Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63(3), p.285 - 300, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:37.86(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Neutron diffraction provides an experimental method of directly locating hydrogen atoms in proteins and DNA oligomers. Three different types of high resolution neutron diffractometers for biological macromolecules have been constructed in Japan, France and the U.S.A., and they have all been actively used in recent years to determine the crystal structures of numerous proteins. Examples include the detailed geometries of hydrogen bonds, information on H/D exchange in proteins, the unambiguous location of protons, the role of key hydrogen atoms in enzymatic activity and thermostability, and the dynamical behavior of hydration structures, all of which have been extracted from these structural results and reviewed in this article. Other important techniques, such as the optimization of growth of large single crystals using phase diagrams, the preparation of fully deuterated proteins, the introduction of cryogenic techniques to neutron protein crystallography, and the establishment of a "hydrogen and hydration in proteins" database, will also be described in this paper.
Niimura, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Bau, R.*
Hydrogen- and Hydration-Sensitive Structural Biology, p.17 - 35, 2005/00
At the JAERI, we have constructed several high-resolution neutron diffractometers dedicated to biological macromolecules (called BIX-type diffractometers), which use a monochromatized neutron beam and a neutron imaging plate detector. In this paper, we review several interesting results regarding hydrogen positions and hydration in proteins, obtained using the two BIX-type diffractometers in JAERI. The general subject of neutron protein crystallography has been reviewed by several authors, and several selected topics have been discussed.
 resolution
resolutionChatake, Toshiyuki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Tsyba, I.*; Bau, R.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 60(8), p.1364 - 1373, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.89(Biochemical Research Methods)A neutron diffraction study has been carried out at 1.6  resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from
resolution on a mutant rubredoxin from 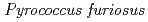 using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from
using the BIX-3 single-crystal diffractometer at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. In order to study the unusual thermostability of rubredoxin from 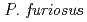 , the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS
, the hydrogen-bonding patterns were compared between the native and a 'triple-mutant' variant where three residues were changed so that they are identical to those in a mesophilic rubredoxin. In the present study, some minor changes were found between the wild-type and mutant proteins in the hydrogen-bonding patterns of the Trp3/Tyr3 region. The H/D-exchange ratios in the protein were also studied. The results suggest that the backbone amide bonds near the four Cys residues of the FeS redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6
redox center are most resistant to H/D exchange. In addition, the 1.6  resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
resolution of the present neutron structure determination has revealed a more detailed picture than previously available of some portions of the water structure, including ordered and disordered O-D bonds.
 by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromolecules
by BIX-3, a single-crystal diffractometer for biomacromoleculesKurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(31), p.11215 - 11220, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:61.13(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structure of a rubredoxin (Rd) from 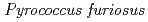 , an organism that grows optimally at 100
, an organism that grows optimally at 100  C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5
C, was determined using the neutron single-crystal diffractometer for biological macromolecules (BIX-3) at the JRR-3 reactor of JAERI. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  , and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of
, and the completeness of the data set was 81.9 %. The model contains 306 H atoms and 50 D atoms. A total of 37 hydration water molecules were identified. The model has been refined to final agreement factors of  = 18.6 % and
= 18.6 % and 
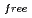 = 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
= 21.7 %. Several orientations of the O-D bonds of side chains, whose assignments from X-ray data were previously ambiguous, were clearly visible in the neutron structure. While most backbone N-H bonds had undergone some degree of H/D exchange throughout the molecule, five H atom positions still had distinctly negative (H) peaks. The neutron Fourier maps clearly showed the details of an extensive set of H bonds involving the ND
 terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
terminus that may contribute to the unusual thermostability of this molecule.
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro; Adams, M. W. W.*; Jenney, F. E. Jr.*; Moiseeva, N.*; Bau, R.*; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol.70, Supplement A, p.400 - 402, 2001/05
With the new single-crystal diffractometer BIX-3 at the JRR-3M reactor of JAERI, a single-crystal neutron diffraction analysis of the structure of the small protein rubredoxin from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus is currently under way. Data were collected at room temperature up to a resolution of 1.5  intervals in
intervals in  and exposure times ranging from 60 to 77 minutes per frame. The completeness factor of the 1.5-
and exposure times ranging from 60 to 77 minutes per frame. The completeness factor of the 1.5- . Included in the refinement are 301 hydrogen atoms and 40 deuterium atoms, and 29 water molecules were also identified. In the present model, the current value for R and R
. Included in the refinement are 301 hydrogen atoms and 40 deuterium atoms, and 29 water molecules were also identified. In the present model, the current value for R and R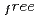 are 24.0
are 24.0  and 26.3
and 26.3  , respectively.
, respectively.