Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Domal, S. J.*; Correa-Alfonso, C. M.*; Paulbeck, C. J.*; Griffin, K. T.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Funamoto, Sachiyo*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; Endo, Akira; Hertel, N. E.*; et al.
Health Physics, 125(4), p.245 - 259, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The RERF Working Group on Organ Dose (WGOD) has established the J45 (Japan 1945) series of high-resolution voxel phantoms, which were derived from the UF/NCI series of hybrid phantoms and scaled to match mid-1940s Japanese body morphometries. In this present study, we present the J45 pregnant female phantoms in both a kneeling and lying posture, and assess the dosimetric impact of these more anatomically realistic survivor models in comparisons to current organ doses given by the DS02 system. For the kneeling phantoms facing the bomb hypocenter, organ doses from bomb source photon spectra were shown to be overestimated by the DS02 system by up to a factor of 1.45 for certain fetal organs and up to a factor of 1.17 for maternal organs. For lying phantoms with their feet in the direction of the hypocenter, fetal organ doses from bomb source photon spectra were underestimated by the DS02 system by factors as low as 0.77 while maternal organ doses were overestimated by up to a factor of 1.38. Results from this study highlight the degree to which the existing DS02 system can differ from organ dosimetry based upon 3D radiation transport simulations using more anatomically realistic models of those survivors exposed during pregnancy while in a kneeling or lying position.
Griffin, K. T.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Funamoto, Sachiyo*; Chizhov, K.*; Domal, S.*; Paulbeck, C.*; Bolch, W.*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; Endo, Akira; et al.
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 61(1), p.73 - 86, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.90(Biology)To evaluate the potential dosimetry improvements that would arise from their use in a Dosimetry System (DS) at RERF, we have evaluated organ doses in the J45 series using the environmental fluence data for twenty generalized survivor scenarios pulled directly from the current DS. The energy- and angle-dependent gamma and neutron fluences were converted to a phase space source term for use in MCNP6, a modern radiation transport code. Overall, the updated phantom series would be expected to provide dose improvements to several important organs, including the active marrow, colon, and stomach wall (up to 20%, 20%, and 15% impact on total dose, respectively). The impacts on dosimetry were especially significant for neutron dose estimates (up to a two-fold difference) and within organs which were unavailable in the previous phantom series, such as the skin, esophagus, and prostate.
Kofler, C.*; Domal, S.*; Satoh, Daiki; Dewji, S.*; Eckerman, K.*; Bolch, W. E.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 58(4), p.477 - 492, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.51(Biology)In the current radiation protection system, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) recommends to use the effective dose for dose estimation. The effective dose is derived from the organ doses calculated using the computational human models (phantoms) defined by the ICRP to represent the reference person at each age. Questions arise, however, among the general public regarding the accuracy of organ and effective dose estimates based upon reference phantom methodologies, especially for those individuals with heights and/or weights that differ from the nearest age-matched reference person. In this paper, the detriment-weighted dose was defined for non-reference persons as the same manner to the effective dose for reference person. The doses were calculated for external exposure to radionuclides in a soil using 351-member phantom library based on the data of the U.S. population reported by the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics. The results for 33 nuclides were listed in the paper. Especially, for the environmental relevant radionuclides of 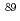 Sr,
Sr,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs, and
Cs, and  I, the detriment-weighted dose of 1-year-old phantom agreed with the effective dose within 5%, while the range of percent differences in these two quantities increased with increases the body size and age, e.g. +15% to -40% for adults.
I, the detriment-weighted dose of 1-year-old phantom agreed with the effective dose within 5%, while the range of percent differences in these two quantities increased with increases the body size and age, e.g. +15% to -40% for adults.