Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuya, Yusuke; McMahon, S. J.*; Butterworth, K. T.*; Naijo, Shingo*; Nara, Isshi*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Saga, Ryo*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Date, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 66(7), p.075014_1 - 075014_11, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.77(Engineering, Biomedical)Hypoxic cancer cells within solid tumours show radio-resistance, leading to malignant progression in fractionated radiotherapy. When prescribing dose to tumours under heterogeneous oxygen pressure with intensity-modulated radiation fields, intercellular signalling could have an impact on radiosensitivity between in-field and out-of-field cells. However, the impact of hypoxia on radio-sensitivity under modulated radiation intensity remains uncertain. In this study, we investigate the impact of hypoxia on in-field and out-of-field radio-sensitivities using two types of cancer cells. These in vitro measurements indicate that hypoxia apparently impacts out-of-field cells, although the OER values in out-of-field cells were smaller compared to those for in-field and uniformly irradiated cells. These decreased radio-sensitivities of out-of-field cells were shown as a consistent tendency for both DSB and cell death endpoints, suggesting that radiation-induced intercellular communication is of importance in treatment planning with intensity-modulated radiotherapy.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakamura, Rui*; Naijo, Shingo*; Date, Hiroyuki*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 65(9), p.095006_1 - 095006_12, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.20(Engineering, Biomedical)Radio-resistance induced under low oxygen pressure plays an important role in malignant progression in fractionated radiotherapy. For the general approach to predict cell killing under hypoxia, cell-killing models (e.g., the Linear-Quadratic model) have to be fitted to  experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the
experimental survival data for both normoxia and hypoxia to obtain the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). However, model parameters for every oxygen condition needs to be considered by model-fitting approaches. This is inefficient for fractionated irradiation planning. Here, we present an efficient model for fractionated radiotherapy the integrated microdosimetric-kinetic model including cell-cycle distribution and the OER at DNA double-strand break endpoint. The cell survival curves described by this model can reproduce the  experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER
experimental survival data for both acute and chronic low oxygen concentrations. The OER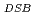 used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.
used for calculating cell survival agrees well with experimental DSB ratio of normoxia to hypoxia. This work provides biological effective dose (BED) under various oxygen conditions including its uncertainty, which can contribute to creating fractionated regimens for multi-fractionated radiotherapy. If the oxygen concentration in a tumor can be quantified by medical imaging, the present model will make it possible to estimate the cell-killing and BED under hypoxia in more realistic intravital situations.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Yoshii, Yuji*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Naijo, Shingo*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Applied Physics, 126(12), p.124701_1 - 124701_8, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.58(Physics, Applied)Biological effects after ionizing radiation exposure arise from initial DNA strand breaks. DNA damage can be estimated from the simulation with both track structure analysis and diffusion of free radicals; however, the simulation is a time-consuming process. In this study, we present a simple model for estimating yields of strand breaks based only on spatial patterns of inelastic interactions (i.e., ionization and electronic excitation) generated by electrons, which are evaluated by PHITS code without considering the production and diffusion of free radicals. In this model, the number of events per track and that of the two events pair within 3.4 nm (corresponding to 10 base pair) were stochastically sampled for calculating SSB and DSB yields, respectively. The calculated results agreed well with other simulations and experimental data on DSB yield and yield ratio of DSB/SSB for the exposure to mono-energetic electrons. The present model also can demonstrate the relative biological effectiveness at the DSB endpoint for various photon exposures. This study indicated that the spatial pattern of inelastic events composed of ionization and electronic excitation is sufficient to obtain the impact of electrons on initial induction to DNA strand break.
Wakai, Takashi; Onizawa, Takashi; Kato, Takehiko*; Date, Shingo*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Ando, Masanori; Hirose, Yuichi*; Date, Shingo*; Watanabe, Sota*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*; Kawasaki, Nobuchika
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 134(6), p.061403_1 - 061403_12, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.91(Engineering, Mechanical)To verify the methods of estimating strain range for discontinues structures, low cycle fatigue tests were carried out with notched specimens. All the specimens were made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo. Displacement control fatigue tests and thermal fatigue tests were performed by ordinary uni-axial push pull test machine and equipment generating the thermal gradient in the notched plate by induction heating. Elastic and inelastic finite element analysis were also performed to estimate strain range for predicting fatigue life. Then these predictions were compared with the test results. Several methods such as stress reduction locus (SRL) method, simple elastic follow-up (SEF) method, Neuber's law and the procedures employed by elevated temperature design codes were applied. Through these comparisons, the applicability and conservativeness of these strain range estimation methods are discussed.
