Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ono, Masao; Iguchi, Yusuke*; Okayasu, Satoru; Esaka, Fumitaka; Kobayashi, Katsura*; Hao, T.; Bagum, R.*; Osawa, Takahito; Fujii, Kimio; Nakamura, Eizo*; et al.
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 289-292, p.63 - 68, 2009/04
The atomic-scale graded structure of In-Pb alloy was formed by an ultracentrifuge experiment under conditions that a gravitational field of 0.81 10
10 G for 100 hours at 150
G for 100 hours at 150  C in solid state in our previous study. The isotope ratio measurements were performed on the centrifuged sample with secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS).
C in solid state in our previous study. The isotope ratio measurements were performed on the centrifuged sample with secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS).  Pb/
Pb/ Pb and
Pb and  Pb/
Pb/ Pb isotope ratio changed with negative gradient in the direction of centrifugal force approximately 1.5% and 0.8%, respectively. And three-isotope diagram of
Pb isotope ratio changed with negative gradient in the direction of centrifugal force approximately 1.5% and 0.8%, respectively. And three-isotope diagram of  Pb/
Pb/ Pb versus
Pb versus  Pb/
Pb/ Pb proved that the isotope fluctuation depends on isotopic mass difference. These results showed that the strong gravitational field not only affected on the inter-diffusion but also on self-diffusion in this alloy as causing isotope fractionation effect, and the isotope fractionation was dependent on mass-difference.
Pb proved that the isotope fluctuation depends on isotopic mass difference. These results showed that the strong gravitational field not only affected on the inter-diffusion but also on self-diffusion in this alloy as causing isotope fractionation effect, and the isotope fractionation was dependent on mass-difference.
Ono, Masao; Iguchi, Yusuke*; Okayasu, Satoru; Esaka, Fumitaka; Kobayashi, Katsura*; Hao, T.; Bagum, R.*; Osawa, Takahito; Fujii, Kimio; Nakamura, Eizo*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.6), p.108 - 110, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)The atomic-scale graded structure of In-Pb alloy was formed by an ultracentrifuge experiment under conditions that a gravitational field of 810,000 G for 100 hours at 150 C (solid state) in our previous study. The isotope fluctuation on this sample was measured using secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS). The ratio both
C (solid state) in our previous study. The isotope fluctuation on this sample was measured using secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS). The ratio both  Pb/
Pb/ Pb and
Pb and  In/
In/ In changed with positive gradient in the direction of centrifugal force approximately 1.2%. These isotope fluctuations were larger than that of starting state of natural state (In
In changed with positive gradient in the direction of centrifugal force approximately 1.2%. These isotope fluctuations were larger than that of starting state of natural state (In 0.2%, Pb
0.2%, Pb 0.1%). These show that the sedimentation of isotopes occurred by solid centrifugation in this alloy, although achieved concentration gradients were small.
0.1%). These show that the sedimentation of isotopes occurred by solid centrifugation in this alloy, although achieved concentration gradients were small.
Ono, Masao; Iguchi, Yusuke*; Bagum, R.*; Fujii, Kimio; Okayasu, Satoru; Esaka, Fumitaka; Mashimo, Tsutomu*
AIP Conference Proceedings 973, p.476 - 481, 2008/03
We had realized atomic-scale graded structures in several miscible alloys by ultracentrifuge experiment. In this study, we performed an ultracentrifuge experiment on a MgCd order-disorder alloy at disordered state of solid solution. The experimental conditions were as follows: maximum acceleration: 610,000 g, temperature: 400 C, composition: Mg:Cd=50:50at%, time duration: 60 h). We investigated the crystal state of the centrifuged sample that had ordered from the disorder state of atomic-scale graded structure. It was found that the graded structure was formed in the centrifuged sample, in which Cd content continuously increased in the direction of gravitational field. It was also found that the different peaks from the starting state appeared in X-ray diffraction patterns of the centrifuged sample. We will present details at the session.
C, composition: Mg:Cd=50:50at%, time duration: 60 h). We investigated the crystal state of the centrifuged sample that had ordered from the disorder state of atomic-scale graded structure. It was found that the graded structure was formed in the centrifuged sample, in which Cd content continuously increased in the direction of gravitational field. It was also found that the different peaks from the starting state appeared in X-ray diffraction patterns of the centrifuged sample. We will present details at the session.
