Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Joung, S.*; Ji, Y.-Y.*; Choi, Y.*; Lee, E.*; Ji, W.*; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 20(4), p.P04027_1 - P04027_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Jin, H.*; Choi, E. S.*; Wu, H.-C.*; Curro, N. J.*; Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Taku*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Klavins, P.*; Taufour, V.*
Physical Review B, 111(3), p.035103_1 - 035103_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:97.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Kitamura, Ryo; Bae, S.*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kim, B.*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Mibe, Tsutomu*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 24(3), p.033403_1 - 033403_9, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.50(Physics, Nuclear)A negative muonium ion (Mu ) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu
) source using an aluminum foil target was developed as a low-energy muon source. An experiment to produce Mu ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu
ions was conducted to evaluate the performance of the Mu ion source. The measured event rate of Mu
ion source. The measured event rate of Mu ions was
ions was 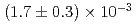 Mu
Mu /s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was
/s when the event rate of the incident muon beam was 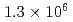 /s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu
/s. The formation probability, defined as the ratio of the Mu ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was
ions to the incident muons on the Al target, was 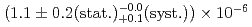 . This Mu
. This Mu ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
ion source boosted the development of the muon accelerator, and the practicality of this low-energy muon source obtained using a relatively simple apparatus was demonstrated.
Zhang, D.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, T.*; Abernathy, D. L.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Foley, B. J.*; Yoon, M.*; Choi, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(22), p.224310_1 - 224310_10, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Herranz, L. E.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Nitheanandan, T.*; Sandberg, N.*; Barr , F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
, F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 127, p.103432_1 - 103432_14, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Woo, W.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Kim, D.-K.*; Lee, C. M.*; Choi, S.-H.*; Suh, J.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.1350_1 - 1350_15, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:95.72(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Carter, L. M.*; Crawford, T. M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Choi, C.*; Kim, C. H.*; Brown, J. L.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Zanzonico, P. B.*; Lewis, J. S.*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 60(12), p.1802 - 1811, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:81.36(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Voxel human phantoms have been used for internal dose assessment. More anatomically accurate representation become possible for skins or layer tissues owing to recent developments of advanced polygonal mesh-type phantoms and thus internal dose assessment using those advanced phantoms are desired. However, the Monte Carlo transport calculation by implementing those phantoms require an advanced knowledge for the Monte Carlo transport codes and it is only limited to experts. We therefore developed a tool, PARaDIM, which enables users to conduct internal dose calculation with PHITS easily by themselves. With this tool, a user can select tetrahedral-mesh phantoms, set radionuclides in organs, and execute radiation transport calculation with PHITS. Several test cases of internal dosimetry calculations were presented and usefulness of this tool was demonstrated.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Bae, S.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kim, B.*; Ko, H. S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 937, p.164 - 167, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.10(Instruments & Instrumentation)A muon linac is under development for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment (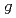 -2) and electric dipole moment (EDM) with a reaccelerated thermal muon beam. An H
-2) and electric dipole moment (EDM) with a reaccelerated thermal muon beam. An H source driven by an ultraviolet light has been developed for the muon acceleration experiment. Prior to the acceleration experiment, a beamline commissioning was performed using this H
source driven by an ultraviolet light has been developed for the muon acceleration experiment. Prior to the acceleration experiment, a beamline commissioning was performed using this H beam, since the accelerated muon intensity is very low. We successfully measured the magnetic rigidity, which is essential for identifying the accelerated muons. This H
beam, since the accelerated muon intensity is very low. We successfully measured the magnetic rigidity, which is essential for identifying the accelerated muons. This H source is capable of utilizing as a general-purpose beam source for other beamline.
source is capable of utilizing as a general-purpose beam source for other beamline.
Yeom, Y. S.*; Han, M. C.*; Choi, C.*; Han, H.*; Shin, B.*; Furuta, Takuya; Kim, C. H.*
Health Physics, 116(5), p.664 - 676, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.10(Environmental Sciences)Recently, Task Group 103 of the ICRP developed the mesh-type reference computational phantoms (MCRPs), which are planned for use in future ICRP dose coefficient calculation. Performance of major Monte Carlo particle transport codes (Geant4, MCNP6, and PHITS) were tested with MCRP. External and internal exposure of various particles and energies were calculated and the computational times and required memories were compared. Additionally calculation for voxel-mesh phantom was also conducted so that the influence of different mesh-representation in each code was studied. Memory usage of MRCP was as large as 10 GB with Geant4 and MCNP6 while it is much less with PHITS (1.2 GB). In addition, the computational time required for MRCP tends to increase compared to voxel-mesh phantoms with Geant4 and MCNP6 while it is equal or tends to decrease with PHITS.
