Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abeykoon, S.*; Howard, C.*; Dominijanni, S.*; Eberhard, L.*; Kurnosov, A.*; Frost, D. J.*; Boffa Ballaran, T.*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 128(9), p.e2023JB026710_1 - e2023JB026710_17, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.37(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Small amounts of iron sulphide minerals are found in most rocks from the Earth's mantle and as inclusions trapped in natural diamonds. Hydrogen may dissolve into iron sulphide minerals under high pressures and temperature, but is most likely lost once pressure and temperature are removed. In this study, we determined deuterium contents in iron sulphide, held under high pressure and temperature conditions, using neutron diffraction measurements with 6-ram multi-anvil press at PLANET, J-PARC. Deuterium contents in iron sulphide were measured at high-P, up to 11.4 GPa and high-T to 1300 K in in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The total deuterium content increases with both P and T. The results are used to estimate hydrogen contents of iron sulphide minerals in the deep continental lithospheric mantle, which are found to be in the range 1700-2700 ppm. This corresponds to approximately 2-3 ppm of hydrogen in the bulk mantle.
Zhou, Z.*; Frost, W.*; Lloyd, D. C.*; Seki, Takeshi*; Kubota, Takahide*; Ramos, R.*; Saito, Eiji; Takanashi, Koki; Hirohata, Atsufumi*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 571, p.170575_1 - 170575_5, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Fujita, Masaki*; Frost, C. D.*; Bennington, S. M.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Arai, Masatoshi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(8), p.084708_1 - 084708_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.93(Physics, Multidisciplinary)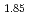 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Matsuura, Masato*; Fujita, Masaki*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Perring, T. G.*; Frost, C. D.*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Physical Review B, 86(13), p.134529_1 - 134529_8, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Tranquada, J. M.*; Frost, C. D.*; Swainson, I.*; Birgeneau, R. J.*
Physica C, 460-462(1), p.166 - 169, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.31(Physics, Applied)Spin excitations of overdoped La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO (
(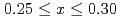 ) have been studied by neutron scattering utilizing triple-axis and time-of-flight spectrometers. Low-energy excitation spectra (
) have been studied by neutron scattering utilizing triple-axis and time-of-flight spectrometers. Low-energy excitation spectra (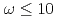
 meV) for all of the superconducting samples show a maximum around
meV) for all of the superconducting samples show a maximum around 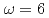 meV with a maximum value of dynamic spin susceptibility
meV with a maximum value of dynamic spin susceptibility 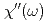 that decreases linearly with
that decreases linearly with 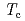 as doping increases. The magnetic scattering cross section finally disappears at
as doping increases. The magnetic scattering cross section finally disappears at 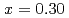 , coincident with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. Time-of-flight measurements for
, coincident with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. Time-of-flight measurements for 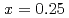 and
and 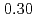 shows markedly suppressed magnetic scattering intensities at intermediate energies (20
shows markedly suppressed magnetic scattering intensities at intermediate energies (20

 80
80 meV) in contrast to those of the stripe-ordered La
meV) in contrast to those of the stripe-ordered La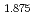 Ba
Ba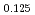 CuO
CuO . These facts imply a cooperative correlation between the dynamic incommensurate state and the superconductivity.
. These facts imply a cooperative correlation between the dynamic incommensurate state and the superconductivity.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Tranquada, J. M.*; Frost, C. D.*; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Zhang, H.*
Physical Review Letters, 98(24), p.247003_1 - 247003_4, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:92.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic excitations for energies up to 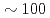 meV are studied for over-doped La
meV are studied for over-doped La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO with
with 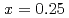 and
and 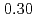 , using time-of-flight neutron spectroscopy. Comparison of spectra integrated over the width of an antiferromagnetic Brillouin zone demonstrates that the magnetic scattering at intermediate energies,
, using time-of-flight neutron spectroscopy. Comparison of spectra integrated over the width of an antiferromagnetic Brillouin zone demonstrates that the magnetic scattering at intermediate energies,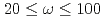 meV, progressively decreases with over-doping. This strongly suggests that the magnetism is not related to Fermi surface nesting, but rather is associated with a decreasing volume fraction of (probably fluctuating) antiferromagnetic bubbles.
meV, progressively decreases with over-doping. This strongly suggests that the magnetism is not related to Fermi surface nesting, but rather is associated with a decreasing volume fraction of (probably fluctuating) antiferromagnetic bubbles.