Ando, Masanori; Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Date, Shingo*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*
Zairyo, 61(4), p.377 - 384, 2012/04
The effect of ratcheting deformation and pre-strain on fatigue and creep-fatigue life in Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel was investigated. Uni-axial fatigue and creep-fatigue tests with pre-strain and progressive strain were performed to evaluate the effect of pre-strain and ratcheting strain on the failure cycle. In the fatigue tests with pre-strain, failure lives were not declined. In the fatigue tests with progressive strain, slight reductions of failure lives were observed, however, they were within a factor of 1.5 of the failure life in normal fatigue test. In the creep-fatigue tests with progressive strain, the same conclusion of the fatigue tests was obtained. In both kinds of tests, maximum mean stresses during the tests were insignificant and/or generated in early cycle in the tests, and this character is considered as a reason of that the effect of ratcheting deformation on the fatigue and creep-fatigue lives are insignificant.
Nagae, Yuji; Enuma, Yasuhiro*; Oshikiri, Masato*; Date, Shingo*; Toyoshi, Akira*; Aizawa, Taiki*; Koyama, Yoichi*; Yanagisawa, Yusuke*
Tainetsu Kinzoku Zairyo Dai-123-Iinkai Kenkyu Hokoku, 52(2), p.161 - 169, 2011/07
no abstracts in English
Wakai, Takashi; Nagae, Yuji; Takaya, Shigeru; Obara, Satoshi; Date, Shingo*; Yamamoto, Kenji*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Tainetsu Kinzoku Zairyo Dai-123-Iinkai Kenkyu Hokoku, 52(2), p.147 - 159, 2011/07
By employing high-Cr ferritic steels to the structural materials for JSFR, a compact plant designing can be achieved. It contributes to reduce the construction cost and to enhance the freedom of designing. Among the high-Cr ferritic steels, modified 9Cr-1Mo steel (compatible to ASTM A335 P91) is a candidate of the structural material for the demonstration facility of JSFR, because the steel has superior microstructure stability at elevated temperature for long time. However, remarkable creep strength degradation has been observed in the welded joint of high-Cr ferritic steels, especially in long-term region. It is known as "Type-IV damage". In the elevated temperature designing for the fast reactors, such creep strength degradation must be taken into account properly. Therefore, the creep strength assessment procedure and the allowable stress for the welded joints made of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel have been proposed. In this study, (1) a series of creep rupture tests to verify the validity of the creep strength assessment procedure was performed. (2) Applicability of the creep strength assessment procedure to the creep fatigue strength assessment of the welded joints made of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel was investigated. (3) Metallurgical examinations of creep ruptured specimens were carried out to confirm the contribution of "Type-IV damage". As a result, it was demonstrated that the creep strength assessment procedure was validated using the long-term creep rupture test results less than 30,000h and that the creep strength assessment procedure was applicable to the creep-fatigue strength assessment based on some uniaxial creep-fatigue test results.
Ando, Masanori; Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Date, Shingo*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*
Dai-48-Kai Koon Kyodo Shimpojiumu Maezurishu, p.110 - 114, 2010/12
no abstracts in English
Wakai, Takashi; Nagae, Yuji; Onizawa, Takashi; Obara, Satoshi; Xu, Y.*; Otani, Tomomi*; Date, Shingo*; Asayama, Tai
Proceedings of 2010 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2010) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/07
Ando, Masanori; Hirose, Yuichi*; Date, Shingo*; Watanabe, Sota*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*; Kawasaki, Nobuchika
Proceedings of 2010 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2010) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/07
To verify the strain prediction method of discontinues structures at evaluated temperature, low cycle fatigue tests were carried out with notched specimens made of Mod.9Cr-1Mo. Deformation control fatigue tests and thermal fatigue tests were performed by ordinary uni-axial push-pull test machine and equipments generating the thermal gradient in the notched plate by induction heating. Crack initiation and propagation process during the fatigue test were observed by the digital micro-scope and replica method. Then the ranges of several strain predictions and estimations were compared with the test results. Stress Reduction Locus (SRL) method, simple elastic follow-up method, Neuber's rule method and the methods supplied by elevated temperature design standards were applied. Through these results, the applicability and conservativeness of these strain prediction and estimation methods is discussed.
Okajima, Satoshi; Date, Shingo*; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Kasahara, Naoto
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2009 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.537 - 538, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Date, Shingo*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Kasahara, Naoto
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2009 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.535 - 536, 2009/07
The effect of ratcheting strain on creep-fatigue strength was investigated in order to adjust the strain limit. Ratcheting creep-fatigue tests were conducted at 600  C with 1 hr hold time. Creep fatigue lives did not decrease when the accumulated strain was superimposed within 5%. Therefore the effect of ratcheting on creep-fatigue strength is negligible when accumulated strain exceeds 2%.
C with 1 hr hold time. Creep fatigue lives did not decrease when the accumulated strain was superimposed within 5%. Therefore the effect of ratcheting on creep-fatigue strength is negligible when accumulated strain exceeds 2%.
