Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chrysalidis, K.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Ahmed, R.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ballof, J.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Harding, R. D.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 463, p.472 - 475, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.83(Instruments & Instrumentation)A number of radiogenically produced dysprosium isotopes have been studied by in-source laser spectroscopy at ISOLDE using the Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS). Isotope shifts were measured relative to  Dy in the
Dy in the 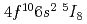 (gs)
(gs) 
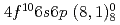 (418.8 nm
(418.8 nm 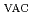 )resonance transition. The electronic factor,
)resonance transition. The electronic factor, 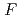 , and mass shift factor, M, were extracted and used for determining the changes in mean-squared charge radii for
, and mass shift factor, M, were extracted and used for determining the changes in mean-squared charge radii for 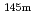 Dy and
Dy and 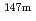 Dy for the first time.
Dy for the first time.
 -decay branching ratio of
-decay branching ratio of  Pt
PtCubiss, J. G.*; Harding, R. D.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Althubiti, N.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; Farooq-Smith, G. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(1), p.014314_1 - 014314_4, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.30(Physics, Nuclear)The  -decay branching ratio of 0.52(5)% from the ground state of
-decay branching ratio of 0.52(5)% from the ground state of  Pt to the ground state of the daughter nucleus
Pt to the ground state of the daughter nucleus  Os has been determined more precisely than before. The
Os has been determined more precisely than before. The  Pt was produced as the
Pt was produced as the  -decay granddaughter of
-decay granddaughter of  Hg which was produced and separated with the CERN-ISOLDE facility. The reduced
Hg which was produced and separated with the CERN-ISOLDE facility. The reduced  -decay width calculated with the present result has provided a new picture of the systematics for the
-decay width calculated with the present result has provided a new picture of the systematics for the  -decay width of neutron-deficient Pt isotopes.
-decay width of neutron-deficient Pt isotopes.
Baron, P.*; Cornet, S. M.*; Collins, E. D.*; DeAngelis, G.*; Del Cul, G.*; Fedorov, Y.*; Glatz, J. P.*; Ignatiev, V.*; Inoue, Tadashi*; Khaperskaya, A.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 117, p.103091_1 - 103091_24, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:94.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The results of an international review of separation processes for spent nuclear fuel (SNF) recycling in future closed fuel cycles with the evaluation of Technology Readiness Level are reported. This study was made by the Expert Group on Fuel Recycling Chemistry (EGFRC) organised by the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). A unique feature of this study was that processes were classified according to a hierarchy of separations aimed at different elements within spent fuel (uranium; uranium-plutonium co-recovery; minor actinides; high heat generating radionuclides) and also the Head-end processes, used to prepare the SNF for chemical separation, were included. Separation processes covered both wet (hydrometallurgical) and dry (pyro-chemical) processes.
 decay of
decay of 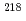 At
AtCubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A. E.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(6), p.064317_1 - 064317_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.17(Physics, Nuclear)An  decay of
decay of 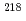 At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence
At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence  -
- data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T
data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T = 1.27(6) s was measured. A new
= 1.27(6) s was measured. A new  -decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the
-decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the  decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J
decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J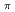 = (3
= (3 ) for the ground state of
) for the ground state of 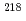 At; however, J
At; however, J = (2)
= (2) cannot be fully excluded.
cannot be fully excluded.
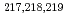 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.82(Physics, Nuclear) -decay study of
-decay study of  Tl
TlAndel, B.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Bree, N.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Comas, V. F.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(5), p.054327_1 - 054327_11, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.88(Physics, Nuclear)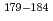 Tl measured by in-source laser spectroscopy
Tl measured by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Cocolios, T. E.*; de Groote, R. P.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; Fink, D. A.*; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(1), p.014324_1 - 014324_12, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:87.72(Physics, Nuclear) -delayed fission and
-delayed fission and  decay of
decay of 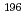 At
AtTruesdale, V. L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Sels, S.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034308_1 - 034308_11, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.30(Physics, Nuclear) -decay study of
-decay study of 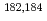 Tl
TlVan Beveren, C.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A. E.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; de Groote, R. P.*; Fedorov, D.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 43(2), p.025102_1 - 025102_22, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.30(Physics, Nuclear)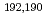 Pb ground states from
Pb ground states from  -decay studies using the total-absorption technique
-decay studies using the total-absorption techniqueEst vez Aguado, M. E.*; Algora, A.*; Agramunt, J.*; Rubio, B.*; Tain, J. L.*; Jord
vez Aguado, M. E.*; Algora, A.*; Agramunt, J.*; Rubio, B.*; Tain, J. L.*; Jord n, D.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Gelletly, W.*; Frank, A.*; Csatl
n, D.*; Fraile, L. M.*; Gelletly, W.*; Frank, A.*; Csatl s, M.*; et al.
s, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 92(4), p.044321_1 - 044321_8, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.03(Physics, Nuclear) ) intruder state in
) intruder state in 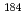 Tl
TlVan Beveren, C.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Fedorov, D.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; Huyse, M.*; K ster, U.*; Lane, J. F. W.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Lane, J. F. W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 92(1), p.014325_1 - 014325_8, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Nuclear)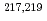 Po
PoFink, D. A.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Bastin, B.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Flanagan, K. T.*; Ghys, L.*; et al.
Physical Review X, 5(1), p.011018_1 - 011018_15, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:78.79(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -delayed fission of
-delayed fission of  Tl
TlElseviers, J.*; Andreyev, A. N.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Bree, N.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Comas, V. F.*; Diriken, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 88(4), p.044321_1 - 044321_13, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:88.44(Physics, Nuclear)Rothe, S.*; Andreyev, A. N.*; Antalic, S.*; Borschevsky, A.*; Capponi, L.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; De Witte, H.*; Eliav, E.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 4, p.1835_1 - 1835_6, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:94.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -decay spectroscopy of the chain
-decay spectroscopy of the chain 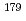 Tl
Tl

