Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhang, D.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, T.*; Abernathy, D. L.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Foley, B. J.*; Yoon, M.*; Choi, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(22), p.224310_1 - 224310_10, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Woo, W.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Kim, D.-K.*; Lee, C. M.*; Choi, S.-H.*; Suh, J.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.1350_1 - 1350_15, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:94.45(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Carter, L. M.*; Crawford, T. M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Choi, C.*; Kim, C. H.*; Brown, J. L.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Zanzonico, P. B.*; Lewis, J. S.*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 60(12), p.1802 - 1811, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:80.34(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Voxel human phantoms have been used for internal dose assessment. More anatomically accurate representation become possible for skins or layer tissues owing to recent developments of advanced polygonal mesh-type phantoms and thus internal dose assessment using those advanced phantoms are desired. However, the Monte Carlo transport calculation by implementing those phantoms require an advanced knowledge for the Monte Carlo transport codes and it is only limited to experts. We therefore developed a tool, PARaDIM, which enables users to conduct internal dose calculation with PHITS easily by themselves. With this tool, a user can select tetrahedral-mesh phantoms, set radionuclides in organs, and execute radiation transport calculation with PHITS. Several test cases of internal dosimetry calculations were presented and usefulness of this tool was demonstrated.
Zhang, Y.*; Guo, H.*; Kim, S. B.*; Wu, Y.*; Ostojich, D.*; Park, S. H.*; Wang, X.*; Weng, Z.*; Li, R.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 19(9), p.1545 - 1555, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:99.63(Biochemical Research Methods)This paper introduces two important advances in recently reported classes of soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic systems for sweat capture and analysis: (1) a simple, broadly applicable means for collection of sweat that bypasses requirements for physical/mental exertion or pharmacological stimulation and (2) a set of enzymatic chemistries and colorimetric readout approaches for determining the concentrations of creatinine and urea in sweat, across physiologically relevant ranges. The results allow for routine, non-pharmacological capture of sweat across patient populations, such as infants and the elderly, that cannot be expected to sweat through exercise, and they create potential opportunities in the use of sweat for kidney disease screening/monitoring.
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 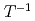 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Bandodkar, A. J.*; Gutruf, P.*; Choi, J.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Reeder, J. T.*; Jeang, W. J.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Lee, S. P.*; Model, J. B.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 5(1), p.eaav3294_1 - eaav3294_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:446 Percentile:99.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Interest in advanced wearable technologies increasingly extends beyond systems for biophysical measurements to those that enable continuous, non-invasive monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. Here, we introduce battery-free, wireless microelectronic platforms that perform sensing via schemes inspired by the operation of biofuel cells. Combining these systems in a magnetically releasable manner with chrono-sampling microfluidic networks that incorporate assays based on colorimetric sensing yields thin, flexible, lightweight, skin-interfaced technologies with broad functionality in sweat analysis. A demonstration device allows simultaneous monitoring of sweat rate/loss, along with quantitative measurements of pH and of lactate, glucose and chloride concentrations using biofuel cell and colorimetric approaches.
Kim, S. B.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Raj, M. S.*; Reeder, J. T.*; Koo, J.*; Hourlier-Fargette, A.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Won, S. M.*; Sekine, Yurina; Choi, J.*; et al.
Small, 14(45), p.1802876_1 - 1802876_9, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:94.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Excretion of sweat from eccrine glands is a dynamic physiological process that varies with body position, activity level, and health status. Information content embodied in sweat rate and chemistry can be used to assess health status and athletic performance. This paper presents a thin, miniaturized, skin-interfaced microfluidic technology that includes a reusable, battery-free electronics module for measuring sweat conductivity and rate in real-time using wireless power from and data communication with capabilities in near field communications (NFC). Systematic studies of these combined microfluidic/electronic systems, accurate correlations of measurements performed with them to those of laboratory standard instrumentation, and field tests on human subjects establish the key operational features and their utility in sweat analytics.
 quantitative analysis of sweat chemistry
quantitative analysis of sweat chemistrySekine, Yurina; Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Xu, S.*; Choi, J.*; Irie, Masahiro*; Ray, T. R.*; Kohli, P.*; Kozai, Naofumi; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 18(15), p.2178 - 2186, 2018/08
The rich composition of solutes and metabolites in sweat and its relative ease of collection upon excretion from skin pores make this class of biofluid an attractive candidate for point of care analysis. Here, we present a complementary approach that exploits fluorometric sensing modalities integrated into a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system which, when paired with a simple smartphone-based imaging module, allows for in-situ measurement of important biomarkers in sweat. A network array of microchannels and a collection of microreservoirs pre-filled with fluorescent probes that selectively react with target analytes in sweat (e.g. probes), enable quantitative, rapid analysis. Field studies on human subjects demonstrate the ability to measure the concentrations of chloride, sodium and zinc in sweat, with accuracy that matches that of conventional laboratory techniques.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Choi, I. W.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Tatsufumi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Daito, Izuru*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_9, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Projection images of a metal mesh produced by directional MeV electron beam together with directional proton beam, emitted simultaneously from a thin foil target irradiated by an ultrashort intense laser. The mesh patterns are projected to each detector by the electron beam and the proton beam originated from tiny virtual sources of  20 micron meter and
20 micron meter and  10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
10 micron meter diameters, respectively. Based on the observed quality and magnification of the projection images, we estimate sizes and locations of the virtual sources for both beams and characterize their directionalities. To carry out physical interpretation of the directional electron beam qualitatively, we perform 2D particle-in-cell simulation which reproduces a directional escaping electron component, together with a non-directional dragged-back electron component, the latter mainly contributes to building a sheath electric field for proton acceleration.
