Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Proceedings of 11th Meeting of the Task Force on Shielding Aspects of Accelerators, Targets and Irradiation Facilities (SATIF-11), p.91 - 98, 2013/10
We have developed the displacement damage model in PHITS using the screened Coulomb scattering and the nuclear reaction model to evaluate the energy of the target PKA created by the projectile and the "secondary particles" which include all particles created from the sequential nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and neutron incident reactions, it was found that a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" is more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Recently, radiation damage models in other codes such as FLUKA, MARS, MCNP have also been developed. As there is few experimental data in a high energy region, an intercomparison of Monte Carlo codes used in the radiation damage calculation is very important for the improvement of models. In the meeting, we will also discuss the comparison between PHITS and FLUKA for the high-energy proton and neutron irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 303, p.120 - 124, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)Recently, the radiation damage model in PHITS has been developed using the screened Coulomb scattering to evaluate the energy of the target PKA (Primary Knock on Atom) created by the projectile and the "secondary particles" which include all particles created from the sequential nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and  He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment. In the meeting, we will also present DPA values and energy spectra for secondary particles created by neutrons in the energy ranges from thermal to around 1 GeV.
He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment. In the meeting, we will also present DPA values and energy spectra for secondary particles created by neutrons in the energy ranges from thermal to around 1 GeV.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 274, p.57 - 64, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:84.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiation damage model in the PHITS has been improved using the screened Coulomb scattering to evaluate the energy of the target PKA (Primary Knock on Atom) created by the projectile and the secondary particles from the nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and  He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Therefore, the improved PHITS can calculate DPA values at high energies and TRIM leads to severe underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment.
He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Therefore, the improved PHITS can calculate DPA values at high energies and TRIM leads to severe underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
JAEA-Conf 2011-002, p.157 - 162, 2011/09
Radiation damage measured as a function of DPA is one of the critical issues for high-intensity beams, especially heavy-ions. The DPA model in PHITS has recently been extended to include contributions from Coulomb elastic scattering of transported charged particles. For the Coulomb elastic scattering, a universal one-parameter differential scattering cross section equation introduced by J. Lindhard et al. is employed instead of the differential Rutherford cross section which is a function of six parameters; charge and mass number of incident and produced particles, kinetic energy of incident particle and scattered angle. In this work, we compare PHITS results for the 130 MeV/u  6Ge+
6Ge+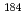 W reaction with calculated results of TRIM which is two-dimensional damage calculation code. Then we calculate DPA for different ions, targets and energies in the energy region from 100 MeV/u to 1 GeV/u and evaluate the systematics of DPA.
W reaction with calculated results of TRIM which is two-dimensional damage calculation code. Then we calculate DPA for different ions, targets and energies in the energy region from 100 MeV/u to 1 GeV/u and evaluate the systematics of DPA.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:175 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 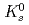 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
 -only isotope
-only isotope  Pb from 1 eV to 440 keV
Pb from 1 eV to 440 keVDomingo-Pardo, C.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 75(1), p.015806_1 - 015806_9, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:86.95(Physics, Nuclear)The neutron capture cross section of  Pb has been measured at the CERN n_TOF installation with high resolution in the energy range from 1 eV to 440 keV. In the interval between 100 keV and 440 keV we report the average cross section. The background in the entire energy range was reliably determined from the measurement of a
Pb has been measured at the CERN n_TOF installation with high resolution in the energy range from 1 eV to 440 keV. In the interval between 100 keV and 440 keV we report the average cross section. The background in the entire energy range was reliably determined from the measurement of a  Pb sample. We obtain a Maxwellian average capture cross section for
Pb sample. We obtain a Maxwellian average capture cross section for  Pb at
Pb at 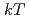 = 30 keV of 79(3) mb, in agreement with previous experiments. However our cross section at
= 30 keV of 79(3) mb, in agreement with previous experiments. However our cross section at 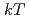 = 5 keV is about 35 % larger than the values reported so far. The implications of the new cross section for the
= 5 keV is about 35 % larger than the values reported so far. The implications of the new cross section for the  -process abundance contributions in the Pb/Bi region are discussed.
