Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Kureta, Masatoshi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; Mondelaers, W.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-36-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/12
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) was developed as a non-destructive assay to quantify U and Pu isotopes in particle-like debris. NRD is composed of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA) or Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). NRCA/PGA in NRD plays a role of identifying impurities in debris under the high-radiation field primarily caused by  Cs. For this purpose, a novel LaBr
Cs. For this purpose, a novel LaBr
 -ray detector employing specific shields has been newly developed. With the developed
-ray detector employing specific shields has been newly developed. With the developed  -ray detector, a demonstration NRCA experiment was performed at a neutron time of flight facility GELINA (Belgium). As a result, samples (Hf, Gd, Ni) placed in a black box that is completely sealed by third party were successfully identified by the experiment. This presentation explains the design concept of the
-ray detector, a demonstration NRCA experiment was performed at a neutron time of flight facility GELINA (Belgium). As a result, samples (Hf, Gd, Ni) placed in a black box that is completely sealed by third party were successfully identified by the experiment. This presentation explains the design concept of the  ray detector including its detection principle and details of the demonstration NRCA experiment.
ray detector including its detection principle and details of the demonstration NRCA experiment.
Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kureta, Masatoshi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; Mondelaers, W.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-36-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/12
From 2012 to 2014, Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) is being developed as a non-destructive assay to quantify U and Pu isotopes. NRD is composed of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA)/Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). NRTA in NRD plays a role of quantifying the amounts of the isotopes of a nuclear fuel material (U, Pu) in molten fuel debris. Therefore, the neutron absorption measurement using Time-of-Flight (TOF) method is carried out. A demonstration NRTA experiment was performed at a neutron time of flight facility GELINA (Belgium). Consequently, we succeeded in iquantifying the randomly selected sample from Au, W, Rh, Nb, Cu. Co, Mn, B contained in a black box. In this presentation, we describe the principle of measurement of the developed NRTA and explain details of the demonstration experiment.
Paradela, C.*; Alaerts, G.*; Becker, B.*; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Moens, A.*; et al.
EUR-27507-EN, 16 Pages, 2015/04
Schillebeeckx, P.*; Becker, B.*; Danon, Y.*; Guber, K.*; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Junghans, A. R.*; Kopecky, S.*; Massimi, C.*; Moxon, M. C.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 113(12), p.3054 - 3100, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:97.09(Physics, Nuclear) Pb beam
Pb beamSteer, S. J.*; Podoly k, Z.*; Pietri, S.*; G
k, Z.*; Pietri, S.*; G rska, M.*; Grawe, H.*; Maier, K.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Grawe, H.*; Maier, K.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 84(4), p.044313_1 - 044313_22, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:94.74(Physics, Nuclear)Heavy neutron-rich nuclei were populated via the fragmentation of a E/A=1 GeV 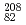 Pb beam. Secondary fragments were separated and identified and subsequently implanted in a passive stopper. By the detection of delayed
Pb beam. Secondary fragments were separated and identified and subsequently implanted in a passive stopper. By the detection of delayed  rays, isomeric decays associated with these nuclei have been identified. A total of 49 isomers were detected, with the majority of them observed for the first time. Possible level schemes are constructed and the structure of the nuclei discussed. To aid the interpretation, shell-model as well as BCS calculations were performed.
rays, isomeric decays associated with these nuclei have been identified. A total of 49 isomers were detected, with the majority of them observed for the first time. Possible level schemes are constructed and the structure of the nuclei discussed. To aid the interpretation, shell-model as well as BCS calculations were performed.
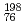 Os
Os
Podoly k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Pietri, S.*; Xu, F. R.*; Liu, H. J.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; G
k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Pietri, S.*; Xu, F. R.*; Liu, H. J.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; G rska, M.*; et al.
rska, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(3), p.031305_1 - 031305_4, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:86.28(Physics, Nuclear) rays de-exciting isomeric states in the neutron-rich nucleus
rays de-exciting isomeric states in the neutron-rich nucleus 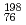 Os
Os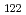 have been observed following relativistic projectile fragmentation of a 1 GeV per nucleon
have been observed following relativistic projectile fragmentation of a 1 GeV per nucleon  Pb beam. The ground-state band has properties compatible with oblate deformation. The evolution of the structure of Os isotopes characterized by sudden prolate-oblate shape change is discussed and contrasted with the smooth change known in the Pt chain.
Pb beam. The ground-state band has properties compatible with oblate deformation. The evolution of the structure of Os isotopes characterized by sudden prolate-oblate shape change is discussed and contrasted with the smooth change known in the Pt chain.
