Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Yokoi, Naoto*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Suzuki, Jun*; Imai, Masaki; Sato, Masahiro*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji*
Physical Review Letters, 134(13), p.130603_1 - 130603_5, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:93.17(Physics, Applied)Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 409, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Miyagawa, Reina*; Kamibayashi, Daisuke*; Nakamura, Hirotaka*; Hashida, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Somekawa, Toshihiro*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Ogura, Hiroyuki*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.20955_1 - 20955_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We evaluated Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structure (LIPSS) crystal structures using the stress imaging station at BL22XU of JAEA-BL on SPring-8. Crystallization of LIPPS was used different two types laser these are Ti:Sapphire laser (wavelength: 800 nm) and MIR-FEL (mid-infrared free electron laser, wavelength 11.4  m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20
m). These lasers are different in the laser pulse structure and the wavelength. We investigated on the effects of formed LIPSS crystallization using different kind of laser. Measured synchrotron X-ray energy is 30 keV and beam size is 20  m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
m. Detector of diffracted X-ray is two-dimensional detector (PILATUS300K, DECTRIS). LIPSS formed using Ti:Sapphire laser has deformed structure with good crystallinity. LIPSS formed using MIR-FEL has dislocation or fault without structural stress. These results show depending on select of laser forming LIPPS structure. These information becomes important a point of the functional application of LIPSS.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.129 - 133, 2022/11
For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors composed of the NE213 liquid organic scintillators and photomultiplier tubes, which were connected to a multi-channel digitizer mounted with a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination applying the gate integration method to the FPGA. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics.
Chudo, Hiroyuki; Imai, Masaki; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(8), p.081003_1 - 081003_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 103(17), p.174308_1 - 174308_10, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru*; Harii, Kazuya*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Express, 13(10), p.109102_1 - 109102_2, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.14(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Somekawa, Hidetoshi*; Basha, D. A.*; Singh, A.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Watanabe, Hiroyuki*
Philosophical Magazine Letters, 100(10), p.494 - 505, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The damping capacity in the vicinity of {10 2} twin boundaries was measured before and after annealing by nano-dynamic mechanical analysis. The subsequent annealing process led to a lower damping capacity in all magnesium binary alloys, which was in contrast to the results in pure magnesium. This is on account of the segregation of solute atoms in incoherent twin boundaries. The alloying elements, which have the characteristic of a low segregation energy for twin boundaries, effectively prevents the damping capacity degradation.
2} twin boundaries was measured before and after annealing by nano-dynamic mechanical analysis. The subsequent annealing process led to a lower damping capacity in all magnesium binary alloys, which was in contrast to the results in pure magnesium. This is on account of the segregation of solute atoms in incoherent twin boundaries. The alloying elements, which have the characteristic of a low segregation energy for twin boundaries, effectively prevents the damping capacity degradation.
Imai, Masaki; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 102(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_5, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Takahashi, Ryo*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Matsuo, Mamoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Onuma, Yuichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3009_1 - 3009_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences) bound state in the
bound state in the  C
C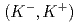 reaction at 1.8 GeV/
reaction at 1.8 GeV/
Nagae, Tomofumi*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji; Nanamura, Takuya*; Naruki, Megumi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 2130, p.020015_1 - 020015_9, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:97.58(Physics, Nuclear)Harii, Kazuya; Seo, Y.-J.*; Tsutsumi, Yasumasa*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Shiomi, Yuki*; Ono, Takahito*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2616_1 - 2616_5, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:80.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Dy
Dy Fe
Fe O
O detected by the Barnett effect
detected by the Barnett effectImai, Masaki; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Matsuo, Mamoru; Onuma, Yuichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 114(16), p.162402_1 - 162402_4, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:70.84(Physics, Applied)Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Ashikaga, Sakiko; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji*; Nanamura, Takuya; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.021D02_1 - 021D02_11, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:83.20(Physics, Multidisciplinary)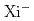 hyperon capture at rest in nuclear emulsion
hyperon capture at rest in nuclear emulsionTheint, A. M. M.*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Yoshida, Junya; 7 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.021D01_1 - 021D01_10, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kimbara, Shinji*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Yoshida, Junya; 12 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(1), p.011H01_1 - 011H01_9, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A development has been achieved in the identification method of the charges 1 to 5 of nuclides from the decay of double hypernuclei to be uniquely recognized by their nuclear species. The method is basically the measurement of track volume by the widths, depths, and angles of tracks of exposed nuclei of  H,
H,  He,
He,  Li,
Li,  Be, and
Be, and  B in nuclear emulsion at Riken Projectile-fragment Separator of RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. After their calibration by
B in nuclear emulsion at Riken Projectile-fragment Separator of RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. After their calibration by  particles, we obtained a quadric function to present a unified recognition of tracks with volume ratios of five nuclei to the
particles, we obtained a quadric function to present a unified recognition of tracks with volume ratios of five nuclei to the  particles. The function in the emulsion has been applied to a candidate event of a
particles. The function in the emulsion has been applied to a candidate event of a  hypernucleus for identification of the production and decay processes. We succeeded in recognizing a daughter nuclear fragment of a single-
hypernucleus for identification of the production and decay processes. We succeeded in recognizing a daughter nuclear fragment of a single- hypernucleus as
hypernucleus as  He with a likelihood ratio of 0.9; the process was then uniquely identified as
He with a likelihood ratio of 0.9; the process was then uniquely identified as 
 +
+  N
N 
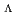
 Be +
Be + 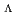
 He +
He +  .
.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:69.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.