Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhan, Y.*; Kuwata, Yusuke*; Maruyama, Kiyotaka*; Okawa, Tomio*; Enoki, Koji*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 112, p.109953_1 - 109953_8, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.31(Thermodynamics)Zhan, Y.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 98, p.86 - 94, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:68.27(Thermodynamics)Kuwata, Yusuke*; Zhan, Y.*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/10
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, effect of viscosity on liquid jet impact on solid surface was studied.
Zhan, Y.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/07
It is important to set the amount of sodium droplet mechanistically for appropriate numerical evaluations of sodium leak and fire behavior in a sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. In the present work, fundamental experiments are performed to measure the splash ratio during the vertical water jet impact onto a horizontal wall. It is shown that the splash ratio can be correlated well as a function of the impact Weber number and dimensionless impact frequency.
Yi, Z.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2016/11
It is important to set the amount of sodium droplet mechanistically for appropriate numerical evaluations of sodium leak and fire behavior in a sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. In the present work, fundamental experiments were performed to measure the splash ratio during the vertical water jet impact onto a horizontal wall. It was shown that the splash ratio can be correlated well as a function of the impact Weber number, the Strouhal number and the Ohnesorge number of the droplets impinging the liquid film.
Yi, Z.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2016/06
It is important to set the amount of sodium droplet mechanistically for appropriate numerical evaluations of sodium leak and fire behavior in a sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. In the present work, fundamental experiments were performed to measure the splash ratio during the vertical water jet impact onto a horizontal wall. It was shown that the splash ratio can be correlated well as a function of the impact Weber number and the Strouhal number of the droplets impinging the liquid film.
 Ti
Ti during hydrogen cycling
during hydrogen cyclingKim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Saita, Itoko*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*; Noguchi, Kazuo*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39(20), p.10546 - 10551, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:32.47(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of the vanadium content on the cyclic stability of V-Ti binary alloys was investigated. V Ti
Ti ,
, 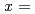 0.2 and 0.5 samples were hydrogenated and dehydrogenated at 410 K and 553 K respectively, for more than 100 times. During hydrogen cycling, reduction in the reversible hydrogen storage capacity was clearly observed from both samples. In addition, the shape of the pressure-composition-isotherm curves was significantly altered over the testing cycle period; the absorption and desorption plateaus got markedly inclined and the hysteresis became evidently smaller. We found that even after the hydrogen storage capacity of V
0.2 and 0.5 samples were hydrogenated and dehydrogenated at 410 K and 553 K respectively, for more than 100 times. During hydrogen cycling, reduction in the reversible hydrogen storage capacity was clearly observed from both samples. In addition, the shape of the pressure-composition-isotherm curves was significantly altered over the testing cycle period; the absorption and desorption plateaus got markedly inclined and the hysteresis became evidently smaller. We found that even after the hydrogen storage capacity of V Ti
Ti was significantly reduced, at low enough temperature V
was significantly reduced, at low enough temperature V Ti
Ti was able to absorb hydrogen as much as it did at the first cycle.
was able to absorb hydrogen as much as it did at the first cycle.
 Fe M
Fe M ssbauer spectroscopy of RFe
ssbauer spectroscopy of RFe (R = Y, Gd) hydrides synthesized under ultra-high-pressure hydrogen
(R = Y, Gd) hydrides synthesized under ultra-high-pressure hydrogenMitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto; Hirao, Naohisa*; Matsuoka, Takehiro*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Sakaki, Koji*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 580(Suppl.1), p.S264 - S267, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.41(Chemistry, Physical) ssbauer study using synchrotron radiation
ssbauer study using synchrotron radiationMasuda, Ryo; Mitsui, Takaya; Ito, Keiji*; Sakaki, Koji*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Seto, Makoto
Hyperfine Interactions, 204(1-3), p.139 - 142, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.57(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We have been developing a system for in situ M ssbauer studies using synchrotron radiation (SR) to elucidate the mechanism of hydrogenation processes. In the system, samples reacts in an atmosphere chamber and SR-based M
ssbauer studies using synchrotron radiation (SR) to elucidate the mechanism of hydrogenation processes. In the system, samples reacts in an atmosphere chamber and SR-based M ssbauer spectra using variable-frequency nuclear monochromator and energy spectra of inelastic nuclear resonant scattering (NRS) of SR are measured. As a feasibility study, the temperature dependence of the M
ssbauer spectra using variable-frequency nuclear monochromator and energy spectra of inelastic nuclear resonant scattering (NRS) of SR are measured. As a feasibility study, the temperature dependence of the M ssbauer and inelastic NRS spectra of
ssbauer and inelastic NRS spectra of  Fe in
Fe in  -GdFe
-GdFe H
H under vacuum were measured. In both spectra, clear differences were observed between 373 K and 573 K. These differences can be interpreted by the change of microscopic environment around Fe at the dehydrogenation. Thus, it is confirmed that this system works well enough to perform the in-situ M
under vacuum were measured. In both spectra, clear differences were observed between 373 K and 573 K. These differences can be interpreted by the change of microscopic environment around Fe at the dehydrogenation. Thus, it is confirmed that this system works well enough to perform the in-situ M ssbauer study on the dehydrogenation of
ssbauer study on the dehydrogenation of  -GdFe
-GdFe H
H .
