Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Joung, S.*; Ji, Y.-Y.*; Choi, Y.*; Lee, E.*; Ji, W.*; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 20(4), p.P04027_1 - P04027_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Metcalfe, R.*; Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Tachi, Yukio
Science of the Total Environment, 958, p.177690_1 - 177690_17, 2025/01
Uplifting fractured granitic rocks occur in substantial areas of countries such as Japan. A repository site would be selected in such an area only if it is possible to make a safety case, accounting for the changing conditions during uplift. The safety case must include robust arguments that chemical processes in the rocks around the repository will contribute sufficiently to minimise radiological doses to biosphere receptors. To provide confidence in the safety arguments, numerical models need to be sufficiently realistic, but also parameterised conservatively (pessimistically). However, model development is challenging because uplift involves many complex couplings between groundwater flow, chemical reactions between water and rock, and changing rock properties. The couplings would affect radionuclide mobilisation and retardation, by influencing diffusive radionuclide fluxes between groundwater flowing in fractures and effectively immobile porewater in the rock matrix and radionuclide partitioning between water and solid phases, via: (i) mineral precipitation/dissolution; (ii) mineral alteration; and (iii) sorption/desorption. It is difficult to represent all this complexity in numerical models while showing that they are parameterised conservatively. Here we present a modelling approach, illustrated by simulation cases for some exemplar radioelements, to identify realistically conservative process conceptualisations and model parameterisations.
Maekawa, Akihiro*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Fan, S.*; Fukuda, Miho*; Nasu, Koki*; Taniguchi, Keisuke*
KEK Proceedings 2024-6, p.7 - 12, 2024/12
no abstracts in English
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Hou, W.-S.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(4), p.043172_1 - 043172_12, 2024/11
Gauge theories with matter fields in various representations play an important role in different branches of physics. Recently, it was proposed that several aspects of the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping may be explained by an emergent SU(2) gauge symmetry. Around the transition with positive hole-doping, one can construct a (2+1)-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory coupled to four adjoint scalar fields which gives rise to a rich phase diagram with a myriad of phases having different broken symmetries. We study the phase diagram of this model on the Euclidean lattice using the Hybrid Monte Carlo algorithm. We find the existence of multiple broken phases as predicted by previous mean field studies. Depending on the quartic couplings, the SU(2) gauge symmetry is broken down either to U(1) or 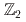 in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.362_1 - 362_7, 2024/11
We study a 3-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory with 4 Higgs fields which transform under the adjoint representation of the gauge group, that has been recently proposed by Sachdev et al. to explain the physics of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping. The symmetric confining phase of the theory corresponds to the usual Fermi-liquid phase while the broken (Higgs) phase is associated with the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprates. We employ the Hybrid Monte-Carlo algorithm to study the phase diagram of the theory. We find the existence of a variety of broken phases in qualitative accordance with earlier mean-field predictions and discuss their role in cuprates. In addition, we investigate the behavior of Polyakov loop to probe the confinement/deconfinement phase transition, and find that the Higgs phase hosts a stable deconfining phase consistent with previous studies.
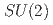 gauge fields
gauge fieldsCatumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.87_1 - 87_9, 2024/11
We study the most general Two Higgs Doublet Model with 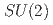 gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
 RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kaneko, Koji; Chen, Y.-S.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Hsu, P.-T.*; Lee, M. K.*; Hall, A. E.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033303_1 - 033303_7, 2024/09
The magnetic excitation extends at least from 0.3 to 140 meV. The integrated inelastic scattering intensity leads to a localized magnetic moment of about 5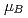 per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61
per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61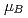 at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn
at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn RhSi.
RhSi.
 Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement
Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcementNakamoto, Mio*; Sugano, Michinaka*; Ogitsu, Toru*; Sugimoto, Masahiro*; Taniguchi, Ryo*; Hirose, Kiyoshige*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Awaji, Satoshi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.8400806_1 - 8400806_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Li, S.; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
 -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatment
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatmentAhmed, A.*; Uttarasak, K.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 988, p.174234_1 - 174234_9, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:96.31(Chemistry, Physical)This study aims to clarify the growth process of the -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the  -phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the
-phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the  -phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}
-phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}  facets at the edges of the
facets at the edges of the  -phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the
-phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the  -phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg
-phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111)
Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111) facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001)
facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001) and (011)
and (011) facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg
facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg Si crystals.
Si crystals.
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Rapp, L.*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Firestein, K. L.*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Habara, Hideaki*; Mukai, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Kazuo*; Gamaly, E. G.*; Kodama, Ryosuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023101_1 - 023101_18, 2024/04
It is generally known that irradiating a solid surface with a laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity generates a plasma on the surface, which in turn creates an ultrahigh pressure inside. In this study, the crystal structure analysis of high-pressure phases generated inside silicon single-crystals irradiated by this laser was performed using the diffraction system at the Stress and Imaging apparatus of BL22XU, which is a JAEA-BL. The results obtained confirm the existence of high-pressure phases that silicon is said to possess: body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal, and tetragonal phases in the interior. We can get the results that the crystal structure of silicon polymorphs of being include body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal-diamond, tetragonal exists. In the future, we will accumulate data and apply them to control the internal structure, strength, and functionality of materials.
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
 ders deformation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel
ders deformation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steelKoyama, Motomichi*; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Morooka, Satoshi; Sawaguchi, Takahiro*; Yang, Z.*; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(3), p.197 - 204, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) condensed state in
condensed state in  Mg using the
Mg using the  C+
C+ C scattering
C scatteringFujikawa, Y.*; Kawabata, T.*; Adachi, S.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Orlandi, R.; Suzaki, Fumi; 13 of others*
Physics Letters B, 848, p.138384_1 - 138384_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:76.15(Astronomy & Astrophysics)