Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Matsui, Ryutaro*; et al.
no journal, ,
In laser-driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, generated ions can be assigned to two components. One is a low energy component produced by Coulomb explosions of clusters. The other is a high energy component produced by a magnetic vortex acceleration mechanism. In the past studies, high energy ions were mainly measured by stacked CR-39 detectors to obtain the energy spectrum. In the present study, to reveal the acceleration mechanism, a spatial distribution of MeV ions was measured by CR-39 detectors which were encircled equidistant from the laser focus spot. The etch pit distribution on the CR-39 suggests that the acceleration mechanism cannot be explained only by Coulomb explosion mechanism, but by other complicated mechanisms.
Kanasaki, Masato*; Jinno, Satoshi; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Matsui, Ryutaro*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Doria, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In the laser-driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, in addition to the isotropic low energy component ( several MeV/n) due to Coulomb explosion of clusters, the directional high energy component (
several MeV/n) due to Coulomb explosion of clusters, the directional high energy component (
 several MeV/n) due to the magnetic vortex acceleration have been observed. In this study, we discuss an ion acceleration mechanism based on the recent measurement of the spatial and energy distributions of the lower energy component.
several MeV/n) due to the magnetic vortex acceleration have been observed. In this study, we discuss an ion acceleration mechanism based on the recent measurement of the spatial and energy distributions of the lower energy component.
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; Matsui, Ryutaro; et al.
no journal, ,
In the laser-driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas target, the acceleration mechanism consists of different processes such as, (a) acceleration of ions due to Coulomb explosion of individual clusters, (b) compression and acceleration of background gas ions due to the Coulomb explosion of clusters, (c) magnetic vortex generation and associated pinching near the rear surface, and (d) sheath acceleration at the interface between the medium and vacuum. To reveal the synergetic interplay between the processes (a) and (b), we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters embedded in background H
clusters embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser. By a careful analysis of CR-39, we have found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon ions are 1.5 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters can be discussed with the help from numerical simulations.
gas with the J-KAREN laser. By a careful analysis of CR-39, we have found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon ions are 1.5 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters can be discussed with the help from numerical simulations.
Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; et al.
no journal, ,
In this study, to understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters embedded in background H
clusters embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser at JAEA-KPSI. As a result, energy spectra for protons (from background gas) and carbon/oxygen ions (from clusters) are obtained separately for the first time. We found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are
gas with the J-KAREN laser at JAEA-KPSI. As a result, energy spectra for protons (from background gas) and carbon/oxygen ions (from clusters) are obtained separately for the first time. We found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are  1.5 MeV and
1.5 MeV and  1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles (EPIC3D).
1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles (EPIC3D).
Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; et al.
no journal, ,
In the laser-driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas target, the acceleration mechanism consists of different processes such as, (a) acceleration of ions due to Coulomb explosion of individual clusters, (b) compression and acceleration of background gas ions due to the Coulomb explosion of clusters, (c) magnetic vortex generation and associated pinching near the rear surface, and (d) sheath acceleration at the interface between the medium and vacuum. To understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters embedded in background H
clusters embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of CR-39, energy spectra for protons (from background gas) and carbon/oxygen ions (from clusters) are obtained separately for the first time. We found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are
gas with the J-KAREN laser at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of CR-39, energy spectra for protons (from background gas) and carbon/oxygen ions (from clusters) are obtained separately for the first time. We found that the maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are  1.5 MeV and
1.5 MeV and  1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles (EPIC3D).
1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles (EPIC3D).
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; Matsui, Ryutaro; et al.
no journal, ,
In the previous laser-driven ion acceleration experiment using cluster-gas target, we have only focused on the high energy ions with energies of multi-tens of MeV. In order to reveal synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas ions, we have measured protons (background gas ions) separately from carbon and oxygen ions (clusters) by using magnetic spectrometer with CR-39 track detectors. We have found that the number of carbon and oxygen ions decrease sharply at 1 MeV/n. On the other hand, the protons show the Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters can be discussed with the help from numerical simulations.
