary and 8 meV at zone center (
=4.2 K) boron-doped and non-doped diamonds. By comparing these two, we found almost no change in the acoustic branch along both [111] and [001] directions. On the other hand, strong softening were observed in the optical branch of the boron-doped diamond in both directions: about 2 meV at Brillouin zone boundary and 8 meV at zone center ( point). From this result we estimated the electron-phonon coupling factor
point). From this result we estimated the electron-phonon coupling factor  =0.33, and this supports theoretical models suggesting a phonon-mediated pairing mechanism via coupling of optical phonon modes to Fermi surfaces around the
=0.33, and this supports theoretical models suggesting a phonon-mediated pairing mechanism via coupling of optical phonon modes to Fermi surfaces around the  point.
point.
Ozawa, Masaki; Tanaka, Yasumasa; Baron, P.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Future Nuclear Systems (GLOBAL'97), 0 Pages, 1997/00
None
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Baron, A.*; Sutter, J. P.*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
Recently the softening of the bond-stretching phonon branch has been studied intensively on perovskite oxides including high-T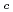 superconductors. We have been studying the
superconductors. We have been studying the  -dependence of the softening in La
-dependence of the softening in La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO , and found that the peak width at low doping region by inelastic X-ray scattering (IXS) is much broader than that by inelastic neutron scattering (INS). In order to figure out the reason we did high energy IXS measurements (energy resolution is about 3meV). The result shows that the energy spectra consists of two peaks. By fitting the spectra with two Lorentzians, we could decide the dispersion, and the lower one was almost the same as the reported INS result. The twinning effect explains the double peak structure, but it cannot explain why INS shows only one branch.
, and found that the peak width at low doping region by inelastic X-ray scattering (IXS) is much broader than that by inelastic neutron scattering (INS). In order to figure out the reason we did high energy IXS measurements (energy resolution is about 3meV). The result shows that the energy spectra consists of two peaks. By fitting the spectra with two Lorentzians, we could decide the dispersion, and the lower one was almost the same as the reported INS result. The twinning effect explains the double peak structure, but it cannot explain why INS shows only one branch.
Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hoesch, M.*; Takenouchi, Tomohiro*; Sutter, J. P.*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A.*; Nagao, Masanori*; Takano, Yoshihiko*; Kawarada, Hiroshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
Diamond is well known for its maximum hardness, large energy gap, high thermal conductivity, and so on. In addition to these, the superconductivity was discovered recently in boron doped (B-doped) diamond, and this was soon confirmed by other groups. We performed inelastic X-ray scattering experiments at BL35XU of SPring-8 to measure phonons in a highly B-doped CVD grown diamond having superconducting transition at 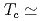 4.2 K. By comparing the experimental results with those from nitrogen doped CVD grown diamond and/or pure diamond, we found that the optical modes are softened especially at around the Brillouin zone center along with a strong broadening, while the acoustic modes do not show both softening and broadening. This confirms the strong electron-phonon coupling in superconducting diamond.
4.2 K. By comparing the experimental results with those from nitrogen doped CVD grown diamond and/or pure diamond, we found that the optical modes are softened especially at around the Brillouin zone center along with a strong broadening, while the acoustic modes do not show both softening and broadening. This confirms the strong electron-phonon coupling in superconducting diamond.