Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Ryoichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 11, p.21_1 - 21_9, 2025/06
The flux distribution tallies using the proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) called "the POD tallies" have been developed in our previous study. The POD tallies can achieve dimensionality and statistical uncertainty reduction for a finely discretized flux distribution. Some characteristics of the POD tallies, which are left by our previous work, are revealed in the present study. Firstly, the POD tallies with the track length estimator are newly implemented. Since the statistical uncertainty of the POD tallies is reduced compared with the cell tallies, the POD tallies with the track length estimator can obtain the most precise result among the present implantations. Secondly, the basis vectors obtained by the deterministic and the stochastic methods are compared. The statistical uncertainty of the snapshot data invokes the degradation of the extracted basis vectors. This result indicates that the deterministic method might be more efficient for the snapshot calculation. Finally, the impact of the covariances of expansion coefficients on the statistical uncertainty of expanded flux distribution is investigated. The reconstructed statistical uncertainty considering only the variances of the expansion coefficients differs from the reference. This result reveals that the covariances of the expansion coefficients are important to estimate the statistical uncertainty of the local flux in the flux distribution.
Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(12), p.1536 - 1545, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this paper, a new tallying method for a neutron flux distribution using the proper orthogonal decomposition is proposed for dimensionality reduction. The target spatial flux distribution is expanded by orthogonal basis vectors. Expansion coefficients are tallied during the random walk of the Monte Carlo calculation. The orthogonal basis vectors are extracted from the pre-calculated snapshots by the singular value decomposition. The proposed method is verified in the multi-group Monte Carlo calculation with the one-dimensional heterogeneous whole core geometry as a feasibility study. The flux distribution for each of the assemblies and energy groups is expanded by the basis vectors. The fewer basis vectors obtained from snapshots can reconstruct the target distribution well compared with the conventional Legendre polynomials used in the functional expansion tallies. The dimension of the solution in the proposed method is reduced by a factor of twenty compared with the conventional cell tally. In addition, the statistical error is reduced through dimensionality reduction thanks to the methodological feature of the proposed method. The results indicate that the proposed method has the capability of dimensionality reduction to tally the finely discretized flux distribution.
Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.04002_1 - 04002_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In the recent study, we have developed an efficient flux distribution tallying method in the Monte Carlo calculation toward the high-fidelity, large scale multi-physics simulation. In this method, the proper orthogonal decomposition is applied to the flux distribution tallies. While the tallying method was implemented with the collision estimator in the previous study, the track length estimator is implemented in the present study to obtain the tally with lower statistical error. The implementation of the flux distribution tally with the track length estimator is compared with that of the collision estimator and the normal track length estimator in a one-dimensional problem. The numerical results reveal that the distribution tally using the POD with the track length estimator can obtain a more precise solution compared with that with the collision estimator. Therefore, in terms of the statistical error, the relationship between the distribution tally with track length and collision estimator is similar to that between the conventional track length and collision estimators.
Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara; Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Chiba, Go*; Ono, Michitaka*; Tojo, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.830 - 839, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:89.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear data processing code is important to connect evaluated nuclear data libraries and radiation transport codes. The nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 1 was released in 2019 to generate ACE formatted cross section files with simple input data. After we released FRENDY version 1, many functions were developed, e.g., neutron multi-group cross section generation, explicit consideration of the resonance interference effect among different nuclides in a material, consideration of the resonance upscattering, ACE file perturbation, and modification of ENDF-6 formatted file. FRENDY version 2 was released including these new functions. It generates GENDF and MATXS formatted neutron multi-group cross section files from an ACE formatted cross section file or an evaluated nuclear data file. This paper explains the features of the new functions implemented in FRENDY version 2 and the verification of the neutron multigroup cross section generation function of this code.
Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Endo, Yoichi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Endo, Keita*; Watanabe, Daisuke*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Ishii, Katsunori; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(3), p.307 - 317, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A flexible waste management system (FWM) is being developed to apply future MA partitioning and transmutation (P&T) technology to current HLLW. This FWM system will store high-level waste (HLLW) in granular form until MA partitioning and transmutation technology is realized. The feasibility of the main process was essentially confirmed by basic experiments and preliminary thermal analysis for granule production by rotary kiln from simulated HLLW and for temporary storage (50 years) of HLW granules at the HLW storage facility, respectively. The granule production experiments revealed that relatively large particles can be produced by the rotary kiln. The results of the thermal analysis showed that the small diameter canisters could be used to safely store the granules at a higher storage density than vitrified HLW. The effectiveness of the FWM system in terms of potential radiotoxicity and repository area was also evaluated, and it was shown that FWM can reduce these factors and has significant advantages in the disposal of HLW generated in current reprocessing plants. Since LWR fuel is stored for a long period of time in Japan and the operation of a reprocessing plant is expected to start soon, the FWM system is considered to be an effective system for reducing the environmental burden of HLW disposal.
