Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Akari*; Chhun, T.*; Oura, Chiharu*; Biswas, K. K.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Baskin, T. I.*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Journal, 47(5), p.788 - 801, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:59.9(Plant Sciences)2,4-D, a chemical analogue of IAA, is widely used as a growth regulator and exogenous source of auxin. It is believed that they share a common response pathway. Here, we show that a mutant, 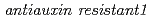 (
(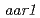 ) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the
) is resistant to 2,4-D, yet nevertheless responds like the wild type to IAA. That the 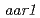 mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the
mutation alters 2,4-D responsiveness specifically was confirmed by analysis of GUS expression in the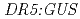 and
and 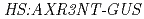 backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of
backgrounds, as well as by real-time PCR quantification of 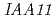 expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a
expression. Complementation and RNAi experiments identified a gene that confers 2,4-D responsiveness. The gene encodes a 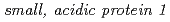 with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
with unknown function and present in plants, animals, and invertebrates. These results suggest that SMAP1 is a regulatory component that mediates responses to 2,4-D and that responsiveness to 2,4-D and IAA are partially distinct.
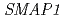 , a gene encoding small acidic protein revealed by mutant screening with antiauxin is involved in 2,4-D sensitivity but not IAA sensitivity in arabidopsis roots
, a gene encoding small acidic protein revealed by mutant screening with antiauxin is involved in 2,4-D sensitivity but not IAA sensitivity in arabidopsis rootsOno, Yutaka; Rahman, A.*; Nakasone, Hikari; Chhun, T.*; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
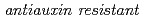 mutants; A Small acidic protein 1 (SMAP1) that mediates responses of the arabidopsis root to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
mutants; A Small acidic protein 1 (SMAP1) that mediates responses of the arabidopsis root to the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acidOno, Yutaka; Rahman, A.*; Biswas, K. K.*; Chhun, T.*; Tsurumi, Seiji*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
The mechanism of plant hormoneauxin action has been revealed by identification of several auxin-related mutants. However, the detailed regulatory system of signaling pathway and whether known auxin receptors TIR1/AFBs accounts for all auxin response largely remains unclear. It is may be possible that other uncharacterized proteins are involved in TIR1/AFBs dependent or independent auxin signaling pathway. To investigate novel factors involved in auxin signaling, we screened new mutants that exhibits a long primary root in presence of antiauxin PCIB. The mutants were classified at least 5 independent loci including two known auxin-related loci 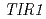 and
and 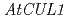 . Furthermore, physiological and molecular characterization of a novel auxin-related mutants,
. Furthermore, physiological and molecular characterization of a novel auxin-related mutants, 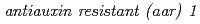 suggested that small acidic protein 1 is a regulatory component that mediates 2,4-D-induced auxin response and mode of action of 2,4-D is distinct from that of IAA at least in part.
suggested that small acidic protein 1 is a regulatory component that mediates 2,4-D-induced auxin response and mode of action of 2,4-D is distinct from that of IAA at least in part.