Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
 1
1 -type AlNi
-type AlNi alloy at high pressure and temperature
alloy at high pressure and temperatureEndo, Naruki*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 645(Suppl.1), p.S61 - S63, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Endo, Naruki*; Saita, Itoko*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40(8), p.3283 - 3287, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:36.94(Chemistry, Physical)Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.5063_1 - 5063_6, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:87.34(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Iron hydride FeH , is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD
, is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD . We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
. We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
 FeH
FeH ; Iron-containing complex hydride with high gravimetric hydrogen density
; Iron-containing complex hydride with high gravimetric hydrogen densitySaito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Iijima, Yuki*; Endo, Naruki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Orimo, Shinichi*
APL Materials (Internet), 2(7), p.076103_1 - 076103_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.14(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Endo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
Materia, 53(3), p.94 - 99, 2014/03
no abstracts in English
 CuH
CuH ; A New class of interstitial aluminum-based alloy hydride
; A New class of interstitial aluminum-based alloy hydrideSaito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Endo, Naruki; Machida, Akihiko; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
APL Materials (Internet), 1(3), p.032113_1 - 032113_7, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Endo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38(16), p.6726 - 6729, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:55.54(Chemistry, Physical) O
O
Yoshii, Kenji; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Matsumoto, Keisuke*; Mori, Shigeo*; Endo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Kambe, Takashi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 428, p.012032_1 - 012032_5, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:96.91(Chemistry, Applied)We have investigated a single crystal of multiferroic YbFe O
O . Its magnetic transition temperature was 250 K. The magnetization along the c-axis was much larger than that within the ab plane, indicating the Ising character of this system. The field-cooled magnetization became negative below 10 K. This was explained in terms of an antiparallel coupling between Yb and Fe moments. Magnetocaloric effects were also observed. The change of entropy was found to show a broad peak with a width of 100 K, which is favorable to application.
. Its magnetic transition temperature was 250 K. The magnetization along the c-axis was much larger than that within the ab plane, indicating the Ising character of this system. The field-cooled magnetization became negative below 10 K. This was explained in terms of an antiparallel coupling between Yb and Fe moments. Magnetocaloric effects were also observed. The change of entropy was found to show a broad peak with a width of 100 K, which is favorable to application.
 ;
;  synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction study
synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction studySato, Ryutaro*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 102(9), p.091901_1 - 091901_4, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:78.27(Physics, Applied) and its synthesis; Mechanism for formation of metallic perovskite
and its synthesis; Mechanism for formation of metallic perovskiteTakagi, Shigeyuki*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Sato, Ryutaro*; Ikeshoji, Tamio*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Miwa, Kazutoshi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 87(12), p.125134_1 - 125134_6, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:65.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) at high pressures and high temperatures
at high pressures and high temperaturesEndo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 546, p.270 - 274, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.91(Chemistry, Physical)Endo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cu alloy under high pressure and temperature
Cu alloy under high pressure and temperatureSaito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Iron hydride FeH , is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. Three hydride phases, bcc-FeH
, is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. Three hydride phases, bcc-FeH (
(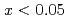 ), dhcp-FeH
), dhcp-FeH (
(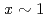 ), and fcc-FeH
), and fcc-FeH (
(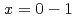 ) were confirmed at 300-2000 K and 0-20 GPa. In situ neutron diffraction measurement on their deutrides have not been reported yet. A high pressure neutron diffractometor, PLANET, constructed at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC, enables us to perform in situ neutoron diffraction measurements on deuterization process of metals at high pressure and high temperature. With PLANET, the deuteration process of iron was investigated at a pressure of about 7 GPa and temperatures up to about 1000 K. This in situ measurement was successfully made using a deuterization reaction cell developed for neutron diffraction measurement. We observed the bcc-fcc transition of pure iron around 800 K and successive deuterization of fcc-Fe around 870 K.
) were confirmed at 300-2000 K and 0-20 GPa. In situ neutron diffraction measurement on their deutrides have not been reported yet. A high pressure neutron diffractometor, PLANET, constructed at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC, enables us to perform in situ neutoron diffraction measurements on deuterization process of metals at high pressure and high temperature. With PLANET, the deuteration process of iron was investigated at a pressure of about 7 GPa and temperatures up to about 1000 K. This in situ measurement was successfully made using a deuterization reaction cell developed for neutron diffraction measurement. We observed the bcc-fcc transition of pure iron around 800 K and successive deuterization of fcc-Fe around 870 K.
 FeH
FeH at high pressures and high temperatures
at high pressures and high temperaturesSaito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Iijima, Yuki*; Endo, Naruki; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 at high pressures and high temperatures
at high pressures and high temperaturesEndo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
The phase diagram and the equation of state of TiH at high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) were carefully investigated in the present study using by using an
at high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) were carefully investigated in the present study using by using an  synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurement for new titanium alloys hydrides development. Summary of the study is as follows: At ambient conditions, the TiH
synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurement for new titanium alloys hydrides development. Summary of the study is as follows: At ambient conditions, the TiH had a face-centered cubic crystal structure (FCC). At high pressure, TiH
had a face-centered cubic crystal structure (FCC). At high pressure, TiH crystallized in a FCC structure above 200
crystallized in a FCC structure above 200 C. In lower temperature range, the TiH
C. In lower temperature range, the TiH structure was not only a FCC structure but also a tetragonal structure. Since the transformation temperature of TiH
structure was not only a FCC structure but also a tetragonal structure. Since the transformation temperature of TiH was increased with increasing pressures, the thermal stability of this phase was increased by pressures. In this presentation, we will report detailed results together with the phase diagram and the equation of TiH
was increased with increasing pressures, the thermal stability of this phase was increased by pressures. In this presentation, we will report detailed results together with the phase diagram and the equation of TiH state at HPHT.
state at HPHT.
Endo, Naruki; Matsumoto, Itoko*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
 (
( = Fe, Co, Ni) alloys at high pressure and temperature
= Fe, Co, Ni) alloys at high pressure and temperatureEndo, Naruki; Ishikawa, Kazuhiro*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English