Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimodaira, Masaki; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Iwata, Keiko; Katsuyama, Jinya; Chimi, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.448 - 458, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke; Lister, D. H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.867 - 880, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)One of the major subjects for evaluating the corrosive conditions in the PWR primary coolant was to determine the optimal hydrogen concentration for mitigating PWSCC without any adverse effects on major structural materials. As suitable procedures for evaluating the corrosive conditions in PWR primary coolant, a couple of procedures, i.e., water radiolysis and ECP analyses, were proposed. The previous article showed the radiolysis calculation in the PWR primary coolant, which was followed by an ECP study here. The ECP analysis, a couple of a mixed potential model and an oxide layer growth model, was developed originally for BWR conditions, which was extended to PWR conditions with adding Li (Na
(Na ) and H
) and H effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within
effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within  100mV discrepancies.
100mV discrepancies.
Hata, Kuniki; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tomonori
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), 14 Pages, 2023/08
Hata, Kuniki; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of International Symposium on Contribution of Materials Investigations and Operating Experience to LWRs' Safety, Performance and Reliability (Fontevraud 10) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/00
Iwata, Keiko; Hata, Kuniki; Tobita, Toru; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
Hanawa, Satoshi; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Water Chemistry in Nuclear Reactor Systems (Internet), 12 Pages, 2019/09
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(9), p.240 - 247, 2019/09
In order to study environment assisted cracking mechanism of stainless steel under BWR primary coolant condition, effects of applied load on oxidation in the vicinity of crack tips of CT specimens were evaluated. Loaded CT specimens were immersed in an aqueous condition at 290 C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe
C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe O
O were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.523 - 531, 2019/08
For structural integrity assessment on reactor internals of light water reactors, empirical equations of tensile properties as a function of neutron dose, and trend curves of stress-strain relations of neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels was proposed by fitting to recently developed database. The data in the database were obtained from reports of national projects in Japan and open literature, which was summarized in the form of data sheets. The empirical equations for tensile properties were formulated by using a saturation-type formulae. The equations were for CW 316 and SA 304/316 stainless steels in the temperature range of 280-350 C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.1345 - 1355, 2019/08
This paper describes empirical equation development of crack growth rates (CGR) in consideration of IASCC of neutron irradiated stainless steel to contribute to structural integrity assessment of BWR reactor internals. Empirical equations of CGR (da/dt) were developed based on a formula of da/dt = M K
K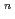 , assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
, assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Fukuya, Koji*; Fujimoto, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Review 2018-013, 171 Pages, 2019/01
For structural integrity assessment of reactor internals of light water reactors, it is important to evaluate and predict the property changes of structural materials, based on existing data obtained from austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons. Compilation of the data into tables is valuable for discussing the representative or the most probable values of the properties applied to the assessment. When the data compilation, the data must be distinguished clearly in consideration of different service conditions of core internals of pressurized water reactors (PWR) and boiling water reactors. Main objective of this work is to provide material property tables of irradiated austenitic stainless steel which will be applicable for assessment of structural integrity of core internals of PWRs. To compile the table, published literature reporting irradiated stainless steel data were surveyed and screened by considering the service conditions of PWRs. In addition to the data, various parameters for the data evaluation, e.g. chemical compositions and pre-treatments of the materials, irradiation and examination conditions, were extracted from the literature, and listed into tables.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Naito, Masanori*; Kojima, Masayoshi*; Kikura, Hiroshige*; Lister, D. H.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 341, p.112 - 123, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Improvement of plant reliability based on reliability-centered-maintenance (RCM) is going to be undertaken in NPPs. RCM is supported by risk-based maintenance (RBM). The combination of prediction and inspection is one of the key issues to promote RBM. Early prediction of IGSCC occurrence and its propagation should be confirmed throughout the entire plant systems which should be accomplished by inspections at the target locations followed by timely application of suitable countermeasures. From the inspections, accumulated data will be applied to confirm the accuracy of the code, to tune some uncertainties of the key data for prediction, and then, to increase their accuracy. The synergetic effects of prediction and inspection on application of effective and suitable countermeasures are expected. In the paper, the procedures for the combination of prediction and inspection are introduced.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Fukuya, Koji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Review 2018-012, 180 Pages, 2018/11
For structural integrity assessment of reactor internals of light water reactors, it is important to evaluate and predict the property changes of structural materials, based on existing data obtained from austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons. Compilation of the data into tables is valuable for discussing the representative or the most probable values of the properties applied to the assessment. In the process of the data compilation, the data must be distinguished clearly in consideration of different service conditions of core internals of boiling water reactors (BWR) and pressurized water reactors. Main objective of this work is to provide material property tables of irradiated austenitic stainless steel which will be applicable for assessment of structural integrity of core internals of BWRs. To compile the table, published literature reporting irradiated stainless steel data were surveyed and screened by considering the service conditions of BWRs. In addition to the data, various parameters for the data evaluation, e.g. chemical compositions and pre-treatments of the materials, irradiation and examination conditions, were extracted from the literature, and listed into the tables.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Kenji*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Umehara, Ryuji*; Hanawa, Satoshi
Proceedings of Contribution of Materials Investigations and Operating Experience to Light Water NPPs' Safety, Performance and Reliability (FONTEVRAUD-9) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2018/09
To investigate the influence of Zinc (Zn) injection on primary water stress corrosion cracking (PWSCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests of 10% cold-worked Alloy 600 were performed in simulated primary water environment of pressurized water reactor (PWR) at 320 C with a low-concentration (5-10 ppb) Zn injection under dissolved hydrogen (DH) conditions of 5, 30, and 50 cc/kgH
C with a low-concentration (5-10 ppb) Zn injection under dissolved hydrogen (DH) conditions of 5, 30, and 50 cc/kgH O. As a result of the crack growth tests, DH-dependence of crack growth rate (CGR) showed a similar tendency to the predicted CGR based on the CGR data without Zn injection, indicating almost no effect of a low-concentration Zn injection on the crack growth behavior. Moreover, the microstructural analyses of oxide films formed inside the crack and on the specimen surface were conducted, and the intake of Zn in the oxides was detected on the specimen surface, but not detected inside the crack. This result was considered to be the cause of no Zn injection effect on the crack growth behavior.