Wakai, Takashi; Sukekawa, Masayuki*; Date, Shingo*; Asayama, Tai; Aoto, Kazumi; Kubo, Shigenobu*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 85(6), p.352 - 359, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.12(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents the provisional material specification and characteristics of the high chromium (Cr) steel for the sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) in Japan and creep-fatigue assessment of the steel. Based on the mechanical test and metallurgical examination results, it is clarified that tungsten (W) should be diminished to achieve better ductility and toughness. Then the provisional specifications of the high Cr steel for SFR components are proposed. Material characteristics, e.g. cyclic stress-strain relationship and creep strain curve, are also presented based on the material test results. Using these characteristics, a creep-fatigue strength assessment of the steel was performed. Conservative predictions were obtained and it was clarified that such conservativeness were resulted from over estimation of creep damage caused by too large initial stress at the beginning of dwell. It can be pointed out there are some rooms for improvement in the assessment procedure.
Wakai, Takashi; Aoto, Kazumi; Sukekawa, Masayuki*; Date, Shingo*; Shibamoto, Hiroshi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 238(2), p.399 - 407, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents the establishment of the provisional specifications and material strength standard of the high chromium (Cr) steels for Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) components. For the improvement of toughness and ductility of the steels, a series of mechanical tests and metallurgical examinations are performed for several kinds of high Cr steels controlled the balance of tungsten (W) and molybdenum (Mo). In addition, the effects of heat treatment conditions on material properties are also investigated. Based on these results, it is revealed that W should be diminished to achieve better ductility and toughness and that it is difficult to improve the long term properties by changing heat treatment conditions. Then the provisional specifications of the high Cr steel for FBR components are given and the provisional material strength standard is proposed for the specifications of the steel. The standard is utilized in the study on the FBR plant design.
Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Sukekawa, Masayuki*; Nakayama, Yasunari*; Date, Shingo*; Otani, Tomomi*; Takahashi, Yukio*; Kasahara, Naoto; Shibamoto, Hiroshi*; Nagashima, Hideaki*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 238(2), p.347 - 352, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effect of ratcheting on fatigue strength was investigated in order to rationalize the strain limit as a design criterion of commercialized fast reactor systems. Ratcheting fatigue tests were conducted at 550 C. Duration of the ratchet straining was set for a certain number of strain cycles taking the loading condition of fast reactors into account, and the number of cycles for strain accumulation was defined as the ratchet-expired cycle. Fatigue lives decrease as the accumulated strain by ratcheting increases. Fatigue life reduction was negligible when the maximum mean stress was less than 25 MPa, corresponding to an accumulated strain of 2.2 percent. Accumulated strain is limited to 2 percent in the present design guidelines and this strain limit is considered effective to avoid reducing fatigue life by ratcheting. Micro-crack growth behaviors were also investigated in these tests in order to discuss the life reduction mechanisms in ratcheting conditions.
C. Duration of the ratchet straining was set for a certain number of strain cycles taking the loading condition of fast reactors into account, and the number of cycles for strain accumulation was defined as the ratchet-expired cycle. Fatigue lives decrease as the accumulated strain by ratcheting increases. Fatigue life reduction was negligible when the maximum mean stress was less than 25 MPa, corresponding to an accumulated strain of 2.2 percent. Accumulated strain is limited to 2 percent in the present design guidelines and this strain limit is considered effective to avoid reducing fatigue life by ratcheting. Micro-crack growth behaviors were also investigated in these tests in order to discuss the life reduction mechanisms in ratcheting conditions.
Wakai, Takashi; Aoto, Kazumi; Inoue, Kazuhiko; Sukekawa, Masayuki*; Date, Shingo*
Dai-30-Kai MPA Semina, 28 Pages, 2004/10
None
Nagae, Yuji; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Date, Shingo*; Aizawa, Taiki*; Yanagisawa, Yusuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ando, Masanori; Kanasaki, Hiroshi*; Date, Shingo*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Takasho, Hideki*; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki
no journal, ,
To assess the failure estimation methods, cyclic thermal loading tests of cylindrical models with thick part were performed. In the tests, crack initiation and propagation processes at stress concentration area were observed by replica method. Besides those, finite element analysis (FEA) was carried out to estimate the number of cycles to failure. The crack initiation life was in a good agreement with the FEA result by considering the short term compressive holding. Through these test and FEA results, fatigue and creep-fatigue life assessment methods of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel including evaluation of cyclic thermal loading, short term compressive holding and failure criterion, were discussed.
Wakai, Takashi; Isobe, Nobuhiro*; Date, Shingo*; Asayama, Tai; Kubo, Shigenobu*
no journal, ,