Choi, I. W.*; Kim, I. J.*; Pae, K. H.*; Nam, K. H.*; Lee, C.-L.*; Yun, H.*; Kim, H. T.*; Lee, S. K.*; Yu, T. J.*; Sung, J. H.*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 99(18), p.181501_1 - 181501_3, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:57.65(Physics, Applied)We report the manufacturing of a thin foil target made of conjugated polymer, and the simultaneous observation of laser accelerated ions and second harmonic radiation, when irradiated with ultrahigh-contrast laser pulse at a maximum intensity of 4 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
. Maximum proton energy of 8 MeV is achieved along the target normal direction. Strong second harmonic with over 6% energy ratio compared to fundamental is emitted along the specular direction. Two-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations confirm the simultaneous generation of protons and high-order harmonics, which demonstrates the feasibility of applications requiring particle and radiation sources at once, effectively using the same laser and target.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 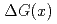 distributions.
distributions.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Choi, J. H.*; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-007, 91 Pages, 2011/06
We first surveyed the classical theories of fracture mechanics, and discussed the subcritical crack growth (SCG), which is observed under less load than the fracture toughness Kc. This SCG is a result of coupled mechanical and chemical effect. The SCG for granite was treated on this basis. We performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of single crystal quartz, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. The series of experiments were managed by a flow-through type changing temperature, pH and applied stress. Si concentrations we here measured. We first surveyed the theories of pressure solution. Then we proposed a theory of saluting velocity of quart which accounts for the effects of temperature, chemical (pH), solid pressure and pore pressure.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:175 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 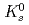 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Yang, H. L.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, H. K.*; Kim, K. M.*; Lee, K. S.*; Kim, H. T.*; Bang, E. N.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Because the 2010 operation of Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) mainly aims to achieve strongly elongated and diverted plasma, all the necessary hardware systems to provide an essential circumstance for the plasma shaping were newly installed and upgraded in 2010. In this paper, general configuration of the upgraded systems described earlier will be outlined. Moreover, several key performances and test results of the systems will be also reported in summary.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Choi, J. H.*; Hirano, Toru; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2009-027, 48 Pages, 2009/10
On the radioactive waste disposal, the long-term mechanical stability of tunnel was required. Therefore, we have been developing the method evaluating the stability. This report describes the works in the FY2008. Chapter 1 is the overview. In Chapter 2 we performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of single crystal quartz, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. After applying stress the surface of contacted area of quartz was observed by microscope and found traces of dissolution and reprecipitation. We managed two types of experiment; a closed solution experiment and a flow-through experiment. We discussed the Si dissolution rate based on the experimental results measured by ICP-AES. Fundamental mechanism of time-dependent creep and stress relaxation for crystalline rocks was discussed in Chapter 3 based on a concept of mechano-chemical coupling phenomena (as treated in Chapter 2) at micro-crack tips.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Daito, Izuru; Ikegami, Masahiro; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 94(6), p.061107_1 - 061107_3, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:87.48(Physics, Applied)A pair of conventional permanent magnet quadrupoles is used to focus a 2.4 MeV laser-driven proton beam at a 1 Hz repetition rate. The magnetic field strengths are 55 T/m and 60 T/m for the first and second quadrupoles respectively. The proton beam is focused to a spot size (full width at half maximum) of 2.7 8 mm
8 mm at a distance of 650 mm from the source. This result is in good agreement with a Monte Carlo particle trajectory simulation.
at a distance of 650 mm from the source. This result is in good agreement with a Monte Carlo particle trajectory simulation.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Daido, Hiroyuki; Yogo, Akifumi; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Ma, J.-L.; Sagisaka, Akito; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 15(5), p.053104_1 - 053104_10, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High-flux energetic protons whose maximum energies are up to 4 MeV are generated by an intense femtosecond Titanium Sapphire laser pulse interacting with a 7.5, 12.5, and 25 m thick Polyimide tape targets. The laser pulse energy is 1.7 J, duration is 34 fs, and intensity is 3
m thick Polyimide tape targets. The laser pulse energy is 1.7 J, duration is 34 fs, and intensity is 3 10
10 Wcm
Wcm . The amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) has the intensity contrast ratio of 4
. The amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) has the intensity contrast ratio of 4 10
10 . The conversion efficiency from laser energy into proton kinetic energies of
. The conversion efficiency from laser energy into proton kinetic energies of  3% is achieved, which is comparable or even higher than those achieved in the previous works with nanometer-thick targets and the ultrahigh contrast laser pulses (
3% is achieved, which is comparable or even higher than those achieved in the previous works with nanometer-thick targets and the ultrahigh contrast laser pulses ( 10
10 ).
).
 m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulses
m thick copper tape target irradiated by s-, circularly-, and p-polarized 55-fs laser pulsesLi, Z.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Bulanov, S. V.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
Physics Letters A, 369(5-6), p.483 - 487, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The energy spectra of energetic protons emitted in the normal direction from a 5- m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9
m thick copper tape irradiated by p-, circularly-, and s-polarized 55-fs laser pulses with intensity of 8-9 10
10 W/cm
W/cm are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3
are measured together with the angular distribution and energy spectra of hot electrons by the target normal direction. The protons with energy up to 1.34 MeV in the rear target normal direction and hot electrons in the laser propagation direction are found. The characters of protons and electrons driven by the circularly-polarized irradiation are close to that driven by the p-polarized one, which is much different from the case at laser intensity of 2-3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.