Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Oba, Yojiro; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Sekine, Yurina; Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1776 - 1783, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.66(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The combination of the existing position-sensitive photomultiplier and the 3He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.735 - 736, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A large area, position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector was developed for upgrading the SENJU, time-of-flight Laue single crystal neutron diffractometer, in J-PARC MLF. The detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512  512 mm with a pixel size of 4
512 mm with a pixel size of 4  4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A
4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A  Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2018) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2019/10
A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector with a submillimeter spatial resolution was developed for pulsed neutron diffraction imaging at the J-PARC MLF. The detector comprised the thin, single ZnS/ LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24
LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24  24 mm
24 mm exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20
exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20 0.06 mm and 0.16
0.06 mm and 0.16 0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7
0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7 for thermal neutrons with a
for thermal neutrons with a  Co
Co  -ray sensitivity in the order of 10
-ray sensitivity in the order of 10 . In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
. In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2016), Vol.2, p.1506 - 1508, 2018/01
Position-dependent neutron sensitivity within an element of the scintillator / wavelength-shifting fiber coil (SFC) was evaluated by using a collimated pulsed neutron beam at the J-PARC/MLF. The collimated beam that has a size of 1  1 mm
1 mm was scanned over the SFC element. The neutron counts were recorded and plotted in each incident position. The scanning results showed less neutron sensitivity at the juncture of the rolled scintillator, suggesting less light collection efficiency or a lack of scintillator materials due to imperfect manufacturing process.
was scanned over the SFC element. The neutron counts were recorded and plotted in each incident position. The scanning results showed less neutron sensitivity at the juncture of the rolled scintillator, suggesting less light collection efficiency or a lack of scintillator materials due to imperfect manufacturing process.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(12), p.C12025_1 - C12025_9, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:5.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)A high-spatial-resolution, large-area position-sensitive scintillation-based neutron detector module has been developed for a new time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed at J-PARC MLF. A first prototype detector implementing commercial  Li:ZnS screens was produced based on a scintillator/wavelength-shifting fibre technology. The detector exhibited a spatial resolution of 2.5 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320
Li:ZnS screens was produced based on a scintillator/wavelength-shifting fibre technology. The detector exhibited a spatial resolution of 2.5 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320  320 mm
320 mm . We report on an initial evaluation of the detector performance, including its spatial resolution, detection efficiency and long-term background measurement, and also provide a brief description of a new neutron instrument.
. We report on an initial evaluation of the detector performance, including its spatial resolution, detection efficiency and long-term background measurement, and also provide a brief description of a new neutron instrument.
 64 cm
64 cm area position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector as an alternative to helium-3 gas based detector
area position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector as an alternative to helium-3 gas based detectorNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2015), Vol.1, p.680 - 683, 2016/11
A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector that has neutron-sensitive area of 64  64 cm
64 cm was developed for neutron scattering instruments by using wavelength shifting fibers technology. We designed the detector to have a pixel size of 20
was developed for neutron scattering instruments by using wavelength shifting fibers technology. We designed the detector to have a pixel size of 20  20 mm
20 mm . In order to compensate light attenuation occurred travelling along the wavelength-shifting fiber the scintillation light was read out from both sides of the fiber. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40% for 1.8
. In order to compensate light attenuation occurred travelling along the wavelength-shifting fiber the scintillation light was read out from both sides of the fiber. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40% for 1.8 neutrons, which was similar to previously developed detector with a smaller size of 32
neutrons, which was similar to previously developed detector with a smaller size of 32  32 cm
32 cm . The detailed detector design and experimental results measured by using the pulsed neutrons at the J-PARC/MLF are presented.