Fukuda, Yuji; Marocchino, A.*; Romagnani, L.*; Levy, A.*; Jinno, Satoshi*; Lancia, L.*; Ravasio, A.*; Schiavi, A.*; Atzeni, S.*; Doria, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated the dynamics of laser-produced blast waves in cluster targets by means of the combined use of two different diagnostics: optical probing (interferometry and Schlieren imaging) and proton probing. Interferometry and Schlieren imaging provided a spatially and temporally resolved mapping of the electron density and density gradient distributions. In addition, spatially and time-resolved proton probing provided mapping of the electric fields and charge density distributions in the plasma in the initial phase of plasma expansion and shock formation.
Fukuda, Yuji; Marocchino, A.*; Romagnani, L.*; Levy, A.*; Jinno, Satoshi*; Lancia, L.*; Ravasio, A.*; Schiavi, A.*; Atzeni, S.*; Doria, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In the ELFIE laser facility at LULI, the dynamics of laser-produced blast waves in cluster targets has been investigated by means of the optical probing (interferometry and Schlieren imaging) and the proton probing. Interferometry and Schlieren imaging have provided a spatially and temporally resolved mapping of the electron density and density gradient distributions. In addition, spatially and time-resolved proton probing has provided mapping of the electric fields and charge density distributions in the plasma in the initial phase of plasma expansion and shock formation.
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; Matsui, Ryutaro; et al.
no journal, ,
In the laser-driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, consisting of a few hundreds nanometer sized clusters and the background gas, the energy spectrum of accelerated ions has two components. The lower energy component is produced by the Coulomb explosions of clusters and the higher one is accelerated by electric fields created by the magnetic vortex. In this study, in order to reveal the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions, we have measured the ion energy spectra for the background gas and for clusters separately. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations.
Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato*; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori; Pikuz, T. A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, an energy spectrum of carbon/oxygen ions from the CO clusters and that of protons from the background hydrogen gas are measured separately at 1
clusters and that of protons from the background hydrogen gas are measured separately at 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm with a careful analysis of etch pit structures on CR-39. The maximum energies of carbon/oxygen ions and protons are determined as 1.1 MeV/n and 1.6 MeV, respectively. Moreover, we present a development of submicron-size hydrogen cluster targets using a cryogenic conical nozzle and their characterization with the Mie scattering method. Above 10
with a careful analysis of etch pit structures on CR-39. The maximum energies of carbon/oxygen ions and protons are determined as 1.1 MeV/n and 1.6 MeV, respectively. Moreover, we present a development of submicron-size hydrogen cluster targets using a cryogenic conical nozzle and their characterization with the Mie scattering method. Above 10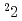 W/cm
W/cm , the anisotropic Coulomb explosion of submicron-size hydrogen clusters could produce directional proton beams with energies of several tens of MeV, quite advantageous to the future applications, since they are inherently impurity-free, high rep.rate, and robust.
, the anisotropic Coulomb explosion of submicron-size hydrogen clusters could produce directional proton beams with energies of several tens of MeV, quite advantageous to the future applications, since they are inherently impurity-free, high rep.rate, and robust.
Fukuda, Yuji; Marocchino, A.*; Romagnani, L.*; Levy, A.*; Jinno, Satoshi*; Lancia, L.*; Ravasio, A.*; Doria, D.*; Borghesi, M.*
no journal, ,
The dynamics of laser-produced blast waves in cluster targets has been investigated by means of the optical probing (interferometry and Schlieren imaging) and the proton probing at the ELFIE laser facility in LULI (2J, 600fs). The Interferometry and Schlieren imagings have provided a spatially and temporally resolved mapping of the electron density and density gradient distributions. In addition, spatially and time-resolved proton probing has provided mapping of the electric fields and charge density distributions in the plasma in the initial phase of plasma expansion and shock formation.