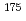 Au
Au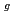

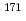 Ir
Ir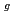

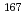 Re
Re
Andreyev, A. N.*; Liberati, V.*; Antalic, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Barzakh, A.*; Bree, N.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Diriken, J.*; Elseviers, J.*; Fedorov, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(5), p.054311_1 - 054311_8, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:71.49(Physics, Nuclear) for lithium batteries proposed by
for lithium batteries proposed by  simulations
simulationsKuzubov, A. A.*; Fedorov, A. S.*; Eliseeva, N. S.*; Tomilin, F. N.*; Avramov, P.; Fedorov, D. G.*
Physical Review B, 85(19), p.195415_1 - 195415_4, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:82.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fedorov, A. S.*; Fedorov, D. A.*; Kuzubov, A. A.*; Avramov, P.; Nishimura, Yoshifumi*; Irle, S.*; Witek, H. A.*
Physical Review Letters, 107(17), p.175506_1 - 175506_5, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:73.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Andreyev, A. N.*; Elseviers, J.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Bree, N.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Comas, V. F.*; Diriken, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 105(25), p.252502_1 - 252502_5, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:209 Percentile:97.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Avramov, P.; Fedorov, D. G.*; Sorokin, P. B.*; Chernozatonskii, L. A.*; Gordon, M. S.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(51), p.18824 - 18830, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.06(Chemistry, Physical)We have systematically constructed a set of stable silicon nanocluster families with large arbitrary fullerenetype hollows inside. In addition, conglomerate structures are designed by connecting the nanoclusters through pentagonal and hexagonal junctions. The atomic and electronic structure of the proposed objects is investigated using the semiempirical quantum-mechanical method. It is shown that within each family the band gap and the stability are inversely proportional to the particle effective size. The clusters inherit a wide variety of structural and symmetry properties from their parent silicon fullerenes. The conglomerates confine electrons like quasi-molecules with a peculiar electronic structure related to the junctions. Quantum dots and their conglomerates can host guest atoms in their hollows and therefore present a new promising type of nanomaterials with tunable electronic properties.
Avramov, P.; Sorokin, P. B.*; Fedorov, A. S.*; Fedorov, D. G.*; Maeda, Yoshihito
Physical Review B, 74(24), p.245417_1 - 245417_8, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The atomic and electronic structure of a set of pristine single wall SiC nanotubes as well as Si-substituted carbon nanotubes and a SiC sheet was studied by the LDA plane wave band structure calculations. Consecutive substitution of carbon atoms by Si leads to a gap opening in the energetic spectrum of the metallic (8,8) SWCNT with approximately quadratic dependence of the band gap upon the Si concentration. The same substitution for the semiconductor (10,0) SWCNT results in a band gap minimum (0.27 eV) at  25% of Si concentration. In the Si concentration region of 12-18%, both types of nanotubes have less than 0.5 eV direct band gaps at the
25% of Si concentration. In the Si concentration region of 12-18%, both types of nanotubes have less than 0.5 eV direct band gaps at the  -
- point. The calculation of the chiral (8,2) SWSi
point. The calculation of the chiral (8,2) SWSi C
C NT system gives a similar (0.6 eV) direct band gap. The regular distribution of Si atoms in the atomic lattice is by
NT system gives a similar (0.6 eV) direct band gap. The regular distribution of Si atoms in the atomic lattice is by  0.1 eV/atom energetically preferable in comparison with a random distribution. Time dependent DFT calculations showed that the silicon substitution sufficiently increases (roughly by one order of magnitude) the total probability of optical transitions in the near infrared region, which is caused by the opening of the direct band gap in metallic SWCNTs, the unification of the nature and energy of band gaps of all SWCNT species, the large values of
0.1 eV/atom energetically preferable in comparison with a random distribution. Time dependent DFT calculations showed that the silicon substitution sufficiently increases (roughly by one order of magnitude) the total probability of optical transitions in the near infrared region, which is caused by the opening of the direct band gap in metallic SWCNTs, the unification of the nature and energy of band gaps of all SWCNT species, the large values of  Si3
Si3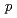
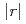 Si3
Si3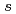
 radial integrals and participation of Si3
radial integrals and participation of Si3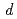 states in chemical bonding in both valence and conductance bands.
states in chemical bonding in both valence and conductance bands.
Nishio, Katsuhisa; Andreyev, A. N.*; Elseviers, J.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Bree, N.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Comas, V. F.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English