Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:94.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ida, Katsumi*; Dong, J. Q.*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kwon, J. M.*; Diamond, P. H.*
Nuclear Fusion, 52(2), p.027001_1 - 027001_10, 2012/02
This conference report summarizes the contributions to, and discussions at, the 1st Asia-Pacific Transport Working Group Meeting held in Toki, Japan, on 14-17 June 2011. The topics of the meeting were organized under four main headings: momentum transport, non-locality in transport, edge turbulence and L to H transition and 3D effects on transport physics. The events which initiated this meeting are also described in this report.
Chen, L.-M.; Kando, Masaki; Xu, M. H.*; Li, Y.-T.*; Koga, J. K.; Chen, M.*; Xu, H.*; Yuan, X.-H.*; Dong, Q. L.*; Sheng, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 100(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_4, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:92.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed the increase of the K- X-ray conversion efficiency (hK) produced by a 60 fs frequency doubled high contrast laser pulse focused on Cu foil, compared to the case of the fundamental laser pulse. hK shows a strong dependence on the nonlinearly skewed shape of the laser pulse. It reaches a maximum for a 100 fs negatively skewed pulse. The electron spectrum shaping contributes to the enhancement of hK. Simulations demonstrate that high contrast lasers are an effective tool for optimizing the X-ray emission, via the enhanced Vacuum Heating mechanism.
X-ray conversion efficiency (hK) produced by a 60 fs frequency doubled high contrast laser pulse focused on Cu foil, compared to the case of the fundamental laser pulse. hK shows a strong dependence on the nonlinearly skewed shape of the laser pulse. It reaches a maximum for a 100 fs negatively skewed pulse. The electron spectrum shaping contributes to the enhancement of hK. Simulations demonstrate that high contrast lasers are an effective tool for optimizing the X-ray emission, via the enhanced Vacuum Heating mechanism.
Fujisawa, Akihide*; Ido, Takeshi*; Shimizu, Akihiro*; Okamura, Shoichi*; Matsuoka, Keisuke*; Iguchi, Harukazu*; Hamada, Yasuji*; Nakano, Haruhisa*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Ito, Kimitaka*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(10), p.S718 - S726, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:106 Percentile:95.20(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Present status of experiments on zonal flows is overviewed. Innovative use of modern diagnostics has revealed the existence of zonal flows, their spatio-temporal characteristics, their relationship with turbulence, and their effects on confinement. Particularly a number of observations have been accumulated on the oscillatory branch of the zonal flow, dubbed as geodesic acoustic modes suggesting necessity of theories to give their proper description. Several new methods have elucidated the zonal flow generation processes from the turbulence. Further investigation of relationship between the zonal flows and confinement is strongly encouraged as cross-device activity.
Dong, M. A.*; Bufford, J. L.*; Ono, Yutaka; Church, K.*; Dau, M. Q.*; Michels, K.*; Haughton, M.*; Tallman, G.*
Plant Physiology, 145(2), p.367 - 377, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.90(Plant Sciences)Cultured guard cell protoplasts (GCP) of Nicotiana glauca, tree tobacco, comprise a novel system for investigating the cell signaling mechanisms that lead to acquired thermotolerance and thermoinhibition. At 32  C in a medium containing an auxin and a cytokinin, GCP expand, regenerate cell walls, dedifferentiate, and divide. At 38
C in a medium containing an auxin and a cytokinin, GCP expand, regenerate cell walls, dedifferentiate, and divide. At 38  C, GCP acquire thermotolerance, but their expansion is limited and they neither regenerate walls nor re-enter the cell cycle. Protoplasts were transformed with the fusion gene of BA auxin-responsive promoter and green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. Heat suppressed auxin-mediated activation of BA. Heat-stressed cells accumulate reactive oxygen species, and H
C, GCP acquire thermotolerance, but their expansion is limited and they neither regenerate walls nor re-enter the cell cycle. Protoplasts were transformed with the fusion gene of BA auxin-responsive promoter and green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. Heat suppressed auxin-mediated activation of BA. Heat-stressed cells accumulate reactive oxygen species, and H O
O suppresses auxin-responsive promoter activation. H
suppresses auxin-responsive promoter activation. H O
O did not suppress BA activation at 32
did not suppress BA activation at 32  C, nor did superoxide and H
C, nor did superoxide and H O
O scavengers prevent BA suppression at 38
scavengers prevent BA suppression at 38  C.
C.
Fujisawa, Akihide*; Ido, Takeshi*; Shimizu, Akihiro*; Okamura, Shoichi*; Matsuoka, Keisuke*; Hamada, Yasuji*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; Nakano, Haruhisa*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2007/03
Present status of experiments on zonal flows is overviewed. Innovative use of traditional and modern diagnostics has revealed unambiguously the existense of the zonal flows, their spatio-temporal caracteristics, their relationship with turbulence, and their effects on confinement. Particularly, a number of observations have been accumulated on the oscillatory branch of zonal flows, dubbed geodesic acoustic modes, suggesting necessity of theories to give their proper description. Furthur investigation of relationship between zonal flows and confinement is strongly encouraged as cross-device activity.
