Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yachi, Yoshie*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.12160_1 - 12160_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:70.65(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Understand mechanisms of radiation cataracts that are of concern in the field of radiation protection and radiation therapy. However, biological effects in HLEC following protracted exposure have not yet fully been explored. Here, we investigated the temporal kinetics of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and cell survival of HLEC after exposure to photon beams at various dose rates, compared to those of human lung fibroblasts (WI-38). In parallel, we quantified the recovery for DSB and cell survival using a biophysical model. The study revealed that HLEC cells have a lower repair rate than WI-38 cells. There is no significant impact of dose rate on cell survival in both cell lines in the dose-rate range of 0.033-1.82 Gy/min. On the other hand, the experimental residual DSBs showed inverse dose rate effects (IDREs) compared to the model prediction, highlighting the importance of the IDREs in evaluating radiation effects on the ocular lens.
 -H2AX focus formation assay based on track-structure simulation
-H2AX focus formation assay based on track-structure simulationYachi, Yoshie*; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Yoshii, Yuji*; Fukunaga, Hisanori*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Kai, Takeshi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Internet), 24(2), p.1386_1 - 1386_14, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.63(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)When living cells are irradiated with radiation and complex damage is formed within a few nanometers of DNA, it is believed to induce biological effects such as cell death. In general, complex DNA damage formed in cells can be detected experimentally by fluorescence microscopy, because the area around the damage site emits light like a focus point when a fluorophore is used. However, this detection method has not been able to analyze the degree of complexity of DNA damage. Therefore, in this study, we addressed on the measured focus size and evaluated the degree of complexity of DNA damage using a track structure analysis code. As a result, we found that as DNA damage becomes more complex, the focus size also increases. Our findings are expected to provide a new analytical method for elucidating the initial factors of radiation biological effects.
Yachi, Yoshie*; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hirata, Yuho; Yoshii, Yuji*; Date, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.16412_1 - 16412_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:34.69(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Recently, magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy (MRgRT) which can visualize tumors in real time has been developed and installed in several clinical facilities. It is known that Lorentz force modulate macroscopic dose distribution by a charged particle, however, the impact by the force on microscopic radiation-track structure and early DNA damage induction remain unclear. In this study, we simulated the electron-track structure in a static magnetic field using a PHITS, and estimated features of biological effects. We indicated that the macroscopic dose distributions are changed by the force, while early DNA damage such as double strand breaks is attributed to the secondary electrons below a few tens of eV which are independent of the force. We expect that our insight significantly contributes to the MRgRT.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Kusumoto, Tamon*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Hirata, Yuho; Miwa, Misako*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Fukunaga, Hisanori*
AIP Advances (Internet), 12(2), p.025013_1 - 025013_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.46(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is a radiation therapy, which can selectively eradicate solid tumors by  -particles and Li ions generated through the nuclear reaction between thermal neutron and
-particles and Li ions generated through the nuclear reaction between thermal neutron and  B in tumor cells. With the development of accelerator-based neutron sources that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. Lithium is one of the targets that can produce thermal neutrons from the
B in tumor cells. With the development of accelerator-based neutron sources that can be installed in medical institutions, accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy is expected to become available at several medical institutes around the world in the near future. Lithium is one of the targets that can produce thermal neutrons from the  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be near-threshold reaction. Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code, which can simulate a variety of diverse particle types and nuclear reactions. The latest PHITS code enables simulating the generation of neutrons from the
Be near-threshold reaction. Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo code, which can simulate a variety of diverse particle types and nuclear reactions. The latest PHITS code enables simulating the generation of neutrons from the  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be reactions by using Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0/HE). In this study, we evaluated the neutron fluence using the PHITS code by comparing it to reference data. The subsequent neutron transport simulations were also performed to evaluate the boron trifluoride (BF
Be reactions by using Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library (JENDL-4.0/HE). In this study, we evaluated the neutron fluence using the PHITS code by comparing it to reference data. The subsequent neutron transport simulations were also performed to evaluate the boron trifluoride (BF ) detector responses and the recoiled proton fluence detected by a CR-39 plastic detector. As a result, these comparative studies confirmed that the PHITS code can accurately simulate neutrons generated from an accelerator using a Li target. The PHITS code has a significant potential for contributing to more precise evaluating accelerator-based neutron fields and understandings of therapeutic effects of BNCT.