-process abundance contributions in the Pb/Bi region are discussed.
 Pb
PbDomingo-Pardo, C.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(5), p.055802_1 - 055802_6, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:81.32(Physics, Nuclear)The radiative neutron capture cross section of  Pb has been measured at the CERN n_TOF facility using the pulse height weighting technique in the resoleved region. The measurement has been performed with an optimized setup of two
Pb has been measured at the CERN n_TOF facility using the pulse height weighting technique in the resoleved region. The measurement has been performed with an optimized setup of two 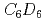 scintillation detectors, which allowed us to reduce scattered neutron backgrounds down to a negligible level. Resonance parameters have been determined for 16 resonances by means of an R-matrix analysis in the neutron energy range from 3 keV to 320 keV. Good agreement with previous measurements was found at low neutron energies, whereas substantial discrepancies appear beyond 45 keV. With the present results, we obtain an s-process contribution of 77
scintillation detectors, which allowed us to reduce scattered neutron backgrounds down to a negligible level. Resonance parameters have been determined for 16 resonances by means of an R-matrix analysis in the neutron energy range from 3 keV to 320 keV. Good agreement with previous measurements was found at low neutron energies, whereas substantial discrepancies appear beyond 45 keV. With the present results, we obtain an s-process contribution of 77 8 % to the solar abundance of
8 % to the solar abundance of  Pb.
Pb.
 Bi
BiDomingo-Pardo, C.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.025807_1 - 025807_10, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:90.41(Physics, Nuclear)The neutron capture cross section of  Bi has been measured at the CERN n_TOF facility by employing the pulse-height-weighting technique. Improvements over previous measurements are mainly because of an optimized detection system, which led to a practically negligible neutron sensitivity. Because
Bi has been measured at the CERN n_TOF facility by employing the pulse-height-weighting technique. Improvements over previous measurements are mainly because of an optimized detection system, which led to a practically negligible neutron sensitivity. Because  Bi is the last stable isotope in the reaction path of the stellar s-process, the Maxwellian averaged capture cross section is important for the recycling of the reaction flow by alpha decays. In the relevant stellar range of thermal energies between
Bi is the last stable isotope in the reaction path of the stellar s-process, the Maxwellian averaged capture cross section is important for the recycling of the reaction flow by alpha decays. In the relevant stellar range of thermal energies between 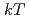 = 5 and 8 keV our new capture rate is about 16% higher than the presently accepted value used for nucleosynthesis calculations. The present cross section measurement is also of relevance for the design of accelerator driven systems based on a liquid metal Pb/Bi spallation target.
= 5 and 8 keV our new capture rate is about 16% higher than the presently accepted value used for nucleosynthesis calculations. The present cross section measurement is also of relevance for the design of accelerator driven systems based on a liquid metal Pb/Bi spallation target.
 Th measured at the n_TOF facility at CERN in the unresolved resonance region up to 1 MeV
Th measured at the n_TOF facility at CERN in the unresolved resonance region up to 1 MeVAerts, G.*; Abbondanno, U.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; Baumann, P.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; Baumann, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 73(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_10, 2006/05
We have measured the neutron capture reaction yield of  Th at the neutron tim-of-flight facility n_TOF at CERN in the energy range from 1 eV to 1 MeV. The average capture cross section has been extracted in the energy range from 4 keV up to 1 MeV with an overall accuracy better than 4 %. An independent IAEA evaluation shows good agreement with the data.
Th at the neutron tim-of-flight facility n_TOF at CERN in the energy range from 1 eV to 1 MeV. The average capture cross section has been extracted in the energy range from 4 keV up to 1 MeV with an overall accuracy better than 4 %. An independent IAEA evaluation shows good agreement with the data.
