Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kashimoto, Shiro*; Kawana, Daichi*; Yamazaki, Teruo*; Machida, Akihiko; Tanaka, Yukinori*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 86(9), p.094201_1 - 094201_6, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:89.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A quasiperiodic, intermediate-valence (IV) system is realized in an icosahedral Au-Al-Yb quasicrystal. X-ray absorption spectroscopy near the Yb 
 -edge indicates that quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions assume a mean valence of 2.61, between a divalent state (4
-edge indicates that quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions assume a mean valence of 2.61, between a divalent state (4
 ,
,  = 0) and a trivalent one (4
= 0) and a trivalent one (4
 ,
,  = 7/2). Magnetization measurements demonstrate that the 4
= 7/2). Magnetization measurements demonstrate that the 4 holes in this quasicrystal have a localized character. The magnetic susceptibility shows a Curie-Weiss behavior above
holes in this quasicrystal have a localized character. The magnetic susceptibility shows a Curie-Weiss behavior above  100 K with an effective magnetic moment of 3.81
100 K with an effective magnetic moment of 3.81 
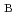 per Yb. Moreover, a crystalline approximant to this quasicrystal is an IV compound. We propose a heterogeneous IV model for the quasicrystal, whereas the crystalline approximant is most likely a homogeneous IV system. At temperatures below
per Yb. Moreover, a crystalline approximant to this quasicrystal is an IV compound. We propose a heterogeneous IV model for the quasicrystal, whereas the crystalline approximant is most likely a homogeneous IV system. At temperatures below  10 K, specific heat and magnetization measurements reveal non-Fermi-liquid behavior in both the quasicrystal and its crystalline approximant without either doping, pressure, or field tuning.
10 K, specific heat and magnetization measurements reveal non-Fermi-liquid behavior in both the quasicrystal and its crystalline approximant without either doping, pressure, or field tuning.
Ida, Mizuho; Chida, Teruo; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Wakai, Eiichi; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.987 - 990, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To clarify IFMIF target back-wall structures and materials with acceptable thermal-stress and deformation due to nuclear heating during the accelerator operation, thermal-stress analysis was done using a code ABAQUS and data of nuclear heating. Two types of back-wall were estimated. One is made of only 316L, and the other is made of 316L at its circumference and F82H a RAF steel at center. Effects of stress-mitigation structure with thickness 2-8 mm, and beam heat loads of 10-100% were estimated. As a result, thermal-stress in the latter back-wall is acceptable level less than 328 MPa for 316L and 455 MPa for F82H even under full heat load, if thickness of the stress-mitigation part is more than 5 mm. On the contrary, thermal-stress in the former is not acceptable. In preliminary tensile tests on dissimilar welding (316L-F82H) specimen, the fracture was occurred in base metal of 316L. Therefore, this welding is expected to be employed as the back-wall.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Agostini, P.*; Ara, Kuniaki; Cevolani, S.*; Chida, Teruo*; Ciotti, M.*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Garin, P.*; Gessii, A.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.1007 - 1014, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:76.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the latest design of liquid lithium target system in IFMIF. Design requirement of the Li target is to provide a stable Li jet with a speed of 20 m/s to handle an averaged heat flux of 1 GW/m . A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
. A double reducer nozzle and a concaved flow are applied to the target design. On Li purification, a cold trap and two kinds of hot trap are applied to control impurities below permissible levels. Nitrogen concentration shall be controlled below 10 wppm by one of the hot trap. Tritium concentration shall be controlled below 1 wppm by an yttrium hot trap. To maintain reliable continuous operation, various diagnostics are attached to the target assembly. Among the target assembly, a back-plate made of RAFM is located in the most severe region of neutron irradiation (50 dpa/y). Therefore, two design options of replaceable back wall and their remote handling systems are under investigation.
Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Chida, Teruo*; Miyashita, Makoto; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Eiichi; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Miyake, Osamu; Hirabayashi, Masaru; Ara, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-008, 38 Pages, 2008/03
Engineering Validation Design and Engineering Design Activity (EVEDA) of the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is under going. IFMIF is an accelerator-based Deuterium-Lithium (D-Li) neutron source to produce intense high energy neutrons and a sufficient irradiation volume for testing candidate materials for fusion reactors. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, nuclear heating due to neutron causes thermal stress especially on a back-wall of the target assembly. In addition, radioactive species such as beryllium-7, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In this report, thermal stress analyses of the back-wall, mechanical tests on weld specimen made of the back-wall material, estimations of beryllium-7 behavior and worker dose at the IFMIF Li loop and consideration on major EVEDA tasks are summarized.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho; Chida, Teruo; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2671 - 2676, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Chida, Teruo; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sato, Toru*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-048, 40 Pages, 2007/08
This report describes results of thermo-structural analysis of a backwall in international fusion material irradiation facilities (IFMIF) lithium target preformed during FY2007. The IFMIF is an accelerator-based intense neutron source for testing candidate materials for fusion reactors. Since the backwall is operating under a severe neutron irradiation of 50 dpa/year and a maximum nuclear heating rate of 25 W/cm , thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Since previous model included only the backwall, a model including a part of target assembly is applied. In this analysis, three models were calculated. First model is a basic geometry adding a part of the target assembly to the backwall. Second model is a modified geometry which has a thin backwall. In a third model, a lip seal with a stress mitigation structure was applied to the second model. Calculation results showed that, in the third model, a thermal stress at a center of the backwall was 146 MPa below a permissible stress of F82H (455MPa: an yield strength at 300
, thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Since previous model included only the backwall, a model including a part of target assembly is applied. In this analysis, three models were calculated. First model is a basic geometry adding a part of the target assembly to the backwall. Second model is a modified geometry which has a thin backwall. In a third model, a lip seal with a stress mitigation structure was applied to the second model. Calculation results showed that, in the third model, a thermal stress at a center of the backwall was 146 MPa below a permissible stress of F82H (455MPa: an yield strength at 300 C) and maximum stress was 286 MPa below a permissible stress of SUS316L (328MPa: 3Sm value at 300
C) and maximum stress was 286 MPa below a permissible stress of SUS316L (328MPa: 3Sm value at 300 C). These results showed a prospect of the present backwall configuration.
C). These results showed a prospect of the present backwall configuration.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho; Chida, Teruo; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1543 - 1548, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The IFMIF is an accelerator-based intense neutron source for testing candidate materials of fusion reactor. Intense neutrons are emitted inside the Li flow through a backwall. The backwall made of 316L stainless steel or RAFM is attached to the target assembly with a lip seal welded by YAG laser. Since the backwall is operating under a severe neutron irradiation of 50 dpa/year and a maximum nuclear heating rate of 25 W/cm , thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Thermal stress was calculated by ABAQUS code. As a permissible stress, yield strength at 300
, thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Thermal stress was calculated by ABAQUS code. As a permissible stress, yield strength at 300 C was used. In a case of the 316 stainless steel backwall, a maximum thermal stress was more than the permissible stress(164MPa). On the other hand, in case of the F82H backwall, a maximum thermal stress is was below the permissible stress(455MPa). Therefore, F82H is recommended as a backwall material.
C was used. In a case of the 316 stainless steel backwall, a maximum thermal stress was more than the permissible stress(164MPa). On the other hand, in case of the F82H backwall, a maximum thermal stress is was below the permissible stress(455MPa). Therefore, F82H is recommended as a backwall material.
Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Tatematsu, Yoshinori*; Numakura, Tomoharu*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Minami, Ryutaro*; Watanabe, Osamu*; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Kamata, Yasuhiro*; Machida, Norihito*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.208 - 212, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kamata, Yasuhiro*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Tatematsu, Yoshinori*; Watanabe, Osamu*; Minami, Ryutaro*; Saito, Teruo*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Machida, Norihito*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.412 - 414, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Chida, Teruo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Review 2006-009, 28 Pages, 2006/03
The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is being jointly planned to provide an accelerator-based Deuterium-Lithium (D-Li) neutron source to produce intense high energy neutrons (2 MW/m ) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm
) up to 200 dpa and a sufficient irradiation volume (500 cm ) for testing candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as
) for testing candidate materials and components up to about a full lifetime of their anticipated use in ITER and DEMO. To realize such a condition, 40 MeV deuteron beam with a current of 250 mA is injected into high speed liquid Li flow with a speed of 20 m/s. In target system, radioactive species such as  Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal structural analysis and the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAEA activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2005.
Be, tritium and activated corrosion products are generated. In addition, back wall operates under severe conditions of neutron irradiation damage (about 50 dpa/y). In this paper, the thermal structural analysis and the accessibility evaluation of the IFMIF Li loop are summarized as JAEA activities on the IFMIF target system performed in FY2005.
 pellet
pelletNakamura, Jinichi; Uchida, Masaaki; Uetsuka, Hiroshi; Furuta, Teruo
IAEA-TECDOC-1036, 0, p.127 - 138, 1998/08
no abstracts in English
Uetsuka, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Jinichi; Nagase, Fumihisa; Uchida, Masaaki; Furuta, Teruo
Fuel Performance Experiment and Analysis and Computerised Man-Machine Communication, p.1 - 11, 1990/09
no abstracts in English
Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Chida, Teruo; Ara, Kuniaki; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Chida, Teruo; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Simakov, S. P.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okabe, Toshihiro*; Ono, Hiroyuki*; Hatayama, Ichiro*; Waguri, Atsushi*; Sawada, Yuzuru*; Tsugawa, Hidehito*; Ichida, Tadao*; Nakane, Akio*; Sano, Teruo*; Tanaka, Kazuaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kawana, Daichi*; Machida, Akihiko; Tsai, A. P.*; Kashimoto, Shiro*; Tanaka, Yukinori*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Teruo*; Sato, Taku*
no journal, ,
Quasiperiodic intermediate-valence systems were prepared by applying pressure to Yb-based quasicrystals. In these systems, each quasiperiodic lattice point has a charge degree of freedom. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments near the Yb L3-edge demonstrate that the Yb valence in a Cd-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal increases continuously upon compression from a divalent state at ambient pressure and reaches 2.33 at 31.7 GPa, where the quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions take a valence fluctuation state. For the case of a Cd-Mg-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal, the Yb valence reaches a value of 2.71 at 57.6 GPa. By following the trend of Yb-based intermediate-valence crystalline compounds, this large valence increase suggests that the 4f electron system in this quasicrystal varies from a valence fluctuation regime to a strong correlated electron regime. Additionally, we have recently found that Au-Al-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal is an IV compound at ambient pressure.
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kawana, Daichi*; Machida, Akihiko; Kashimoto, Shiro*; Tanaka, Yukinori*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Teruo*; Sato, Taku*; Tsai, A. P.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kashimoto, Shiro*; Yamazaki, Teruo*; Kawana, Daichi*; Machida, Akihiko; Tanaka, Yukinori*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Sato, Taku*
no journal, ,
A quasiperiodic, intermediate-valence (IV) system is realized in an icosahedral Au-Al-Yb quasicrystal. X-ray absorption spectroscopy near the Yb L3-edge indicates that quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions assume a mean valence of 2.61, between a divalent state (4f14, J = 0) and a trivalent one (4f13, J = 7/2). Magnetization measurements demonstrate that the 4f holes in this quasicrystal have a localized character. The magnetic susceptibility shows a Curie-Weiss behavior above 100 K with an effective magnetic moment of 3.81 muB per Yb. Moreover, a crystalline approximant to this quasicrystal is an IV compound. We propose a heterogeneous IV model for the quasicrystal, whereas the crystalline approximant is most likely a homogeneous IV system. At temperatures below 10 K, specific heat and magnetization measurements reveal non-Fermi-liquid behavior in both the quasicrystal and its crystalline approximant without either doping, pressure, or field tuning.