Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:91.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:93.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -type PbS
-type PbSRathore, E.*; Juneja, R.*; Sarkar, D.*; Roychowdhury, S.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Singh, A. K.*; Biswas, K.*
Materials Today Energy (Internet), 24, p.100953_1 - 100953_9, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:79.59(Chemistry, Physical)Zhang, D.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, T.*; Abernathy, D. L.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Foley, B. J.*; Yoon, M.*; Choi, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(22), p.224310_1 - 224310_10, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Gao, D.*; Li, Y.*; Zheng, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Fu, R.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(41), p.17662 - 17669, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:79.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Solid-state topochemical polymerization (SSTP) is a promising method to construct functional crystalline polymeric materials, but in contrast to various reactions that happen in solution, only very limited types of SSTP reactions are reported. Diels-Alder (DA) and dehydro-DA (DDA) reactions are textbook reactions for preparing six-membered rings in solution but are scarcely seen in solid-state synthesis. Here, using multiple cutting-edge techniques, we demonstrate that the solid 1,4-diphenylbutadiyne (DPB) undergoes a DDA reaction under 10-20 GPa with the phenyl as the dienophile. The crystal structure at the critical pressure shows that this reaction is "distance-selected". The distance of 3.2 between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
Gonzal z, M. A.*; Borodin, O.*; Kofu, Maiko; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Xu, K.*; Price, D. L.*; Saboungi, M.-L.*
z, M. A.*; Borodin, O.*; Kofu, Maiko; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Xu, K.*; Price, D. L.*; Saboungi, M.-L.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(17), p.7279 - 7284, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:80.04(Chemistry, Physical) O
O
Allenspach, S.*; Biffin, A.*; Stuhr, U.*; Tucker, G. S.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Voneshen, D. J.*; Boehm, M.*; Normand, B.*; Laflorencie, N.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(17), p.177205_1 - 177205_7, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, X.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Zhao, E.*; Zhang, Z.*; Guide, T.*; Le, M. D.*; Avdeev, M.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.942_1 - 942_9, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:93.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In high-performance thermoelectric materials, there are two main low thermal conductivity mechanisms: the phonon anharmonic and phonon scattering resulting from the dynamic disorder, which have been successfully revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Using neutron scattering and ab initio calculations, we report here a mechanism of static local structure distortion combined with phonon-anharmonic-induced ultralow lattice thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in
-MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
-MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
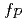 shell; Lifetime measurements in
shell; Lifetime measurements in  Zn
ZnQueiser, M.*; Vogt, A.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Reiter, P.*; Togashi, Tomoaki*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Homma, Michio*; Petkov, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044313_1 - 044313_13, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb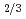 )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Taniguchi, Hiroki*; Fu, D.*
Ferroelectrics, 513(1), p.1 - 6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An EXAFS study of lead magnesium niobate was performed at the Nb K edge and at the Pb L3 edge at 300 K. Two Nb-O bond lengths of 1.91 and 2.10 are observed and there is no significant modification of the local environment of the Nb atoms compared with NaNbO
are observed and there is no significant modification of the local environment of the Nb atoms compared with NaNbO and AgNbO
and AgNbO . The weak Pb L3 EXAFS signal indicated a strong static disorder, which can be extracted by PDF analysis.
. The weak Pb L3 EXAFS signal indicated a strong static disorder, which can be extracted by PDF analysis.
 and AgNbO
and AgNbO modified by Li substitution
modified by Li substitutionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Aoyagi, Rintaro*; Fu, D.*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(10S), p.10TC04_1 - 10TC04_5, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.52(Physics, Applied)We analyzed the local structures of NaNbO and Na
and Na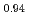 Li
Li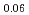 NbO
NbO by combining the X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) techniques. NaNbO
by combining the X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) techniques. NaNbO is known to be an antiferroelectric material at room temperature. It also undergoes a diffuse phase transition, in which an orthorhombic and a rhombohedral phases coexist over a wide temperature range. We identified a rhombohedral ground state structure of NaNbO
is known to be an antiferroelectric material at room temperature. It also undergoes a diffuse phase transition, in which an orthorhombic and a rhombohedral phases coexist over a wide temperature range. We identified a rhombohedral ground state structure of NaNbO and assumed an order-disorder-type phase. We also found a disorder feature in the nearest-neighbor bond distance corresponding to the Nb-O bonds. The disordered bond distribution disappeared when Na was substituted for Li. A similar disorder feature was found in AgNbO
and assumed an order-disorder-type phase. We also found a disorder feature in the nearest-neighbor bond distance corresponding to the Nb-O bonds. The disordered bond distribution disappeared when Na was substituted for Li. A similar disorder feature was found in AgNbO .