O. As a result of the crack growth tests, DH-dependence of crack growth rate (CGR) showed a similar tendency to the predicted CGR based on the CGR data without Zn injection, indicating almost no effect of a low-concentration Zn injection on the crack growth behavior. Moreover, the microstructural analyses of oxide films formed inside the crack and on the specimen surface were conducted, and the intake of Zn in the oxides was detected on the specimen surface, but not detected inside the crack. This result was considered to be the cause of no Zn injection effect on the crack growth behavior.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
Warm pre-stress (WPS) effect is a phenomenon that after applying a load at a high temperature fracture does not occur in unloading during cooling, and then the fracture toughness in reloading at a lower temperature increases effectively. Engineering evaluation models to predict an apparent fracture toughness in reloading are established using experimental data with linear elasticity. However, there is a lack of data on the WPS effect for the effects of specimen size and surface crack in elastic-plastic regime. In this study, fracture toughness tests were performed after applying load-temperature histories which simulate pressurized thermal shock transients to confirm the WPS effect. The experimental results of an apparent fracture toughness tend to be lower than the predictive results using the engineering evaluation models in the case of a high degree of plastic deformation in preloading. Considering the plastic component of preloading can refine the engineering evaluation models.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1039 - 1054, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been performed in simulated Boiling Water Reactor water conditions at  288
288 C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at
C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at  12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at
12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at 
 2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 480, p.386 - 392, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper addresses influence of two different temperature profiles during startup periods in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor and a boiling water reactor upon microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons to about 1 dpa and 3 dpa. Tensile tests at 290 C and Vickers hardness tests at room temperature were carried out, and their microstructures were observed by FEG-TEM. Influence of difference in the temperature profiles was observed obviously in interstitial cluster formation, in particular, growth of Frank loops. The influence was also found certainly in loss of strain hardening capacity and ductility, although the influence on the yield strength and the Vickers hardness was not clearly observed. As a result, Frank loops, which were observed in austenitic stainless steel irradiated at doses of 1 dpa or more, were considered to contribute to deformation of the austenitic stainless steel.
C and Vickers hardness tests at room temperature were carried out, and their microstructures were observed by FEG-TEM. Influence of difference in the temperature profiles was observed obviously in interstitial cluster formation, in particular, growth of Frank loops. The influence was also found certainly in loss of strain hardening capacity and ductility, although the influence on the yield strength and the Vickers hardness was not clearly observed. As a result, Frank loops, which were observed in austenitic stainless steel irradiated at doses of 1 dpa or more, were considered to contribute to deformation of the austenitic stainless steel.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Iwata, Keiko; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 307, p.411 - 417, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate influential parameters for irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, we attempt to analyze statistically existing data on the crack growth rate (CGR) in irradiated austenitic stainless steels (SSs) in boiling water reactor (BWR) environments using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method. From the probability distribution of CGR and some input parameters, such as yield stress of irradiated material (
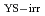 ), stress intensity factor (
), stress intensity factor ( ), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
), electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP), and fast neutron fluence, the mean CGR is estimated and compared with the measured CGR. The analytical results show good reproducibility of the measured CGR. The results also indicate the possible neutron fluence effects on CGR in high CGR region (i.e., high neutron fluence condition) by radiation-induced segregation (RIS), localized deformation, and/or other mechanisms than radiation hardening.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th Nuclear Plant Chemistry International Conference (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
The authors proposed and ECP evaluation model introducing irradiation-induced diffusion in the oxide layer to simulate neutron irradiation effect, and predicted with this model that ECP is started to depress from the neutron flux of about ten to the fourteenth per square meter. As the JMTR has in-pile loops applicable to water chemistry experiments, degree of irradiation effect on ECP appears in the in-pile loop was estimated by the model. Under oxygen injected condition, ECP in a capsule becomes constant along the vertical direction due to the presence of high amount of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide in a capsule. However, if neutron irradiation depress ECP, ECP in a capsule along vertical direction wouldn't become constant, and the degree to the decrement is detectable by experiments.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th Nuclear Plant Chemistry International Conference (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2016/10
ECP is the exclusive index to evaluate corrosion condition directly at the points of interest in the mixing of neutron and  -ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.
-ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.