. The detailed detector design and experimental results measured by using the pulsed neutrons at the J-PARC/MLF are presented.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.202 - 207, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector incorporating an interpolation method readout by wavelength-shifting (WLS) fiber was developed to make an effective pixel size smaller than the physical pitch of the WLS fibre array. The detector that was made with the crossed arranged WLS fiber arrays where the fibers were placed in a regular pitch of 2.5 mm in  and
and  directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
 Ce
Ce O
O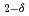 for electrolyte by Rietveld/ maximum entropy method
for electrolyte by Rietveld/ maximum entropy methodTaguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.339 - 342, 2015/06
Rare-earth doped ceria exhibits both ionic and electronic conductions, and those ceria with higher ratio of ionic conduction against electronic conduction is used as a solid electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. The electron density distributions in crystals are closely related to the electron diffusing pathway which affects the electronic conduction. In this study, we investigated the electron density distribution of doped ceria as a function of the content of Nd O
O -dopant to deduce the ratio of the electronic to ionic conduction. The crystal structure was refined with the space group,
-dopant to deduce the ratio of the electronic to ionic conduction. The crystal structure was refined with the space group, 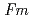 -3
-3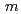 , which is the same as undoped ceria. Ce and Nd ions randomly occupied the 4
, which is the same as undoped ceria. Ce and Nd ions randomly occupied the 4 site and O ion the 8
site and O ion the 8 site. The electron conduction pathway was distributed through the 4
site. The electron conduction pathway was distributed through the 4 -8
-8 and 8
and 8 -8
-8 sites. The relationship between crystal structural change and electron density distribution as a function of the content of Nd
sites. The relationship between crystal structural change and electron density distribution as a function of the content of Nd O
O dopant will be discussed.
dopant will be discussed.
 O
O analyzed by combination of Rietveld/ maximum entropy method
analyzed by combination of Rietveld/ maximum entropy methodIgawa, Naoki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.247 - 252, 2015/05
The nuclear and electron density distributions of LiMn O
O which is one of the primitive cathode materials for secondary Li-ion batteries, were analyzed by applying Rietveld refinement and MEM to neutron and X-ray diffraction data, to estimate the Li diffusing pathway. The crystal structure of LiMn
which is one of the primitive cathode materials for secondary Li-ion batteries, were analyzed by applying Rietveld refinement and MEM to neutron and X-ray diffraction data, to estimate the Li diffusing pathway. The crystal structure of LiMn O
O could be refined with the space group,
could be refined with the space group, 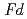 -3
-3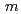 in the temperature range from 240 to 573 K. The structure was transformed to
in the temperature range from 240 to 573 K. The structure was transformed to 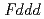 below 240 K. The isotropic thermal displacement parameter of Li was proportional to the temperature excluding 240 to 300 K. According to the MEM analyses it was indicated that the Li ions diffuse through 8
below 240 K. The isotropic thermal displacement parameter of Li was proportional to the temperature excluding 240 to 300 K. According to the MEM analyses it was indicated that the Li ions diffuse through 8 and 16
and 16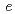 around 300 K.
around 300 K.
 He at J-PARC/MLF
He at J-PARC/MLFNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012042_1 - 012042_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Optics)A wavelength-shifting fiber based scintillator detector has been developed as a helium-3 alternative detector in J-PARC/MLF. The detector is aimed at using for an inelastic neutron scattering instrument in a pulsed neutron source. The detector should have a capability to have a large-area coverage with a moderate pixel size as well as high detector efficiency, low  sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20
sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20  20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320
20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320  320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.
320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.
 B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay system
He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay systemNakamura, Tatsuya; Ozu, Akira; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Takase, Misao; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 763, p.340 - 346, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron-sensitive ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/
He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm
ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm  250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4
250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4  0.1 cps
0.1 cps nv for thermal neutrons, a
nv for thermal neutrons, a  Cs
Cs  -ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9
-ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9 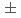 0.2
0.2  10
10 and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24
and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24 0.05% /
0.05% /  C over the temperature range of 20-50
C over the temperature range of 20-50 C.
C.