 Th measured at the n_TOF facility at CERN in the unresolved resonance region up to 1 MeV
Th measured at the n_TOF facility at CERN in the unresolved resonance region up to 1 MeVAerts, G.*; Abbondanno, U.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; Baumann, P.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; Baumann, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 73(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_10, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:89.88(Physics, Nuclear)We have measured the neutron capture reaction yield of  Th at the neutron time-of-flight facility n_TOF at CERN in the energy range from 1 eV to 1 MeV. The average capture cross section has been extracted in the energy range from 4 keV up to 1 MeV with an overall accuracy better than 4%. An independent IAEA evaluation shows good agreement with the data.
Th at the neutron time-of-flight facility n_TOF at CERN in the energy range from 1 eV to 1 MeV. The average capture cross section has been extracted in the energy range from 4 keV up to 1 MeV with an overall accuracy better than 4%. An independent IAEA evaluation shows good agreement with the data.
 Pb and termination of the
Pb and termination of the  -process
-processDomingo-Pardo, C.*; O'Brien, S.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 819, p.288 - 292, 2006/03
The neutron capture cross sections of  Pb and
Pb and  Pb have been measured at the CERN n_TOF installation using the time of flight method with the pulse height weighting technique. In a preliminary analysis of
Pb have been measured at the CERN n_TOF installation using the time of flight method with the pulse height weighting technique. In a preliminary analysis of  Pb we have determined by first time the capture cross sections for two strong
Pb we have determined by first time the capture cross sections for two strong  -wave resonances below 2.5 keV. In
-wave resonances below 2.5 keV. In  Pb we have determined capture cross sections for a large number of resonances, which were not reported in the two previous capture measurements. We discuss preliminary implications of the new cross sections in the stellar nucleosynthesis of the Pb isotopes.
Pb we have determined capture cross sections for a large number of resonances, which were not reported in the two previous capture measurements. We discuss preliminary implications of the new cross sections in the stellar nucleosynthesis of the Pb isotopes.
 La(
La( ,
, ) cross section
) cross sectionTerlizzi, R.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 819, p.283 - 287, 2006/03
We measured the neutron capture cross section of  La relative to
La relative to  Au in the energy range of 0.6 eV to 9 keV at n_TOF, the neutron time-of-flight facility at CERN. The data were fitted using R-matrix formalism to extract resonance parameters which were used to calculate average level spacings. The data were used to determine Maxwellian-averaged neutron capture cross sections which, in turn, were used to calculate the
Au in the energy range of 0.6 eV to 9 keV at n_TOF, the neutron time-of-flight facility at CERN. The data were fitted using R-matrix formalism to extract resonance parameters which were used to calculate average level spacings. The data were used to determine Maxwellian-averaged neutron capture cross sections which, in turn, were used to calculate the  La abundance synthesized in a steller model of the main component of the
La abundance synthesized in a steller model of the main component of the  process.
process.
Mastinu, P. F.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 41, p.352 - 360, 2006/00
A neutron Time-of-Flight facility (n_TOF) is operative at CERN since 2001. The innovative features of the neutron beam, in particular the high instantaneous flux, the wide energy range, the high resolution and the low background, makes this facility unique for measurements of neutron induced reactions relevant to the field of Emerging Nuclear Technologies, as well as to Nuclear Astrophysics and fundamental Nuclear Physics. The scientific motivations that have led to the construction of this new facility are here presented.
Cano-Ott, D.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*;
lvarez, H.*;  lvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
lvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Assimakopoulos, P.*; Audouin, L.*; Badurek, G.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1442 - 1445, 2005/05
Accurate and reliable neutron cross section data for actinides are necessary for the proper design, safety reguartion and precise performance assessment of transmutaion devices. In particular, the neutron capture cross sections of  Np,
Np,  Pu and
Pu and  Am play a key role in the design and optimization of a strategy for the Nuclear Waste Transmutation. The listed cross sections have been measured in 2004 at n_TOF with a high accuracy due to a combination of features unique in the world.
Am play a key role in the design and optimization of a strategy for the Nuclear Waste Transmutation. The listed cross sections have been measured in 2004 at n_TOF with a high accuracy due to a combination of features unique in the world.
