Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Bi
Bi
Park, P.*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Spargue, M.*; Sakuya, A. P.*; Chen, S. A.*; Frontzek, M. D.*; Tian, W.*; Sibille, R.*; Mazzone, D. G.*; Tabata, Chihiro; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.4384_1 - 4384_9, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Chen, Z.*; Lobzenko, I.; Inui, Haruyuki*
Materia, 63(10), p.695 - 702, 2024/10
VNbMoTaW, a typical high-entropy alloy with the BCC phase, is composed of metals with high melting points, and is called a reflectory high-entropy alloy. TiZrNbTaHf, which are also known as typical high-entropy alloys with the BCC phase, are also single phase and have a melting point 500  C lower than that of VNbMoTaW, but are known to exhibit excellent ductility at low temperatures below room temperature. Understanding what properties govern the mechanical properties is essential for designing alloys such as high-temperature resistant alloys with excellent high-temperature strength and low-temperature ductility. Given that both VNbMoTaW and TiZrNbTaHf are single-phase alloys, the key lies in the relationship between the constituent elements and the properties underlying the deformation, such as dislocations. This paper presents the results of the differences in mechanical properties of these two refractory high-entropy alloys, using experimental, theoretical, and computer simulations to investigate the key factors controlling ductility and strength.
C lower than that of VNbMoTaW, but are known to exhibit excellent ductility at low temperatures below room temperature. Understanding what properties govern the mechanical properties is essential for designing alloys such as high-temperature resistant alloys with excellent high-temperature strength and low-temperature ductility. Given that both VNbMoTaW and TiZrNbTaHf are single-phase alloys, the key lies in the relationship between the constituent elements and the properties underlying the deformation, such as dislocations. This paper presents the results of the differences in mechanical properties of these two refractory high-entropy alloys, using experimental, theoretical, and computer simulations to investigate the key factors controlling ductility and strength.
 archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elements
archaea host diverse and interacting extrachromosomal elementsShi, L.-D.*; West-Roberts, J.*; Schoelmerich, M. C.*; Penev, P. I.*; Chen, L.-X.*; Amano, Yuki; Lei, S.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 9(9), p.2422 - 2433, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:39.49(Microbiology) RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kaneko, Koji; Chen, Y.-S.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Hsu, P.-T.*; Lee, M. K.*; Hall, A. E.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033303_1 - 033303_7, 2024/09
The magnetic excitation extends at least from 0.3 to 140 meV. The integrated inelastic scattering intensity leads to a localized magnetic moment of about 5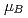 per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61
per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61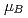 at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn
at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn RhSi.
RhSi.
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Zhou, L.*; Xu, P. G.; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Chen, J.*; Wu, S. C.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 306, p.110267_1 - 110267_18, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:55.14(Mechanics)Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:98.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
R hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
Journal of Medical Physics - Zeitschrift f r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.4 - 13, 2024/02
r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.4 - 13, 2024/02
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) provides independent recommendations on radiological protection for the public benefit. For more than 90 years, the ICRP System of Radiological Protection has been guiding the development and implementation of national and international standards and regulations on radiological protection. In 2019, ICRP established Task Group (TG) 115 to address a broader range of topics related to dose and risk assessment for radiological protection of astronauts. This paper gives an overview of the System of Radiological Protection and a brief summary of ICRP's work on radiological protection of astronauts.
Shavers, M. R.*; Semones, E. J.*; Shurshakov, V.*; Dobynde, M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Tomi, L.*; Chen, J.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Straube, U.*; et al.