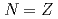 nuclei; Metastable state decays in the proton dripline nuclei
nuclei; Metastable state decays in the proton dripline nuclei 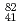 Nb and
Nb and 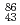 Tc
TcGarnsworthy, A. B.*; Regan, P. H.*; C ceres, L.*; Pietri, S.*; Sun, Y.*; Rudolph, D.*; G
ceres, L.*; Pietri, S.*; Sun, Y.*; Rudolph, D.*; G rska, M.*; Podoly
rska, M.*; Podoly k, Z.*; Steer, S. J.*; Hoischen, R.*; et al.
k, Z.*; Steer, S. J.*; Hoischen, R.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 660(4), p.326 - 330, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:79.09(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The low-lying structures of the self-conjugate (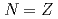 ) nuclei
) nuclei 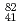 Nb and
Nb and 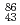 Tc have been investigated using isomeric-decay spectroscopy following the projectile fragmentation of a
Tc have been investigated using isomeric-decay spectroscopy following the projectile fragmentation of a  Ag beam. These represent the heaviest odd-odd
Ag beam. These represent the heaviest odd-odd 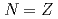 nuclei in which internal decays have been identified to date. The resulting level schemes shed light on the shape evolution along the
nuclei in which internal decays have been identified to date. The resulting level schemes shed light on the shape evolution along the 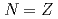 line between the doubly-magic systems
line between the doubly-magic systems 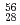 Ni and
Ni and 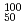 Sn and support a preference for
Sn and support a preference for 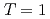 states in
states in 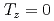 odd-odd nuclei at low excitation energies associated with a
odd-odd nuclei at low excitation energies associated with a 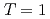 neutron-proton pairing gap. Comparison with Projected Shell Model calculations suggests that the decay in
neutron-proton pairing gap. Comparison with Projected Shell Model calculations suggests that the decay in 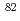 Nb may be interpreted as an isospin-changing
Nb may be interpreted as an isospin-changing  isomer.
isomer.
 Pt and
Pt and 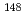 Tb
TbPodoly k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Pietri, S.*; Werner-Malento, E.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; G
k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Pietri, S.*; Werner-Malento, E.*; Regan, P. H.*; Rudolph, D.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Hoischen, R.*; G rska, M.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
European Physical Journal; Special Topics, 150(1), p.165 - 168, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.68(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Relativistic energy projectile fragmentation of  Pb has been used to produce a range of exotic nuclei. The nuclei of interest were studied by detecting delayed
Pb has been used to produce a range of exotic nuclei. The nuclei of interest were studied by detecting delayed  rays following the decay of isomeric states. Experimental information on the excited states of the neutron-rich
rays following the decay of isomeric states. Experimental information on the excited states of the neutron-rich  Pt N=126 nucleus, following internal decay of two isomeric states, was obtained for the first time. In addition, decays from the previously reported isomeric
Pt N=126 nucleus, following internal decay of two isomeric states, was obtained for the first time. In addition, decays from the previously reported isomeric 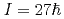 and
and 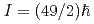 states in
states in 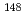 Tb and
Tb and 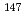 Gd, respectively, have been observed. These isomeric decays represent the highest discrete states observed to date following a prejectile fragmentation reaction, and opens up the possibilty of doing "high-spin physics" using this technique.
Gd, respectively, have been observed. These isomeric decays represent the highest discrete states observed to date following a prejectile fragmentation reaction, and opens up the possibilty of doing "high-spin physics" using this technique.
Pietri, S.*; Regan, P. H.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; Rudolph, D.*; Steer, S. J.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Werner-Malento, E.*; Hoischen, R.*; G
k, Zs.*; Rudolph, D.*; Steer, S. J.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Werner-Malento, E.*; Hoischen, R.*; G rska, M.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 261(1-2), p.1079 - 1083, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:98.43(Instruments & Instrumentation)The first results from the stopped beam RISING experimental campaign performed at the GSI laboratory in Darmstadt, Germany, are presented. RISING constitutes a major new experimental program in European nuclear structure physics research aimed at using relativistic energy (typically around 1 GeV per nucleon) projectile fragmentation reactions to populate nuclei with highly exotic proton-to-neutron ratios compared to the line of beta stability. In its high-efficiency stopped beam configuration, the RISING  -ray spectrometer consists of 105 individual germanium crystals which view a focal plane in which the exotic nuclei are brought to rest. Here, decays from metastable states with half-lives in the nano to milliseconds range can be observed. Results of initial commissioning experiments are also shown and details of the planned future experimental program are given.
-ray spectrometer consists of 105 individual germanium crystals which view a focal plane in which the exotic nuclei are brought to rest. Here, decays from metastable states with half-lives in the nano to milliseconds range can be observed. Results of initial commissioning experiments are also shown and details of the planned future experimental program are given.
 80
80 90
90Regan, P. H.*; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Pietri, S.*; Caceres, L.*; G rska, M.*; Rudolph, D.*; Podoly
rska, M.*; Rudolph, D.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Hoischen, R.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
k, Zs.*; Steer, S. J.*; Hoischen, R.*; Gerl, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 787(1), p.491c - 498c, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:90.74(Physics, Nuclear)Relativistic energy projectile fragmentation of  Pb has been used to produce neutron-rich nuclei with N
Pb has been used to produce neutron-rich nuclei with N 126. The nuclei of interest were studied by detecting delayed
126. The nuclei of interest were studied by detecting delayed  rays following the decay of isomeric states. Experimental information on the excited states of the neutron-rich
rays following the decay of isomeric states. Experimental information on the excited states of the neutron-rich  Pt N=126 nucleus, following internal decay of two isomeric states, was obtained for the first time. Raw experimental data and shell-model calculations are presented.