 He-gas-based detector for neutron-scattering instruments
He-gas-based detector for neutron-scattering instrumentsNakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki*; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 741, p.42 - 46, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)A position-sensitive tubular scintillator-based neutron detector is proposed as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector. The detector has a neutron-detecting element constructed from rolled ZnS/
He-gas-based detector. The detector has a neutron-detecting element constructed from rolled ZnS/ LiF scintillator screens that sandwich wavelength-shifting (WLS) fibre coils (SFC element). Multiple SFC elements are enclosed in an aluminium tube in a row to form a one-dimensional position-sensitive neutron detector. The design of the WLS fibre coil, which was determined by performing basic experiments, comprised two 0.75-mm-diameter WLS fibres wound in parallel at a pitch of 1.5 mm. A 64-element detector with a pixel size of 22 mm
LiF scintillator screens that sandwich wavelength-shifting (WLS) fibre coils (SFC element). Multiple SFC elements are enclosed in an aluminium tube in a row to form a one-dimensional position-sensitive neutron detector. The design of the WLS fibre coil, which was determined by performing basic experiments, comprised two 0.75-mm-diameter WLS fibres wound in parallel at a pitch of 1.5 mm. A 64-element detector with a pixel size of 22 mm  20 mm (width
20 mm (width  length) successfully demonstrated the detection principle. The tubular shape of the new detector is similar to the usual 25-mm-diameter
length) successfully demonstrated the detection principle. The tubular shape of the new detector is similar to the usual 25-mm-diameter  He tube, making this an alternative detector with the potential to be installed in a vacuum tank for inelastic-neutron-scattering instruments.
He tube, making this an alternative detector with the potential to be installed in a vacuum tank for inelastic-neutron-scattering instruments.
 m spatial resolution comprising a fibre-optic taper with wavelength-shifting fibre readout for time-of-flight neutron imaging
m spatial resolution comprising a fibre-optic taper with wavelength-shifting fibre readout for time-of-flight neutron imagingNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Honda, Katsunori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 737, p.176 - 183, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:70.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)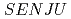 single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLF
single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLFKawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 735, p.444 - 451, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:80.14(Instruments & Instrumentation) LiF scintillator and wavelength shifting fibers with high spatial resolution and with low gamma-ray sensitivity
LiF scintillator and wavelength shifting fibers with high spatial resolution and with low gamma-ray sensitivityNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference; 21st International Symposium on Room-Temperature Semiconductor X-ray and  -ray detectors (NSS/MIC 2014), p.1751 - 1753, 2014/00
-ray detectors (NSS/MIC 2014), p.1751 - 1753, 2014/00
The ZnS scintillator-based two-dimensional detector was developed for a time-of-flight neutron imaging with a high spatial resolution and a low  -ray sensitivity. The detector is comprised of a thin ZnS scintillator with crossed wavelength-shifting-fibers (WLS fibers) arrays equipped with the fiber optic taper (FOT). The developed detector based on a neutron counting method has a high spatial resolution of less than 100 um (in FWHM) with a moderate count rate capability of several tens of thousands of cps. Of particular interest is its low
-ray sensitivity. The detector is comprised of a thin ZnS scintillator with crossed wavelength-shifting-fibers (WLS fibers) arrays equipped with the fiber optic taper (FOT). The developed detector based on a neutron counting method has a high spatial resolution of less than 100 um (in FWHM) with a moderate count rate capability of several tens of thousands of cps. Of particular interest is its low  -ray sensitivity of 10
-ray sensitivity of 10 . Imaging capabilities of the detector are demonstrated by using a high-intensity pulsed neutron beam at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in the Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC/MLF).
. Imaging capabilities of the detector are demonstrated by using a high-intensity pulsed neutron beam at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in the Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC/MLF).
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Honda, Katsunori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (2013 NSS/MIC), Vol.4, p.2367 - 2369, 2013/00
The detection efficiency of a ZnS-based neutron scintillator detector was evaluated as a function of the incident angle and the wavelength of a neutron. A pulsed neutron beam that has a wavelength from 1 to 8 was incident to the test detector that implemented a ZnS/
was incident to the test detector that implemented a ZnS/ LiF and ZnS/
LiF and ZnS/ B
B O
O scintillator that have thicknesses of 0.45 and of 0.20 mm, respectively. In each scintillator the detection efficiency increased as the incident angle increased for neutrons with a wavelength shorter than about 3
scintillator that have thicknesses of 0.45 and of 0.20 mm, respectively. In each scintillator the detection efficiency increased as the incident angle increased for neutrons with a wavelength shorter than about 3 . A comparison between the experimental results and the model fitting are presented.