 (Sr,Ba)
(Sr,Ba) CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Fujita, Masaki*; Gu, G.*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Matsuda, Masaaki; Takeda, Masayasu; Tranquada, J. M.*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Frost, C. D.*
no journal, ,
To study effects of the stripe structure to the magnetic excitations in the high- cuprates, we have performed polarized neutron scattering study on La
cuprates, we have performed polarized neutron scattering study on La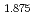 Ba
Ba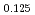 CuO
CuO and La
and La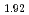 Sr
Sr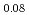 CuO
CuO . The former shows robust stripe order whereas the latter has only weak order of stripes. The former shows spin fluctuations which are confined in the CuO
. The former shows robust stripe order whereas the latter has only weak order of stripes. The former shows spin fluctuations which are confined in the CuO plane, correspondingly to the confinement of the ordered spins in the plane. The latter shows nearly isotropic spin fluctuations. These observations imply that the low-energy spin excitations are strongly affected by the stripe order, which is important to understand the origin of the universal magnetic dispersion in the high-
plane, correspondingly to the confinement of the ordered spins in the plane. The latter shows nearly isotropic spin fluctuations. These observations imply that the low-energy spin excitations are strongly affected by the stripe order, which is important to understand the origin of the universal magnetic dispersion in the high- cuprates.
cuprates.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Tranquada, J. M.*; Frost, C. D.*; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Zhang, H.*
no journal, ,
Neutron scattering experiments have been performed on the overdoped La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO (
(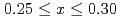 ). Low energy magnetic excitations (
). Low energy magnetic excitations (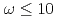 meV) show incommensurate peaks for the superconducting samples with a maximum at
meV) show incommensurate peaks for the superconducting samples with a maximum at 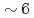 meV in the energy spectrum. As doping increases, the maximum of the dynamic susceptibility decreases linearly with
meV in the energy spectrum. As doping increases, the maximum of the dynamic susceptibility decreases linearly with  and, finally, the low energy excitations become unobservable at
and, finally, the low energy excitations become unobservable at 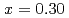 coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. Time-of-flight measurements revealed that magnetic excitations for
coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. Time-of-flight measurements revealed that magnetic excitations for 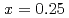 are markedly suppressed in the intermediate energy range (
are markedly suppressed in the intermediate energy range (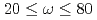 meV), which is apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation into a superconducting region which retains the antiferromagnetic correlations and a Fermi liquid region which has no magnetic correlations.
meV), which is apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation into a superconducting region which retains the antiferromagnetic correlations and a Fermi liquid region which has no magnetic correlations.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Birgeneau, R. J.*; Frost, C. D.*; Kagedan, A.*; Kim, H.*; Swainson, I.*; Tranquada, J. M.*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Zhang, H.*
no journal, ,
Spin excitations of LSCO in the overdoped regime has been studied by neutron scattering. Incommensurate excitations around 6 meV which are clearly observed in the 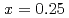 sample decrease with
sample decrease with  as doping increases, and finally, become unobservable at
as doping increases, and finally, become unobservable at 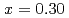 coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. High-energy measurements performed at the MAPS spectrometer show remarkably weakened magnetic excitations of the overdoped samples also in the high energy region. These observations are apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation of the overdoped samples into the superconducting and Fermi liquid phases based on muSR results. In contrast, magnetization measurements of overdoped LSCO with and without Zn impurities have revealed that the superconductivity vanishes in the overdoped regime as a result of a competition between the superconductivity and paramagnetism which is induced even in the Zn-free overdoped LSCO.
coincidentally with the disappearance of bulk superconductivity. High-energy measurements performed at the MAPS spectrometer show remarkably weakened magnetic excitations of the overdoped samples also in the high energy region. These observations are apparently consistent with a microscopic phase separation of the overdoped samples into the superconducting and Fermi liquid phases based on muSR results. In contrast, magnetization measurements of overdoped LSCO with and without Zn impurities have revealed that the superconductivity vanishes in the overdoped regime as a result of a competition between the superconductivity and paramagnetism which is induced even in the Zn-free overdoped LSCO.