.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Nagata, Hajime*; Fu, D.*; Takenaka, Tadashi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 39(4), p.455 - 458, 2014/12
NaNbO , KNbO
, KNbO , and AgNbO
, and AgNbO have rhombohedral structure at low temperatures. The phase transition depends on
have rhombohedral structure at low temperatures. The phase transition depends on 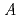 -site ion with NbO
-site ion with NbO octahedron. NaNbO
octahedron. NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO have structural phase transition from rhombohedral to orthorhombic with increasing temperature. On the other hand, the phase transition of AgNbO
have structural phase transition from rhombohedral to orthorhombic with increasing temperature. On the other hand, the phase transition of AgNbO occurs from rhombohedral to monoclinic. Since the rhombohedral structure is a highly ordered average structure, it tends to be subject to the influence of local randomness. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF). The Nb-O bond clearly appeared in the observed distribution for NaNbO
occurs from rhombohedral to monoclinic. Since the rhombohedral structure is a highly ordered average structure, it tends to be subject to the influence of local randomness. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF). The Nb-O bond clearly appeared in the observed distribution for NaNbO , but degraded in that for AgNbO
, but degraded in that for AgNbO . The difference of local structures causes different successive phase transitions for the Nb-related perovskite materials.
. The difference of local structures causes different successive phase transitions for the Nb-related perovskite materials.
 Na
Na )TiO
)TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Aoyagi, Rintaro*; Fu, D.*; Takenaka, Tadashi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 39(3), p.247 - 250, 2014/09
Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO are
are 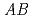 O
O perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi
perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.
to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.

Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*; Kohara, Shinji*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 502(1), p.012022_1 - 012022_4, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:98.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)NaNbO has an antiferroelectric structure at room temperature and finds important technological applications. It exhibits an unusual complex sequence of temperature- and pressure-driven structural phase transitions. NaNbO
has an antiferroelectric structure at room temperature and finds important technological applications. It exhibits an unusual complex sequence of temperature- and pressure-driven structural phase transitions. NaNbO shows unambiguous evidence for the presence of the ferroelectric
shows unambiguous evidence for the presence of the ferroelectric 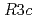 phase coexisting with an antiferroelectric phase (
phase coexisting with an antiferroelectric phase (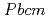 ) over a wide range of temperatures. We have carried out atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) analysis on NaNbO
) over a wide range of temperatures. We have carried out atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) analysis on NaNbO to understand the phase transitions. High-energy X-ray PDF using powder samples were carried out at the SPring-8, which is provided to become rhombohedral structure if
to understand the phase transitions. High-energy X-ray PDF using powder samples were carried out at the SPring-8, which is provided to become rhombohedral structure if 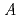 -site atoms did order and to become antiferroelectric phase if
-site atoms did order and to become antiferroelectric phase if 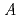 -site atoms did disorder.
-site atoms did disorder.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Matsuura, Masato*; Fujita, Masaki*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Perring, T. G.*; Frost, C. D.*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Physical Review B, 86(13), p.134529_1 - 134529_8, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
O ceramic powder from high-energy X-ray diffraction
ceramic powder from high-energy X-ray diffractionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*
no journal, ,
 Ba
Ba Nb
Nb O
O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*
no journal, ,
It has been reported that a ferroelectric having a tungsten bronze structure has an electro-optic effect, a nonlinear effect, and a relaxor-like behavior. BaNb O
O , which has an orthorhombic structure at room temperature, shows a single-phase tetragonal structure in the composition range of 0.19
, which has an orthorhombic structure at room temperature, shows a single-phase tetragonal structure in the composition range of 0.19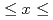 0.32 when Ca is added to the Ba site. I understand. In addition, disorder was generated in the
0.32 when Ca is added to the Ba site. I understand. In addition, disorder was generated in the 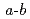 plane due to the substitution effect, and superlattice reflection was observed in the
plane due to the substitution effect, and superlattice reflection was observed in the  -axis direction despite the ceramic sample. Currently, a local structure model is being constructed based on these phenomena.
-axis direction despite the ceramic sample. Currently, a local structure model is being constructed based on these phenomena.
 Ba
Ba Nb
Nb O
O in high-temperature phase
in high-temperature phaseYoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*
no journal, ,
Ca Ba
Ba Nb
Nb O
O (CBN) in which Ba of BaNb
(CBN) in which Ba of BaNb O
O is replaced with Ca, which is a ferroelectric substance having a tungsten bronze structure, A single-phase tetragonal phase appears in the composition range where the amount of Ca substitution is 0.19
is replaced with Ca, which is a ferroelectric substance having a tungsten bronze structure, A single-phase tetragonal phase appears in the composition range where the amount of Ca substitution is 0.19 
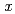
 0.32. For CBN, superlattice reflection appears in the powder X-ray diffraction pattern even in ceramic samples. There is a long-period structure that is deviated from the average structure. Since superlattice reflection is still observed in the high-temperature phase, structural analysis was performed in the high-temperature phase. It was found that the average structure of the high-temperature phase well reflected the local structure of the room temperature phase. It is considered to be a phenomenon that reflects the reentrant phase transition peculiar to tungsten bronze.
0.32. For CBN, superlattice reflection appears in the powder X-ray diffraction pattern even in ceramic samples. There is a long-period structure that is deviated from the average structure. Since superlattice reflection is still observed in the high-temperature phase, structural analysis was performed in the high-temperature phase. It was found that the average structure of the high-temperature phase well reflected the local structure of the room temperature phase. It is considered to be a phenomenon that reflects the reentrant phase transition peculiar to tungsten bronze.