Pt N=126 nucleus, following internal decay of two isomeric states, was obtained for the first time. Raw experimental data and shell-model calculations are presented.
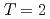 mirrors
mirrors  Ca and
Ca and  S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplines
S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplinesDoornenbal, P.*; Reiter, P.*; Grawe, H.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Al-Khatib, A.*; Banu, A.*; Beck, T.*; Becker, F.*; Bednarczyk, P.*; Benzoni, G.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 647(4), p.237 - 242, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:86.95(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The first excited state of  Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured
Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured 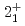 energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus
energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus  S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the
S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the 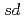 valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the
valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the 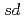 shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
 and heavy ion damage on the impulse response and pulsed gain of a low breakdown voltage Si avalanche photodiode
and heavy ion damage on the impulse response and pulsed gain of a low breakdown voltage Si avalanche photodiodeLaird, J. S.*; Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Ito, Hisayoshi; Becker, H.*; Johnston, A.*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 53(6), p.3786 - 3793, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.98(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
 and heavy ion damage on the time-resolved gain of a low breakdown voltage Si avalanche photodiode
and heavy ion damage on the time-resolved gain of a low breakdown voltage Si avalanche photodiodeLaird, J. S.*; Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Becker, H.*; Johnston, A.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-7), p.37 - 40, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Schlattl, H.*; Zankl, M.*; Becker, J.*; Saito, Kimiaki; Endo, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Schillebeeckx, P.*; Alaerts, G.*; Becker, B.*; Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Vendelbo, D.*; Wynants, R.*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
no journal, ,
The appearance of resonance structures in neutron induced reaction cross sections are fingerprints to study properties of materials and objects. Resonance structures are the basis of an analytical technique, i.e. Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA), which is being developed at the time-of-flight facility GELINA of the JRC-IRMM to characterize special nuclear materials. NRTA is based on the analysis of dips in a transmission spectrum that is obtained from a measurement of the attenuation of the neutron beam by a sample. To apply NRTA for the analysis of particle like debris samples of melted fuel produced in a severe nuclear accident is not evident. From this work one concludes that the accuracy of the results is strongly affected by the characteristics of the samples, in particular by the presence of neutron absorbing impurities, e.g.  B, and the variety in shape and size of the particle like debris samples. To account for these effects, improved data analysis procedures and interpretation models have been developed. These procedures and models will be presented and validated by results of measurements carried out at GELINA. It will be demonstrated that the relative amount of fissile material can be derived absolutely with an accuracy better than 2% without the need of calibration samples, even in the presence of strong neutron absorbing materials.
B, and the variety in shape and size of the particle like debris samples. To account for these effects, improved data analysis procedures and interpretation models have been developed. These procedures and models will be presented and validated by results of measurements carried out at GELINA. It will be demonstrated that the relative amount of fissile material can be derived absolutely with an accuracy better than 2% without the need of calibration samples, even in the presence of strong neutron absorbing materials.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Kureta, Masatoshi; Takamine, Jun; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Heyse, J.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) is a non-destructive method using a pulsed neutron beam in order to quantify nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel that is generated by a severe accident like the one at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. It is a combination of neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) and neutron resonance captures analysis (NRCA) or Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). NRCA/PGA in NRD, using a newly designed  -ray detector, plays a role of measuring impurities in debris that would have high radioactivity derived from
-ray detector, plays a role of measuring impurities in debris that would have high radioactivity derived from  Cs. Especially, the
Cs. Especially, the  -ray detector was specially designed to measure 478-keV
-ray detector was specially designed to measure 478-keV  rays radiated by
rays radiated by  B under the presence of
B under the presence of  Cs. Then utilizing information on the amount of impurities obtained by NRCA/PGA, NRTA quantifies special nuclear materials in debris. To verify the effectiveness of NRD for quantifying nuclear materials, NRTA and NRCA/PGA experiments were conducted at GELINA, IRMM, by an international collaboration of JAEA and EC/JRC/IRMM. In addition, achievable accuracy concerning NRD was studied by Monte Carlo simulations. In this contribution, these achievements on NRD as well as its concept are reviewed.
Cs. Then utilizing information on the amount of impurities obtained by NRCA/PGA, NRTA quantifies special nuclear materials in debris. To verify the effectiveness of NRD for quantifying nuclear materials, NRTA and NRCA/PGA experiments were conducted at GELINA, IRMM, by an international collaboration of JAEA and EC/JRC/IRMM. In addition, achievable accuracy concerning NRD was studied by Monte Carlo simulations. In this contribution, these achievements on NRD as well as its concept are reviewed.
Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
no journal, ,
A new concept named as neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) has been proposed by JAEA to quantify the amounts of special nuclear materials included in samples with unknown elemental and isotopic composition, such as melted fuel debris generated in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as Fukushima Daiichi. JAEA and JRC-IRMM has started the international collaboration on the feasibility study aiming at development of a quantifying technique of nuclear materials by a non-destructive method NRD. The highlights of the significant results such as detector development, validation measurements using a U sample and a heterogeneous sample, the advanced analysis method are presented together with the concept of the NRD.