Zhang, Y.*; Guo, H.*; Kim, S. B.*; Wu, Y.*; Ostojich, D.*; Park, S. H.*; Wang, X.*; Weng, Z.*; Li, R.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 19(9), p.1545 - 1555, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:187 Percentile:99.70(Biochemical Research Methods)This paper introduces two important advances in recently reported classes of soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic systems for sweat capture and analysis: (1) a simple, broadly applicable means for collection of sweat that bypasses requirements for physical/mental exertion or pharmacological stimulation and (2) a set of enzymatic chemistries and colorimetric readout approaches for determining the concentrations of creatinine and urea in sweat, across physiologically relevant ranges. The results allow for routine, non-pharmacological capture of sweat across patient populations, such as infants and the elderly, that cannot be expected to sweat through exercise, and they create potential opportunities in the use of sweat for kidney disease screening/monitoring.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.57(Quantum Science & Technology) Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 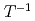 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Bandodkar, A. J.*; Gutruf, P.*; Choi, J.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Reeder, J. T.*; Jeang, W. J.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Lee, S. P.*; Model, J. B.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 5(1), p.eaav3294_1 - eaav3294_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:554 Percentile:99.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Interest in advanced wearable technologies increasingly extends beyond systems for biophysical measurements to those that enable continuous, non-invasive monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. Here, we introduce battery-free, wireless microelectronic platforms that perform sensing via schemes inspired by the operation of biofuel cells. Combining these systems in a magnetically releasable manner with chrono-sampling microfluidic networks that incorporate assays based on colorimetric sensing yields thin, flexible, lightweight, skin-interfaced technologies with broad functionality in sweat analysis. A demonstration device allows simultaneous monitoring of sweat rate/loss, along with quantitative measurements of pH and of lactate, glucose and chloride concentrations using biofuel cell and colorimetric approaches.
Kim, S. B.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Raj, M. S.*; Reeder, J. T.*; Koo, J.*; Hourlier-Fargette, A.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Won, S. M.*; Sekine, Yurina; Choi, J.*; et al.
Small, 14(45), p.1802876_1 - 1802876_9, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:94 Percentile:94.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Excretion of sweat from eccrine glands is a dynamic physiological process that varies with body position, activity level, and health status. Information content embodied in sweat rate and chemistry can be used to assess health status and athletic performance. This paper presents a thin, miniaturized, skin-interfaced microfluidic technology that includes a reusable, battery-free electronics module for measuring sweat conductivity and rate in real-time using wireless power from and data communication with capabilities in near field communications (NFC). Systematic studies of these combined microfluidic/electronic systems, accurate correlations of measurements performed with them to those of laboratory standard instrumentation, and field tests on human subjects establish the key operational features and their utility in sweat analytics.
Otani, Masashi*; Sue, Yuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Iijima, Toru*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1067(5), p.052012_1 - 052012_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:44.76(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have measured the muon beam profile after acceleration using a radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ). Positive muons are injected to an aluminum degrader and negative muoniums (Mu ) are generated. The generated Mu
) are generated. The generated Mu s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu
s are extracted by an electrostatic lens and accelerated to 89 keV by the RFQ. The accelerated Mu s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
s are transported to a beam profile monitor (BPM) through a quadrupole magnet pair and a bending magnet. The BPM consists of a micro-channel plate, a phospher screen, and a CCD camera. Measured profile in the vertical direction is consistent to the simulation. This profile measurement is one of milestones for realizing a muon linac for measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
 quantitative analysis of sweat chemistry
quantitative analysis of sweat chemistrySekine, Yurina; Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Xu, S.*; Choi, J.*; Irie, Masahiro*; Ray, T. R.*; Kohli, P.*; Kozai, Naofumi; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 18(15), p.2178 - 2186, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:183 Percentile:99.61(Biochemical Research Methods)The rich composition of solutes and metabolites in sweat and its relative ease of collection upon excretion from skin pores make this class of biofluid an attractive candidate for point of care analysis. Here, we present a complementary approach that exploits fluorometric sensing modalities integrated into a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system which, when paired with a simple smartphone-based imaging module, allows for in-situ measurement of important biomarkers in sweat. A network array of microchannels and a collection of microreservoirs pre-filled with fluorescent probes that selectively react with target analytes in sweat (e.g. probes), enable quantitative, rapid analysis. Field studies on human subjects demonstrate the ability to measure the concentrations of chloride, sodium and zinc in sweat, with accuracy that matches that of conventional laboratory techniques.