Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Schaffer, M. J.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Evans, T. E.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Gao, X.*; Garofalo, A. M.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103028_1 - 103028_11, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Experiments at DIII-D investigated the effects of ferromagnetic error fields similar to those expected from proposed ITER Test Blanket Modules (TBMs). Studied were effects on: plasma rotation and locking; confinement; L-H transition; edge localized mode (ELM) suppression by resonant magnetic perturbations; ELMs and the H-mode pedestal; energetic particle losses; and more. The experiments used a 3-coil mock-up of 2 magnetized ITER TBMs in one ITER equatorial port. The experiments did not reveal any effect likely to preclude ITER operations with a TBM-like error field. The largest effect was slowed plasma toroidal rotation v across the entire radial profile by as much as 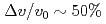 via non-resonant braking. Changes to global
via non-resonant braking. Changes to global 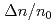 ,
, 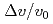 and
and 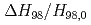 were
were  3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher
3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher  and lower
and lower 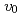 . Other effects were smaller.
. Other effects were smaller.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Boedo, J. A.*; Eich, T.*; Federici, G.*; Fenstermacher, M.*; Finken, K.*; Herrmann, A.*; Terry, J.*; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(7), p.s43 - s62, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:91.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Edge Localized Mode (ELM) measurements in the tokamaks, including JT-60U, DIII-D, ASDEX-U and JET, are reviewed. The followings are outlines of this presentation. (1) ELM Types and basic scaling, (2) Small ELM regimes and ELM mitigation, (3) ELM filament formation and transverse motion, (4) Power deposition on divertor targets and main chamber wall.
Loarte, A.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Kukushkin, A. S.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Stangeby, P. C.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Counsell, G. F.*; Federici, G.*; Kallenbach, A.*; Krieger, K.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S203 - S263, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:864 Percentile:98.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress, since the ITER Physics Basis publication (1999), in understanding the processes that will determine the properties of the plasma edge and its interaction with material elements in ITER is described. Significant progress in experiment area: energy and particle transport, the interaction of plasmas with the main chamber material elements, ELM energy deposition on material elements and the transport mechanism, the physics of plasma detachment and neutral dynamics, the erosion of low and high Z materials, their transport to the core plasma and their migration at the plasma edge, retention of tritium in fusion devices and removal methods. This progress has been accompanied by the development of modelling tools for the physical processes at the edge plasma and plasma-materials interaction. The implications for the expected performance in ITER and the lifetime of the plasma facing materials are discussed.
Lipschultz, B.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Bonnin, X.*; Coster, D. P.*; Counsell, G.*; Doerner, R.*; Dux, R.*; Federici, G.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Fundamenski, W.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
The work of the ITPA SOL/divertor group is reviewed. The high-n nature of ELMs has been elucidated and new measurements have determined that they carry 10-20% of the ELM energy to the far SOL with implications for ITER limiters and the upper divertor. Analysis of ELM measurements imply that the ELM continuously loses energy as it travels across the SOL. The prediction of ITER divertor disruption power loads have been reduced as a result of finding that the divertor footprint broadens during the thermal quench and that the plasma can lose up to 80% of its thermal energy before the thermal quench (not for VDEs or ITBs). Disruption mitigation through massive gas puffing has been successful at reducing divertor heat loads but estimates of the effect on the main chamber walls indicate 10s of kG of Be would be melted/mitigation. Long-pulse studies have shown that the fraction of injected gas that can be recovered after a discharge decreases with discharge length. The use of mixed materials gives rise to a number of potential processes.
Baylor, L. R.*; Parks, P. B.*; Jernigan, T. C.*; Caughman, J. B.*; Combs, S. K.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Foust, C. R.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; Lasnier, C. J.*; Maruyama, So; et al.
no journal, ,
Pellet injection is the primary fuelling technique for efficient core fuelling of ITER burning plasma. Pellet survivability and pellet mass loss have been demonstrated using a mockup of ITER inboard injection line. This experiment has revealed that pellets survive intact up to 300m/s, which is required for inboard injection. The series of experiments have demonstrated that pellet mass loss at extremely high back pressure remains  20% (
20% ( 10% at
10% at  300m/s). The pellet mass deposition has been numerically evaluated. It shows that inboard launching, present ITER reference, of 3 mm and 5mm cylindrical pellets at 300 m/s has a capability to fuel well inside the separatrix. The fuelling efficiency is predicted to be nearly 100%, which will help to minimize the tritium retention of the first wall. Pellet injected in to the present day tokamaks have been found to trigger ELMs in H-mode plasma. ITER will have the pellet injection technology as an ELM mitigation system.
300m/s). The pellet mass deposition has been numerically evaluated. It shows that inboard launching, present ITER reference, of 3 mm and 5mm cylindrical pellets at 300 m/s has a capability to fuel well inside the separatrix. The fuelling efficiency is predicted to be nearly 100%, which will help to minimize the tritium retention of the first wall. Pellet injected in to the present day tokamaks have been found to trigger ELMs in H-mode plasma. ITER will have the pellet injection technology as an ELM mitigation system.
Snipes, J. A.*; Schaffer, M. J.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Evans, T. E.*; Gao, X. M.*; Garofalo, A.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A series of experiments was performed on DIII-D to mock-up the field that will be induced in a pair of ferromagnetic Test Blanket Modules (TBMs) in ITER to determine the effects of such error fields on plasma operation and performance. A set of coils producing both poloidal and toroidal fields was placed inside a re-entrant horizontal port close to the plasma. The coils produce a localized ripple due to the toroidal field (TF) + TBM up to 5.7%, which is more than four times that expected from a pair of representative 1.3 ton TBMs in ITER. The experiments show that the reduction in the toroidal rotation is sensitive to the ripple. On the other hand, the confinement is reduced by up to 15-18% for local ripple 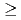 3% but is hardly affected at 1.7% local ripple.
3% but is hardly affected at 1.7% local ripple.