Tada, Kenichi; Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.624 - 631, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)The sensitivity analysis and the uncertainty quantification have an important role in improving the evaluated nuclear data library. The current computational performance enables us to the sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantification using the continuous energy Monte Carlo calculation code. The ACE file perturbation tool was developed for these calculations using modules of FRENDY. This tool perturbs the microscopic cross section, the number of neutrons per fission, and the fission spectrum. The uncertainty quantification using the random sampling method is also available if the user prepares the covariance matrix. The uncertainty of the k-effective using the perturbation tool was compared to the current sensitivity analysis codes SCALE/TSUNAMI and MCNP/KSEN. The comparison results indicated that the random sampling method using this tool accurately estimates the uncertainty of k-effective.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisKinoshita, Norikazu*; Noto, Takuma*; Nakajima, Hitoshi*; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Kato, Takahiro*; Kuroiwa, Yoichi*; Kurabe, Misako*; Sasaki, Yuki*; Torii, Kazuyuki*; Maeda, Makoto; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.479 - 486, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Chemistry, Analytical)Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Seto, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 562, p.148 - 154, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kondo, Ryoichi*; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*; Tada, Kenichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2019) (CD-ROM), p.1493 - 1502, 2019/00
A perturbation capability of ACE formatted cross section files was developed using the modules of FRENDY. Uncertainty quantification using MCNP was carried out for the Godiva critical experiment by the RS method. We verified the results of the RS method by comparing with those obtained by the conventional sensitivity analyses. Moreover, uncertainty reduction using the bias factor method with the RS technique was applied to kinetic parameter, i.e., neutron generation time.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Seto, Hideki; Ito, Shinichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Shibata, Kaoru; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; General Subjects, 1861(1), p.3651 - 3660, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.18(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)J-PARC, Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex provides short pulse proton beam at a repetition rate 25 Hz and the maximum power is expected to be 1 MW. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments have already been operated or under construction / commissioning. There are 6 inelastic / quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectrometers and the complementary use of these spectrometers will open new insight for life science.
Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Minami, Ryutaro*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Eguchi, Taku*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Numakura, Tomoharu*; Endo, Yoichi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8, p.1205107_1 - 1205107_2, 2013/10
Minami, Ryutaro*; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Numakura, Tomoharu*; Endo, Yoichi*; Nakabayashi, Hidetaka*; Eguchi, Taku*; Shimozuma, Takashi*; Kubo, Shin*; Yoshimura, Yasuo*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 53(6), p.063003_1 - 063003_7, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:44.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Minami, Ryutaro*; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Numakura, Tomoharu*; Endo, Yoichi*; Nakabayashi, Hidetaka*; Eguchi, Taku*; Shimozuma, Takashi*; Kubo, Shin*; Yoshimura, Yasuo*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 53(6), p.063003_1 - 063003_7, 2013/06
 F]fluoro-
F]fluoro- -methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[
-methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[ F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography
F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomographyOhshima, Yasuhiro; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Kanai, Yoshikatsu*; Kaira, Kyoichi*; Yamaguchi, Aiko*; Nagamori, Shushi*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; Tsushima, Yoshito*; Endo, Keigo*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 27(4), p.314 - 324, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:52.10(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)
Ishii, Kenji; Ishihara, Sumio*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kuzushita, Kaori*; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Yoshida, Masahiro; Jarrige, I.; Tatami, Naka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 83(24), p.241101_1 - 241101_4, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Endo, Akira; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Watanabe, Fusao*; Sakurai, Hiroki*; Arai, Yoichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 637(1), p.149 - 157, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)A dose and spectrum monitoring system applicable to neutrons, photons and muons over wide ranges of energy, designated as DARWIN, has been developed for radiological protection in high-energy accelerator facilities. The performance of the upgraded DARWIN was examined in various radiation fields, including an operational field in J-PARC. The experiments revealed that the dose rates and spectra measured by the upgraded DARWIN are quite reasonable, even in radiation fields with peak structures in terms of both spectrum and time variation. These results clearly demonstrate the usefulness of DARWIN for improving radiation safety in high-energy accelerator facilities.
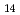 Cu
Cu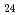 O
O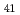 studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringYoshida, Masahiro; Ishii, Kenji; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Jarrige, I.; Murakami, Yoichi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Tsutsui, Kenji; Toyama, Takami*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Kudo, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physica C, 470(Suppl.1), p.S145 - S146, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.87(Physics, Applied)Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.