Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Akari*; Chhun, T.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Biswas, K. K.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Baskin, T. I.*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Journal, 47(5), p.788 - 801, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:59.9(Plant Sciences)2,4-D, a chemical analogue of IAA, is widely used as a growth regulator and exogenous source of auxin. It is believed that they share a common response pathway. Here, we show that a mutant, 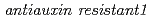 (
(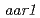 ) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the
) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the 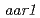 mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the
mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the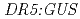 and
and 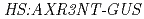 backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of
backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of 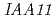 expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a
expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a 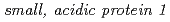 with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.