 Np fission cross section from 5 eV to 1 MeV
Np fission cross section from 5 eV to 1 MeVFurman, W.*; Cennini, P.*; Ketlerov, V.*; Goverdovski, A.*; Konovalov, V.*; Abbondanno, U.*; Aerts, G.*;  lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; et al.
lvarez, H.*; Alvarez-Velarde, F.*; Andriamonje, S.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1039 - 1042, 2005/05
A series of measurements of  Np fission cross section have been performed at the CERN spallation neutron source facility n_TOF. A fast ionization chamber was used as a fission fragment detector. Total experimental uncertainties are determined to be at the level of 3%. Analysis of experimental data in the neutron energy from 5 eV to 1 MeV showed a systematic deviation from the evaluated data (ENDF/B-VI). This discrepancy amounts to up to the factor of 3 for resolved resonances in the neutron energy range of 5 eV - 2 keV, and is in good agreement with some previous experiments. A similar disagreement at the level of 6-7% was found for higher energies around the threshold. This energy range is essential for the transmutation of neptunium in ADS or fast reactors. It is concluded that an updated evaluation of nuclear data for
Np fission cross section have been performed at the CERN spallation neutron source facility n_TOF. A fast ionization chamber was used as a fission fragment detector. Total experimental uncertainties are determined to be at the level of 3%. Analysis of experimental data in the neutron energy from 5 eV to 1 MeV showed a systematic deviation from the evaluated data (ENDF/B-VI). This discrepancy amounts to up to the factor of 3 for resolved resonances in the neutron energy range of 5 eV - 2 keV, and is in good agreement with some previous experiments. A similar disagreement at the level of 6-7% was found for higher energies around the threshold. This energy range is essential for the transmutation of neptunium in ADS or fast reactors. It is concluded that an updated evaluation of nuclear data for  Np is required.
Np is required.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
no journal, ,
The DPA (Displacement per Atom) model in the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) has recently been developed using Coulomb scattering to evaluate the energy of target PKA's created by the projectile and the secondary from nuclear reactions. We compared PHITS results for the 130 MeV/u  Ge and proton into W reactions with calculated results of TRIM, which is widely used but does not include nuclear reactions. PHITS gives good agreements with TRIM results for DPA values by PKA's created directly by the projectile such as
Ge and proton into W reactions with calculated results of TRIM, which is widely used but does not include nuclear reactions. PHITS gives good agreements with TRIM results for DPA values by PKA's created directly by the projectile such as  Ge and proton. On the other hands, for the proton incident reaction, PKA's created by the secondary particles is more dominant than PKA's by the projectile itself in DPA calculations. Therefore, TRIM leads to sever underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. PHITS is more reliable code than TRIM for DPA calculations, especially in the high-energy region and proton incidence.
Ge and proton. On the other hands, for the proton incident reaction, PKA's created by the secondary particles is more dominant than PKA's by the projectile itself in DPA calculations. Therefore, TRIM leads to sever underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. PHITS is more reliable code than TRIM for DPA calculations, especially in the high-energy region and proton incidence.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Harada, Masahide; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
no journal, ,
Recently, we have developed a calculation method of the displacement cross-sections in the energy range from 10 MeV to 3 GeV, including event generator and Coulomb scattering in the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Including the defect production efficiencies as a function of the damage energy, calculated results for low-energy neutron and proton irradiation on copper and 1.1 and 1.94 GeV protons on copper gave good agreements with experimental data. As a results of application of J-PARC ADS target test facility (TEF-T) at a beam window and a irradiation specimen, the contribution of protons to DPA values is higher than that of neutrons by a factor of about three.
MeV to 3 GeV, including event generator and Coulomb scattering in the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Including the defect production efficiencies as a function of the damage energy, calculated results for low-energy neutron and proton irradiation on copper and 1.1 and 1.94 GeV protons on copper gave good agreements with experimental data. As a results of application of J-PARC ADS target test facility (TEF-T) at a beam window and a irradiation specimen, the contribution of protons to DPA values is higher than that of neutrons by a factor of about three.