Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ling, B.-K.*; Chang, M.*; Zhai, Y.-Q.*; Deng, J.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Guo, H.*; Zhao, J.*; Fu, Z.*; Zheng, Y.-Z.*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(13), p.10935 - 10942, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:91.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:91.57(Physics, Applied) SnSe
SnSe
Ren, Q.*; Gupta, M. K.*; Jin, M.*; Ding, J.*; Wu, J.*; Chen, Z.*; Lin, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Rodriguez-Velamazan, J. A.*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Materials, 22(8), p.999 - 1006, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:99.20(Chemistry, Physical)Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) BaCo(PO
BaCo(PO )
)
Sheng, J.*; Wang, L.*; Candini, A.*; Jiang, W.*; Huang, L.*; Xi, B.*; Zhao, J.*; Ge, H.*; Zhao, N.*; Fu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(51), p.e2211193119_1 - e2211193119_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:93.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences) ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
Yoshida, Shuhei*; Fu, R.*; Gong, W.; Ikeuchi, Takuto*; Bai, Y.*; Feng, Z.*; Wu, G.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Hansen, N.*; Huang, X.*; et al.
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 1249, p.012027_1 - 012027_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:80.61(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) -dependent collective relaxation dynamics of glass-forming liquid Ca
-dependent collective relaxation dynamics of glass-forming liquid Ca K
K (NO
(NO )
)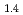 investigated by wide-angle neutron spin-echo
investigated by wide-angle neutron spin-echoLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Falus, P.*; Garc a Sakai, V.*; Hartl, M.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Z, Y.*
a Sakai, V.*; Hartl, M.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Z, Y.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.2092_1 - 2092_9, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:73.92(Multidisciplinary Sciences) at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeakLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(1), p.392 - 398, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:37.22(Chemistry, Physical)Using neutron spin-echo spectroscopy, we studied the microscopic structural relaxation of a prototypical network ionic liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is 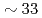 % higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point
% higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point 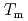 . Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the
. Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the 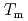 . These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl
. These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
Nagai, Yuki; Qi, Y.*; Isobe, Hiroki*; Kozii, V.*; Fu, L.*
Physical Review Letters, 125(22), p.227204_1 - 227204_7, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:70 Percentile:95.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Gao, D.*; Li, Y.*; Zheng, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Fu, R.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(41), p.17662 - 17669, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:79.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Solid-state topochemical polymerization (SSTP) is a promising method to construct functional crystalline polymeric materials, but in contrast to various reactions that happen in solution, only very limited types of SSTP reactions are reported. Diels-Alder (DA) and dehydro-DA (DDA) reactions are textbook reactions for preparing six-membered rings in solution but are scarcely seen in solid-state synthesis. Here, using multiple cutting-edge techniques, we demonstrate that the solid 1,4-diphenylbutadiyne (DPB) undergoes a DDA reaction under 10-20 GPa with the phenyl as the dienophile. The crystal structure at the critical pressure shows that this reaction is "distance-selected". The distance of 3.2 between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
between the phenyl and the phenylethynyl facilitates the DDA reaction, while the distances for other DDA and 1,4-addition reactions are too large to allow the bonding. The obtained products are crystalline armchair graphitic nanoribbons, and hence our studies open a new route to construct the crystalline carbon materials with atomic-scale control.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, X.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Zhao, E.*; Zhang, Z.*; Guide, T.*; Le, M. D.*; Avdeev, M.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.942_1 - 942_9, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:93.33(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In high-performance thermoelectric materials, there are two main low thermal conductivity mechanisms: the phonon anharmonic and phonon scattering resulting from the dynamic disorder, which have been successfully revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Using neutron scattering and ab initio calculations, we report here a mechanism of static local structure distortion combined with phonon-anharmonic-induced ultralow lattice thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in
-MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
-MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
Wu, P.*; Zhang, B.*; Peng, K. L.*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kofu, Maiko; Lee, S. H.*; Kumigashira, Hiroshi*; Hu, C. S.*; Qi, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering, we have studied how electronic structures and lattice dynamics evolve with temperature in Na-doped SnSe.
Nagai, Yuki; Shen, H.*; Qi, Y.*; Liu, J.*; Fu, L.*
Physical Review B, 96(16), p.161102_1 - 161102_6, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:87.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C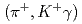 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 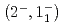 was measured to be
was measured to be 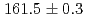 (stat)
(stat)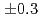 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 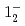 and
and 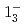 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 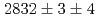 , keV and
, keV and 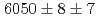 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Wan, L. K.*; Peng, J.*; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Fu, H. Y.*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 81(5), p.524 - 530, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.70(Chemistry, Physical)Rate constants of common crown ethers ((C H
H O)
O) , n=4, 5, 6) and their model compound, 1,4-dioxane(6C2) with some important oxidative radicals,
, n=4, 5, 6) and their model compound, 1,4-dioxane(6C2) with some important oxidative radicals, 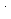 OH, SO
OH, SO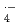 , and NO
, and NO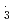 were determined in various aqueous solutions using pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis techniques. The rate constants for 6C2 and crown ethers with
were determined in various aqueous solutions using pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis techniques. The rate constants for 6C2 and crown ethers with  OH and SO
OH and SO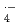 increase with the number of H-atom in the ethers, indicating that H-abstraction is dominant reaction between crown ethers and these two radicals. The presence of cations in solution has negligible effect on the rate constants for
increase with the number of H-atom in the ethers, indicating that H-abstraction is dominant reaction between crown ethers and these two radicals. The presence of cations in solution has negligible effect on the rate constants for  OH and SO
OH and SO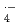 . However, for NO
. However, for NO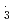 , the rate constants is not in proportional to H-atom number in crown ethers, and the 12-crown-4 is most reactive compared with the others. For the studied crown ethers, the rate constants of these oxidative radicals have the order:
, the rate constants is not in proportional to H-atom number in crown ethers, and the 12-crown-4 is most reactive compared with the others. For the studied crown ethers, the rate constants of these oxidative radicals have the order:  OH
OH  SO
SO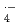
 NO
NO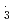 . This is the first report on the kinetic behavior of crown ethers with NO
. This is the first report on the kinetic behavior of crown ethers with NO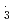 , and it would be helpful for the understanding of stability of crown ethers in the nuclear fuel reprocessing.
, and it would be helpful for the understanding of stability of crown ethers in the nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Fu, H. Y.*; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Research on Chemical Intermediates, 38(1), p.135 - 145, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:2.69(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In the present work, pulse radiolysis was used to demonstrate the oxidizing nature of various intermediates of  -AcMetNH
-AcMetNH and
and  -AcMetOMe via the oxidation of tryptophan (Trp) in a free aqueous solution. The reaction was examined at different pH levels. Electron transfer processes involving Trp and the sulfur-containing three-electron-bonded intermediates were investigated. The results revealed that Trp-Met pairs can form very favorable redox couples in biological systems, which is consistent with earlier reports of more efficient and rapid intramolecular charge transfers in synthetic as well as natural peptides containing methionine (Met).
-AcMetOMe via the oxidation of tryptophan (Trp) in a free aqueous solution. The reaction was examined at different pH levels. Electron transfer processes involving Trp and the sulfur-containing three-electron-bonded intermediates were investigated. The results revealed that Trp-Met pairs can form very favorable redox couples in biological systems, which is consistent with earlier reports of more efficient and rapid intramolecular charge transfers in synthetic as well as natural peptides containing methionine (Met).