) detector responses and the recoiled proton fluence detected by a CR-39 plastic detector. As a result, these comparative studies confirmed that the PHITS code can accurately simulate neutrons generated from an accelerator using a Li target. The PHITS code has a significant potential for contributing to more precise evaluating accelerator-based neutron fields and understandings of therapeutic effects of BNCT.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Satou, Yukihiko; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Cancers (Internet), 14(4), p.1045_1 - 1045_15, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.65(Oncology)An insoluble cesium-bearing microparticle (Cs-BMP) was discovered after the incident at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. Radiation risk by intake of internal exposure to radioactive cesium is conventionally estimated from organ dose, assuming that soluble cesium is uniformly distributed throughout human body. Meanwhile, such Cs-BMPs are assumed to adhere in the long term to normal tissue, leading to chronic non-uniform exposure. In this study, to clarify the normal tissue effects for Cs-BMP exposure, we investigated the relationship between the inflammatory responses and DNA damage induction. From experiments focusing on the inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF- B p65 and COX-2, compared to the uniform exposure to
B p65 and COX-2, compared to the uniform exposure to  -rays, NF-
-rays, NF- B p65 tended to be more activated in the cells proximal to the Cs-BMP, while both NF-
B p65 tended to be more activated in the cells proximal to the Cs-BMP, while both NF- B p65 and COX-2 were significantly activated in the distal cells. Experiments with inhibitors for NF-
B p65 and COX-2 were significantly activated in the distal cells. Experiments with inhibitors for NF- B p65 and COX-2 suggested involvement of such inflammatory responses both in the reduced radiosensitivity of the cells proximal to Cs-BMP and the enhanced radiosensitivity of the cells distal from Cs-BMP. These results suggested that radiation effects for Cs-BMP exposure can differ from that estimated based on conventional uniform exposure to normal tissues.
B p65 and COX-2 suggested involvement of such inflammatory responses both in the reduced radiosensitivity of the cells proximal to Cs-BMP and the enhanced radiosensitivity of the cells distal from Cs-BMP. These results suggested that radiation effects for Cs-BMP exposure can differ from that estimated based on conventional uniform exposure to normal tissues.
Fukui, Roman*; Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Tomita, Kazuo*; Kuwahara, Yoshikazu*; Ouchi, Kentaro*; Sato, Tomoaki*; Okumura, Kazuhiko*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Fukumoto, Manabu*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.1056_1 - 1056_12, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:90.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Alive cancer cells after fractionated irradiations with 2 Gy X-rays per day for more than 30 days show clinically relevant radioresistant. Such radioresistance is experimentally interpreted to attributed to the increment of stem-like cell content. However, only an experimental approach cannot clarify the cell responses (DNA damage and cell death induction) of cancer stem cells, so the radioresistant mechanisms remain uncertain. In addition to the conventional cell experiments using radio-resistant cell lines established after fractionated irradiations, in this study we developed a mathematical model (so called integrated microdosimetric-kinetic (IMK) model) explicitly considering cancer stem-like cell content and DNA damage responses and investigated radioresistant mechanisms acquired after fractionated irradiations. The IMK model analysis suggested that the changes of stem-like cell fraction and DNA repair efficiency play important roles of radioresisitance acquired after irradiations. Considering these into the IMK model, we successfully reproduced the experimental survival of various cell lines and various irradiation conditions. This work would contribute to not only the precise understanding of the radioresistant mechanisms induced after irradiation but also predicting curative effects with high precision.
Matsuya, Yusuke; McMahon, S. J.*; Butterworth, K. T.*; Naijo, Shingo*; Nara, Isshi*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Saga, Ryo*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Date, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 66(7), p.075014_1 - 075014_11, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.86(Engineering, Biomedical)Hypoxic cancer cells within solid tumours show radio-resistance, leading to malignant progression in fractionated radiotherapy. When prescribing dose to tumours under heterogeneous oxygen pressure with intensity-modulated radiation fields, intercellular signalling could have an impact on radiosensitivity between in-field and out-of-field cells. However, the impact of hypoxia on radio-sensitivity under modulated radiation intensity remains uncertain. In this study, we investigate the impact of hypoxia on in-field and out-of-field radio-sensitivities using two types of cancer cells. These in vitro measurements indicate that hypoxia apparently impacts out-of-field cells, although the OER values in out-of-field cells were smaller compared to those for in-field and uniformly irradiated cells. These decreased radio-sensitivities of out-of-field cells were shown as a consistent tendency for both DSB and cell death endpoints, suggesting that radiation-induced intercellular communication is of importance in treatment planning with intensity-modulated radiotherapy.
Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Takahashi, Rei*; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.8258_1 - 8258_10, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.41(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU) is a candidate of radiosensitizers in X-ray therapy. The curative effects under such 4-MU administration have been investigated in vitro; however, the radiosensitizing mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we investigated the radiosensitizing effects under 4-MU treatment from cell experiments and model estimations. We generated experimental surviving fractions of human fibrosarcoma cells (HT1080) after 4-MU treatment combined with X-ray irradiation. Meanwhilst, we also modelled the pharmacological effects of 4-MU treatment and theoretically analyzed the synergetic effects between 4-MU treatment and X-ray irradiation. The results show that the enhancement of cell killing by 4-MU treatment is the greatest in the intermediate dose range of around 4 Gy, which indicates the involvement of intercellular communication. In addition, the oxidative stress level, which leads to DNA damage induction, significantly increased under 4-MU treatment, and the radiosensitization by 4-MU can be suppressed by the inhibitors for intercellular communication. These findings suggest that the synergetic effects between 4-MU treatment and irradiation are predominantly attributed to intercellular communication and provide more efficient tumour control than conventional X-ray therapy.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Fukunaga, Hisanori*; Omura, Motoko*; Date, Hiroyuki*
Cells, 9(5), p.1117_1 - 1117_16, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:66.96(Cell Biology)When delivering a high absorbed dose to cancer cells following boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), heterogeneous dose distribution, the time line of  B concentrations and the long dose-delivery time must be considered. Changes in radiosensitivity during such a long dose-delivery time can reduce the probability of tumor control; however, such change has not yet been evaluated. Here, we developed a cell-killing model that accounts for changes in microdosimetric quantities and dose rates depending on the
B concentrations and the long dose-delivery time must be considered. Changes in radiosensitivity during such a long dose-delivery time can reduce the probability of tumor control; however, such change has not yet been evaluated. Here, we developed a cell-killing model that accounts for changes in microdosimetric quantities and dose rates depending on the  B concentration and investigated dose-rate effects (cell recovery during BNCT irradiation) of melanoma. The developed model shows good agreement with in-vitro experimental survival data for exposure to
B concentration and investigated dose-rate effects (cell recovery during BNCT irradiation) of melanoma. The developed model shows good agreement with in-vitro experimental survival data for exposure to  Co
Co  -rays, thermal neutrons, and BNCT. The model estimation suggests that the impact of cell recovery during BNCT irradiations with high linear energy transfer (LET) is reduced compared to
-rays, thermal neutrons, and BNCT. The model estimation suggests that the impact of cell recovery during BNCT irradiations with high linear energy transfer (LET) is reduced compared to  Co
Co  -rays irradiation with low LET. The present model is expected to predict radio-sensitivity for BNCT irradiations.
-rays irradiation with low LET. The present model is expected to predict radio-sensitivity for BNCT irradiations.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakamura, Rui*; Naijo, Shingo*; Date, Hiroyuki*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 65(9), p.095006_1 - 095006_12, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:41.54(Engineering, Biomedical)Radio-resistance induced under low oxygen pressure plays an important role in malignant progression in fractionated radiotherapy. For the general approach to predict cell killing under hypoxia, cell-killing models (e.g., the Linear-Quadratic model) have to be fitted to  experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the
experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the  experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER
experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER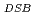 used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.
used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.
Yachi, Yoshie*; Yoshii, Yuji*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Mori, Ryosuke*; Oikawa, Joma*; Date, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.17649_1 - 17649_8, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.70(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Radiation weighting factor for photon and electron is defined as 1.0 independently these energies. However, it should be noted that the biological effects after 29 kVp X-rays is relative higher than standard 200 kVp X-rays at the endpoint of  . And it is of importance to evaluate electrons generated via interaction of photons with matter. Here, we evaluated the energy concentration along electron track (dose-mean lineal energy) on chromosome (micron-meter) scales by Monte Carlo simulation, and measured the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) induction. From the cell experiments, the DSBs induction after diagnostic X-rays exposure (60-100 kVp) is higher than those with therapeutic X-rays (6 MV). In the relation between the dose-mean lineal energy and the number of DSBs, it was shown that lower energy photons might induce more biological impact due to the interaction by low energy electron. This study implies that radiation weighting factor for photon and electron should not be unity.