. A comparison between the experimental results and the model fitting are presented.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; To, Kentaro; Oikawa, Kenichi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 686, p.64 - 70, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:90.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)A two-dimensional scintillator-based neutron detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 256  256 mm
256 mm with a pixel size of 4 mm was developed. The detector was designed to be compact and modular with the smallest dead area for the SENJU time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed in the Materials and Life Experimental Science Facility at the Japanese Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Two ZnS/
with a pixel size of 4 mm was developed. The detector was designed to be compact and modular with the smallest dead area for the SENJU time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed in the Materials and Life Experimental Science Facility at the Japanese Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Two ZnS/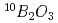 scintillator screens with an optimized scintillator thickness sandwiched the cross-arranged Wavelength-shifting fibre arrays to ensure a high detection efficiency for thermal neutrons. The prototype detector exhibited a detector efficiency of 40
scintillator screens with an optimized scintillator thickness sandwiched the cross-arranged Wavelength-shifting fibre arrays to ensure a high detection efficiency for thermal neutrons. The prototype detector exhibited a detector efficiency of 40  1 % for 1.6-
1 % for 1.6- neutrons and a
neutrons and a  Co
Co  -ray sensitivity of 6.0
-ray sensitivity of 6.0 0.1
0.1 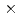
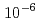 , which fulfilled the required detector specifications for SENJU.
, which fulfilled the required detector specifications for SENJU.
Igawa, Naoki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ishii, Yoshinobu*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18, p.022021_1 - 022021_4, 2011/05
The neutron scattering length density distributions of Xe deuterohydrate were analyzed by Rietveld and MEM analysis applied to neutron powder diffraction data to clarify the Xe behavior in the temperature range from 10 to 245 K. A spherical positive scattering length density attributed to the Xe atom was observed at the center of the small cage of the hydrate. On the other hand, an ellipsoid shaped scattering length density distribution at the center of the large cage was observed; the major axis of the ellipsoid scattering length density was directed toward the center of a hexagonal facet of the large cage. The distributions of the Xe atom in the both cages were almost the same at any temperature.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Yasuda, Ryo; Katagiri, Masaki*; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2011), Vol.1, p.382 - 384, 2011/00
The neutron image detector that was based on wavelength-shifting-fibers (WLS fibres) equipped with the fibre optic taper (FOT) was developed. By inserting the FOT in between the scintillator and WLS fibers the measured neutron image was magnified on the WLS fibres, resulting in better spatial resolution. We have tested two FOTs; a square shaped one in a size of 2.6  2.6 mm and a round shaped with a diameter of 20 mm. Both FOTs have identical magnification ratios of 3.1. By implementing the larger FOT the detector has the neutron-sensitive area of 314 mm
2.6 mm and a round shaped with a diameter of 20 mm. Both FOTs have identical magnification ratios of 3.1. By implementing the larger FOT the detector has the neutron-sensitive area of 314 mm with the effective pixel size of 0.17
with the effective pixel size of 0.17  0.17 mm
0.17 mm whilst the light transmission rate decreased 20% less compared to that with the small FOT. The detector equipped with the larger FOT exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.26
whilst the light transmission rate decreased 20% less compared to that with the small FOT. The detector equipped with the larger FOT exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.26  0.07 mm, which was similar to the one with the small FOT.
0.07 mm, which was similar to the one with the small FOT.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 604(1-2), p.158 - 160, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.6(Instruments & Instrumentation)The effective pixel size of a two-dimensional wavelength-shifting-fibre (WLS-fibre)-based neutron image detector was improved from 0.5 to 0.16 mm by including a fibre-optic taper (FOT) between the scintillator screen and the WLS fibre. The WLS-fibre-based detector consisted of a thin ZnS/ LiF screen, a FOT and WLS ribbons crossed in the x and y directions. The demonstrator detector had 16 fibre channels in each direction, and the light signals in each fibre were read out individually. The FOT was constructed from fine glass fibres with a taper ratio of 3.1, and served as an image magnifier. The prototype detector equipped with the FOT exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.3 mm, compared to the spatial resolution of 0.8 mm for the original detector without the FOT.
LiF screen, a FOT and WLS ribbons crossed in the x and y directions. The demonstrator detector had 16 fibre channels in each direction, and the light signals in each fibre were read out individually. The FOT was constructed from fine glass fibres with a taper ratio of 3.1, and served as an image magnifier. The prototype detector equipped with the FOT exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.3 mm, compared to the spatial resolution of 0.8 mm for the original detector without the FOT.