Journal of Medical Physics - Zeitschrift f r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.31 - 43, 2024/02
r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.31 - 43, 2024/02
The Partner Agencies of the International Space Station (ISS) present an intracomparison of the ionizing radiation absorbed dose and risk quantities used to characterize example mission lunar space. The results and the work itself provide insights to the level of agreement with which space agencies can perform organ dosimetry and calculate effective dose. This work was performed in collaboration with the advisory and guidance efforts of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) Task Group 115 and will be presented in an ICRP Report
Tsuru, Tomohito; Han, S.*; Matsuura, Shutaro*; Chen, Z.*; Kishida, Kyosuke*; Lobzenko, I.; Rao, S.*; Woodward, C.*; George, E.*; Inui, Haruyuki*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1706_1 - 1706_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:98.70(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) have attracted attention because of their potential for use in ultrahigh-temperature applications. Unfortunately, their body-centered-cubic (BCC) crystal structures make them more brittle than the ductile and fracture-resistant face-centered-cubic (FCC) HEAs. RHEAs also display significantly lower creep strengths than a leading Ni-base superalloy and its FCC matrix. To overcome these drawbacks and develop RHEAs into viable structural materials, improved fundamental understanding is needed of factors that control strength and ductility. Here we investigate two model RHEAs, TiZrHfNbTa and VNbMoTaW, and show that the former is plastically compressible down to 77 K, whereas the latter is not below 298 K. We find that hexagonal close-packed (HCP) elements in TiZrHfNbTa lower its dislocation core energy, increase its lattice distortion, and lower its shear modulus relative to VNbMoTaW whose elements are all BCC, leading to the formers higher ductility and modulus-normalized yield strength. Consistent with our yield strength models, primarily screw dislocations are present in TiZrHfNbTa after deformation, but equal numbers of edge and screw segments in VNbTaMoW. Dislocation cores are compact in VNbTaMoW and extended in TiZrHfNbTa, and different macroscopic slip planes are activated in the two RHEAs, which we attribute to the concentration of HCP elements. Our findings demonstrate how electronic structure changes related to the ratio of HCP to BCC elements can be used to control strength, ductility, and slip behavior to develop the next generation of high-temperature materials for more efficient power plants and transportation.
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Zhang, A.*; Deng, K.*; Sheng, J.*; Liu, P.*; Kumar, S.*; Shimada, Kenya*; Jiang, Z.*; Liu, Z.*; Shen, D.*; Li, J.*; et al.
Chinese Physics Letters, 40(12), p.126101_1 - 126101_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(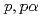 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (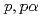 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
 RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Hall, A. E.*; Chen, Y.-S.*; Lee, M. K.*; Balakrishnan, G.*; Chang, L.-J.*
Communications Physics (Internet), 6, p.248_1 - 248_6, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:38.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We show that the local spin correlation order has a spiral structure by neutron scattering measurement of a Mn RhSi single crystal. The possible origins of the magnetic cluster formation are discussed in terms of the Lifshitz invariant and the Griffiths phase, and compared with the room-temperature skyrmion phase of Co
RhSi single crystal. The possible origins of the magnetic cluster formation are discussed in terms of the Lifshitz invariant and the Griffiths phase, and compared with the room-temperature skyrmion phase of Co Zn
Zn Mn
Mn and non-Fermi liquid behavior of
and non-Fermi liquid behavior of  -Mn.
-Mn.
Yang, D. S.*; Wu, Y.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Avila, R.*; Zhou, M.*; Bai, Y.*; Chen, S.*; Sekine, Yurina; Kim, J.*; Deng, Y.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(11), p.4992 - 5003, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:78.05(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents a set of findings that enhances the performance of these systems through the use of microfluidic networks, integrated valves and microscale optical cuvettes formed by three-dimensional printing in hard/soft hybrid materials systems, for accurate spectroscopic and fluorometric assays. Field studies demonstrate the capability of these microcuvette systems to evaluate the concentrations of copper, chloride, and glucose in sweat, along with the sweat pH, with laboratory grade accuracy and sensitivity.
 SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Materials, 22(8), p.999 - 1006, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:99.19(Chemistry, Physical)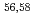 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 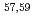 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 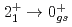 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 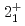 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 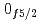 and
and 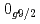 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
Dong, F.*; Chen, S.*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Yoshikawa, Masanori; Seki, Akiyuki; Takaya, Shigeru
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 404, p.112161_1 - 112161_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:99.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)