Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:49.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered van der Waals halides are particularly sensitive to external pressure, suggesting a feasible route to pinpoint their structure with extraordinary behavior. However, a very sensitive pressure response usually lead to a detrimental phase transition and/or lattice distortion, making the approach of materials manipulation in a continuous manner remain challenging. Here, the extremely weak interlayer coupling and high tunability of layered RhI crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
Liss, K.-D.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi*
Advanced Engineering Materials, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Liu, X. J.*; Xu, P. G.; Shiro, Ayumi*; Zhang, S. Y.*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Akita, Koichi*; Zolotoyabko, E.*; Liss, K.-D.*
Journal of Materials Science, 57(46), p.21446 - 21459, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mattan, K.*; Ono, Toshio*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Nambu, Yusuke*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 105(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_8, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
Trkov, A.*; Griffin, P. J.*; Simakov, S. P.*; Greenwood, L. R.*; Zolotarev, K. I.*; Capote, R.*; Aldama, D. L.*; Chechev, V.*; Destouches, C.*; Kahler, A. C.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 163, p.1 - 108, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:99.77(Physics, Nuclear)The version II of the International Reactor Dosimetry and Fusion File (IRDFF-II) has been released as a consistent set of nuclear data for fission and fusion neutron metrology applications up to 60 MeV neutron energy. The library is intended to support: (a) applications in research reactors; (b) safety and regulatory applications in the nuclear power generation in commercial fission reactors; and c) material damage studies in support of the research and development of advanced fusion concepts. The paper describes the contents of the library, documents the thorough verification process used in its preparation, and provides an extensive set of validation data gathered from a wide range of neutron benchmark fields. The new library is expected to become the international reference in neutron metrology for multiple applications.
Lin, P.*; Xu, C.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Chen, H.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Xing, W.*; Sun, L.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Yamazaki, Hideo*; Kokubu, Yoko; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 678, p.409 - 418, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:48.62(Environmental Sciences)Nagasaki sediments containing bomb-derived Pu provided a unique opportunity to explore the long term geochemical behavior of Pu. Through a combination of selective extractions and molecular characterization via electrospray ionization Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, we determined that 55  3% of the
3% of the 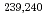 Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these
Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these 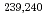 Pu (31
Pu (31  2% on average), and less than 20% of the
2% on average), and less than 20% of the 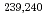 Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
 -phase in
-phase in  -based titanium aluminide intermetallics
-based titanium aluminide intermetallicsLiss, K.-D.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Reid, M.*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Shobu, Takahisa; Akita, Koichi
Metals, 6(7), p.165_1 - 165_22, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:67.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Titanium aluminides find application in modern light-weight, high-temperature turbines, such as aircraft engines, but suffer from poor plasticity during manufacturing and processing. Huge forging presses enable materials processing in the 10 GPa range and hence, it is necessary to investigate the phase-diagrams of candidate materials under these extreme conditions. Here we report on an in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study in a large-volume-press of a modern (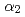 +
+  ) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation
) two-phase material, Ti-45Al-7.5Nb-0.25C, under pressures up to 9.6 GPa and temperatures up to 1686 K. At room temperature, the volume response to pressure is accommodated by the transformation 

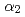 rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of
rather than volumetric strain, expressed by apparently high bulk moduli of both constituent phases. Crystallographic aspects, specifically lattice strain and atomic order are discussed in detail. It is interesting to note that this transformation takes place despite an increase in atomic volume, which is due to the high ordering energy of  . Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and
. Upon heating under high pressure, both the eutectoid and  -solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic
-solvus transition temperatures are elevated, and a third, cubic  -phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this
-phase is stabilized above 1350 K. Earlier research has shown that this  -phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental
-phase is very ductile during plastic deformation, essential in near-conventional forging processes. Here, we were able to identify an ideal processing window for near-conventional forging, while the presence of the detrimental  -phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
-phase is not present under operating conditions. Novel processing routes can be defined from these findings.
; Takanobu, Osamu; Matsuda, Kenji*; M.Uruno; K.Shibata; T.Kitamura*; Umetsu, H.*
IAEA(RU:TECDOC Sakusei Ni Kansuru Kaigi), 0 Pages, 2003/00
PNC(JNC) undertook technological development for the RU use in collaboration with an electric companies. The condition of RU in Japan and some experience of the RU use in JNC are introduced in this paper.
Xu, P. G.; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Harjo, S.; Shobu, Takahisa; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Takamura, Masato*; Otake, Yoshie*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Sato, Shigeo*; Liss, K.-D.*
no journal, ,