.
Zhan, Y.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Ohno, Shuji; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, droplets were generated by collision of downward liquid jet onto a horizontal solid surface. We studied the mechanism of droplet generation and the empirical correlation of droplet amount.
Zhan, Y.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Ohno, Shuji; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, droplets were generated by collision of breakup liquid jet onto a solid surface. We studied the mechanism of droplet generation and the empirical correlation of droplet amount.
 ssbauer study on the hydrides of C15 RFe
ssbauer study on the hydrides of C15 RFe (R=Sm,Gd) compounds
(R=Sm,Gd) compoundsMasuda, Ryo; Mitsui, Takaya; Ito, Keiji*; Sakaki, Koji*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Kitao, Shinji*; Seto, Makoto
no journal, ,
Zhan, Y.*; Maruyama, Kiyotaka*; Kuwata, Yusuke*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, falling droplets are investigated by observation of upward liquid jet collision onto a solid surface.
Oya, Naoki*; Okawa, Tomio*; Enoki, Koji*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
It is important to set the diameter of leakage sodium droplet mechanistically for appropriate numerical evaluations of sodium leak and fire behavior in a sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. We performed a fundamental experiment with water in order to clarify mechanism of droplet generation in this study. Impinging water jet on a flat plate was tested for various cases of jet velocity, nozzle diameter and nozzle height. The impinging behavior was visualized by using a high-speed video camera. We measured the amount of generated droplet and the maximum droplet diameter. Observed jet flow was categorized into following three modes: drop mode which is droplet state flow, jet mode which is straight flow and lump mode which is partially constricted flow. The amount of generated droplet had a strong correlation with the impact frequency. Larger droplet diameter was observed for the drop and lump modes.
Kuwata, Yusuke*; Zhan, Y.*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, effect of viscosity on liquid jet impact on solid surface was studied.
Okawa, Tomio*; Oya, Naoki*; Yi, Z.*; Enoki, Koji*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
It is important to set the amount of sodium droplet mechanistically for appropriate numerical evaluations of sodium leak and fire behavior in a sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. In the present work, fundamental experiments were performed to measure the rate of splashing during the vertical water jet impact onto a horizontal wall. It was found that the splashing rate is negligibly small when the water jet is continuous at the impact point. Whilst, the splashing rate increased rapidly with an increase in the jet velocity when the jet was broken into droplets at the impact point. Therefore, when the fall height is longer than the breakup length, it was suggested that the dimensionless splashing rate scaled by the liquid jet flow rate can be expressed as a function of the modified Weber number of the primary droplets impacting the target. A semi-empirical method to estimate the splashing rate during liquid jet impact onto a horizontal wall was proposed based on linear stability theory.
Oya, Naoki*; Zhan, Y.*; Okawa, Tomio*; Enoki, Koji*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Ohno, Shuji; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, droplets were generated by collision of downward liquid jet onto a horizontal solid surface. We studied the mechanism of droplet generation and the empirical correlation of droplet amount.
Zhan, Y.*; Oya, Naoki*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Ohno, Shuji; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, droplets were generated by collision of downward liquid jet onto a horizontal solid surface. We studied the mechanism of droplet generation and the empirical correlation of droplet amount.
Zhan, Y.*; Kuwata, Yusuke*; Maruyama, Kiyotaka*; Enoki, Koji*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, splashing droplets are investigated by observation of liquid jet collision onto a solid surface.
Zhan, Y.*; Sun, G.*; Okawa, Tomio*; Enoki, Koji*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
no journal, ,
This study aims improvement of safety analysis for sodium fire accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. In the experiment, secondary droplets are investigated by observation of upward spray flow collision onto a solid surface.
Oya, Naoki*; Okawa, Tomio*; Enoki, Koji*; Ohno, Shuji; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
This study aimed at improvement of sodium fire analysis method for coolant leakage in sodium-cooled fast reactor. A semi-empirical method to estimate the splashing rate during liquid jet impact onto a horizontal wall was proposed based on consideration of splashing mechanism.