Li, J.*; Uzawa, Ken*; Lin, Z.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsumoto, Taro; Dong, J. Q.*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
The dynamics of secondary, anisotropic coherent structures behaving as a stationary wave, including zonal/mean flows, streamers and low-frequency long wavelength fluctuations, in multiple-scale turbulence in tokamak plasmas is investigated by performing 3D simulations as well as 2D modeling analyses. The role of nonlinear mode coupling is specifically discussed as a ubiquitous principal interaction mechanism in the dual processes of the generation and back-action of secondary structures on ITG and ETG turbulence. Here two new results are evidently presented on the importance of the mode coupling interaction: (1) While secondary zonal flows and long wavelength modes are generated through nonlinear mode coupling, the same back-action process can deform the spectral distribution in inertia range from the power-law scaling into an exponential-law dependence. The turbulence may be reduced due to the local and/or nonlocal free energy transfer to stable region. (2) Streamer-like long wavelength fluctuations driven by the most unstable ETG modes, can saturate slab ETG turbulence through producing a 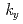 -mode coupling that corresponds to the toroidal mode coupling in tokamak plasma, suggesting a low ETG fluctuation level and electron transport. Furthermore, the effect of ITG generated zonal flows regarded as a wave-type mean flow on the generation of zonal flows in ETG turbulence is also discussed with an emphasis on the role of nonlinear mode coupling.
-mode coupling that corresponds to the toroidal mode coupling in tokamak plasma, suggesting a low ETG fluctuation level and electron transport. Furthermore, the effect of ITG generated zonal flows regarded as a wave-type mean flow on the generation of zonal flows in ETG turbulence is also discussed with an emphasis on the role of nonlinear mode coupling.
Li, J.*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsumoto, Taro; Dong, J. Q.*
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1173 - 1177, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dynamics of secondary fluctuations with poloidal long wavelength and low frequency in electron-temperature-gradient (ETG) turbulence saturation is considered in sheared slab geometry. A simplified modeling analysis shows that this kind of large-scale structure including streamers may saturate primary ETG instability through poloidal mode coupling. Spectral analyses in three-dimensional ETG simulations clearly exhibit the secondary excitation and the probable relevancy to ETG saturation. The result may implicate a lower fluctuation level in ETG turbulence.
 source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic Engineering
source from high contrast fs laser plasmas in regime of Relativistic EngineeringChen, L.-M.; Koga, J. K.; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Xu, M. H.*; Li, Y.-T.*; Dong, Q. L.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Interaction of intense Ti: Sapphire laser with Cu foil targets has been studied by measuring hard X-ray generation. Hard X-ray spectroscopy and K X-ray conversion efficiency (
X-ray conversion efficiency (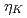 ) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs
) from Cu plasma have been studied as a function of laser intensity via pulse duration scan (60 fs  600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ
600 fs), laser pulse energy scan (60 mJ  600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I
600 mJ) and target displacement scan from best focus. For intensity I 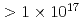 W/cm
W/cm , the Cu
, the Cu 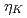 keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of
keep on increasing to reach a maximum value of 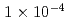 at an intensity
at an intensity 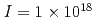 W/cm
W/cm . The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10
. The focusing is varied widely to give a range of intensities from 10 W/cm
W/cm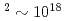 W/cm
W/cm . Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to
. Comparing to a recent publication, two individual emission peaks are obtained, one is at best focal spot and the other is at larger target offset corresponding to 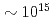 W/cm
W/cm . Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows
. Each peak is corresponding to different energy absorption mechanism. In addition, when we introduce slightly detuning of compressor gratings at the best focal condition, it shows 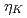 generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach
generated by negatively skewed 100 fs pulse width laser irradiation reach 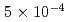 and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
and almost 7 times greater than the case of positively skewed pulse. Vacuum Heating is greatly stimulated in this case and preciously control of pre-plasma is the key factor in tuning control of X-ray emission in relativistic fs regime.
Dong, M.*; Bufford, J. L.*; Ono, Yutaka; Church, K.*; Dau, M. Q.*; Michels, K.*; Haughton, M.*; Tallman, G.*
no journal, ,
At 32 C in media containing an auxin and a cytokinin, cultured guard cell protoplasts (GCP) of Nicotiana glauca (Graham), expand, regenerate cell walls, dedifferentiate, and divide. At 38
C in media containing an auxin and a cytokinin, cultured guard cell protoplasts (GCP) of Nicotiana glauca (Graham), expand, regenerate cell walls, dedifferentiate, and divide. At 38 C, GCP acquire thermotolerance within 24 h but their expansion is limited and they neither regenerate walls nor re-enter the cell cycle. Protoplasts were transformed with BA-mgfp5-ER. After 21 h in media with NAA, 49.0% and 7.9% of GCP transformed with BA-mgfp5-ER expressed GFP at 32
C, GCP acquire thermotolerance within 24 h but their expansion is limited and they neither regenerate walls nor re-enter the cell cycle. Protoplasts were transformed with BA-mgfp5-ER. After 21 h in media with NAA, 49.0% and 7.9% of GCP transformed with BA-mgfp5-ER expressed GFP at 32 C and 38
C and 38 C, respectively. Expression at 38
C, respectively. Expression at 38 C was not increased by incubating GCP for 48 h or by increasing NAA concentrations 20X. Tiron and N-acetylcysteine, superoxide and H
C was not increased by incubating GCP for 48 h or by increasing NAA concentrations 20X. Tiron and N-acetylcysteine, superoxide and H O
O scavengers, respectively, did not prevent BA suppression at 38
scavengers, respectively, did not prevent BA suppression at 38 C nor did H
C nor did H O
O suppress BA activation at 32
suppress BA activation at 32 C.
C.