. And it is of importance to evaluate electrons generated via interaction of photons with matter. Here, we evaluated the energy concentration along electron track (dose-mean lineal energy) on chromosome (micron-meter) scales by Monte Carlo simulation, and measured the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) induction. From the cell experiments, the DSBs induction after diagnostic X-rays exposure (60-100 kVp) is higher than those with therapeutic X-rays (6 MV). In the relation between the dose-mean lineal energy and the number of DSBs, it was shown that lower energy photons might induce more biological impact due to the interaction by low energy electron. This study implies that radiation weighting factor for photon and electron should not be unity.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Yoshii, Yuji*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Naijo, Shingo*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Applied Physics, 126(12), p.124701_1 - 124701_8, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.27(Physics, Applied)Biological effects after ionizing radiation exposure arise from initial DNA strand breaks. DNA damage can be estimated from the simulation with both track structure analysis and diffusion of free radicals; however, the simulation is a time-consuming process. In this study, we present a simple model for estimating yields of strand breaks based only on spatial patterns of inelastic interactions (i.e., ionization and electronic excitation) generated by electrons, which are evaluated by PHITS code without considering the production and diffusion of free radicals. In this model, the number of events per track and that of the two events pair within 3.4 nm (corresponding to 10 base pair) were stochastically sampled for calculating SSB and DSB yields, respectively. The calculated results agreed well with other simulations and experimental data on DSB yield and yield ratio of DSB/SSB for the exposure to mono-energetic electrons. The present model also can demonstrate the relative biological effectiveness at the DSB endpoint for various photon exposures. This study indicated that the spatial pattern of inelastic events composed of ionization and electronic excitation is sufficient to obtain the impact of electrons on initial induction to DNA strand break.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Satou, Yukihiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.10365_1 - 10365_9, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Insoluble radioactive microparticles (so called Cs-bearing particles) have been assumed to adhere in the long term to trachea after aspirated into respiratory system, leading to heterogeneous dose distribution within healthy tissue around the particles. The biological effects posed by such a particle remain unclear. Here, we show cumulative DNA damage in cultured cells proximal and distal to the particle under localized chronic exposure in comparison with uniform exposure. We placed the particle-contained microcapillary onto a glass-base dish containing normal human lung cells in vitro, and observed a significant change in nuclear  -H2AX foci after 24 h or 48 h exposure to the particle. The dose calculation by a Monte Carlo simulation and the comparison with nuclear foci under uniform exposure suggested that the localized exposure to a Cs-bearing particle leads to not only signal-induced DNA damage to distal cells but also the reduction of DNA damage induction yield to proximal cells (protective effects). Considering the small organ dose, the conventional radiation risk assessment is adequate. This study is the first to quantify the spatial distribution of cumulative DNA lesions under heterogeneous exposure by insoluble Cs-bearing particles.
-H2AX foci after 24 h or 48 h exposure to the particle. The dose calculation by a Monte Carlo simulation and the comparison with nuclear foci under uniform exposure suggested that the localized exposure to a Cs-bearing particle leads to not only signal-induced DNA damage to distal cells but also the reduction of DNA damage induction yield to proximal cells (protective effects). Considering the small organ dose, the conventional radiation risk assessment is adequate. This study is the first to quantify the spatial distribution of cumulative DNA lesions under heterogeneous exposure by insoluble Cs-bearing particles.
Matsuya, Yusuke; McMahon, S. J.*; Ghita, M.*; Yoshii, Yuji*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Date, Hiroyuki*; Prise, K. M.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.9483_1 - 9483_12, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:64.91(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In radiotherapy, intensity modulated radiation fields and complex dose-delivery are used to prescribe doses to tumors. Here, we analyzed the impact of modulated field on radio-sensitivity and cell recovery during irradiation time. The dose was delivered to either 50% of the area of the flask containing cells (half-field) or 100% of the flask (uniform-field). We also modelled cell-killing considering dose-rate effects and intercellular signals. It is found that (i) in-field cell survival under half-field exposure is higher than uniform-field exposure even with the same dose; (ii) the importance of sub-lethal damage repair in normal human skin fibroblast cells under the half-field is reduced; (iii) the increase of cell survival under half-field is predominantly attributed to not rescue effects (increased repair) but protective effects (reduced initial DNA lesion yield). These findings provide new understanding of radio-sensitivity for hit and non-hit cells under non-uniform exposure.
Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Takahashi, Rei*; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
Journal of Radiation Research, 60(3), p.298 - 307, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:77.77(Biology)In radiotherapy, it is recognized that cancer stem cells (CSCs) in tumor tissue shows radio-resistance. However, the relationship between content percentage of the CSCs and dose-response curve on cell survival remain unclear. In this study, we developed a stochastic model considering progeny cells and stem cells, and investigated the impact of stem cells on radio-sensitivity. From the flow-cytometric analysis (cell experiments), the content percentage of stem cells was 3.2% or less which agreed well with the model estimation from the cell survival curve. Based on the verification, it is suggested that cell survival in high-dose range is largely affected by the CSCs. In addition, regarding the sub-population of stem cells, the present model well reproduces the dose response on lethal lesions to DNA comparing with the conventional LQ model. This outcome indicates that the stem cells must be considered for describing the dose-response curve in wide dose range.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.61(Quantum Science & Technology)Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.35(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Sutherland, K.*; Miyajima, Satoshi*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Shirato, Hiroki*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Murakami, Masao*; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Bolton, P.; Tajima, Toshiki
Radiological Physics and Technology, 3(1), p.16 - 22, 2010/01
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:141 Percentile:97.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).