 C from irradiated graphite materials, 1; Oxidation behaviors and the changes in pore structure of Q1 and IG-110 graphite due to the air reaction (Joint research)
C from irradiated graphite materials, 1; Oxidation behaviors and the changes in pore structure of Q1 and IG-110 graphite due to the air reaction (Joint research)Fujii, Kimio
JAERI-Tech 2005-048, 108 Pages, 2005/09
The graphite-moderated power reactor was shut down in 1998 and its decommissioning program is being planned. Various graphites are used in the core of magnox-type reactors and HTTR as core-support structural materials and moderating materials of fast neutrons. For the nuclear graphite disposal, it is necessary to determine especially the treatment of long-lived nuclides, such as  C which are generated in the graphite components during reactor operation. As a research, which solves the problem of the
C which are generated in the graphite components during reactor operation. As a research, which solves the problem of the  C concentration, the cooperative research is concluded between JAERI and Japan Nuclear Power Corp. in 1999, and the research for the basic data acquisition has been advanced up to the present. To find the optimum conditions for
C concentration, the cooperative research is concluded between JAERI and Japan Nuclear Power Corp. in 1999, and the research for the basic data acquisition has been advanced up to the present. To find the optimum conditions for  C reduction, basic data on oxidation reaction and the structure of graphite materials are indispensable. In the present experiment, we measure the air oxidation characteristics in the temperature range 450
C reduction, basic data on oxidation reaction and the structure of graphite materials are indispensable. In the present experiment, we measure the air oxidation characteristics in the temperature range 450 800
800 C in Quality1 graphite and IG-110 graphite. Changes in pore diameter and pore size distribution due to air oxidation are discussed.
C in Quality1 graphite and IG-110 graphite. Changes in pore diameter and pore size distribution due to air oxidation are discussed.
Otsuki, Ryusei*; Nasu, Shoichi*; Ohashi, Kentaro*; Yamamoto, Ryoichi*; Fujii, Kimio; Okubo, Keisuke*
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 51(8), p.626 - 629, 2004/08
The He, Ar and the Penning gas pressureeffects on the preparation yieldsof the fullerenes were investigated by means of the arc discharge method using graphite(PGX) anode buried in a tungsten rod and tungsten cathode for collector radii of 50mm. The maximum yield showed about 13-14 % at 67KPa in He gas. The yields in the mixtures of He and Ne gases (the Penning effect) were similar to those obtained in He gas. Weight ratios of C to (C
to (C +C
+C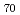 ) were about 20% in Ar gas, while those in He and Penning gas were about 60%. Ultra sonic vibration was effective to separate C
) were about 20% in Ar gas, while those in He and Penning gas were about 60%. Ultra sonic vibration was effective to separate C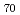 from soot.
from soot.
Otsuki, Ryusei*; Nasu, Shoichi*; Fujimori, Ryosuke*; Anada, Kinji*; Ohashi, Kentaro*; Yamamoto, Ryoichi*; Fujii, Kimio; Okubo, Keisuke*
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 51(8), p.622 - 625, 2004/08
Effects of carbon materials on weight yield of (C +C
+C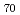 ) and weight ratios of C
) and weight ratios of C to (C
to (C +C
+C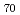 ) in soot were examined by the Joule resistive heating of four kinds of carbon materials at He gas pressures from 0.7
) in soot were examined by the Joule resistive heating of four kinds of carbon materials at He gas pressures from 0.7 10
10
 8.0
8.0 10
10 Pa for collector radii of 45, 50 and 55mm. The yields were in the range of 1 to 8% for graphite with hexagonal lattice, and better than those for glassy carbon. The most effective He gas pressure for the fullerene yield were in the range of 4.0
Pa for collector radii of 45, 50 and 55mm. The yields were in the range of 1 to 8% for graphite with hexagonal lattice, and better than those for glassy carbon. The most effective He gas pressure for the fullerene yield were in the range of 4.0 5.3
5.3 10
10 Pa. Any collector radii dependence of the yields was not observed. The weight ratios of C
Pa. Any collector radii dependence of the yields was not observed. The weight ratios of C to (C
to (C +C
+C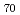 ) were about 60 to 70%, and showed neither He gas pressure depenndennce nor collector radii depenndence four kinds of carbon materials.
) were about 60 to 70%, and showed neither He gas pressure depenndennce nor collector radii depenndence four kinds of carbon materials.
Otsuki, Ryusei*; Nasu, Shoichi*; Matsushita, Masaki*; Fujii, Kimio; Ohashi, Kentaro*; Yamamoto, Ryoichi*
Funtai Oyobi Fummatsu Yakin, 51(8), p.633 - 634, 2004/08
We examined effects of deposition temperatures and collector radii onthe yields of fullerenes by arc discharge. Yields of fullerenes were 7-10%, 4-6% and 0.5-1% in the liquid nitrogen-cooling, water-cooling, non-cooling, respectively, and were better with a collector radius of 50mm than with that of 30mm. The weight ratios of C /C
/C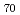 are about one for all runs of experiments.
are about one for all runs of experiments.
Fujii, Kimio; Matsuo, Hideto*
JAERI-Review 2002-034, 44 Pages, 2002/12
Graphite material is used as a moderator and reflector of graphite-moderated gas-cooled reactors such as the Tokai Nuclear Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company. For the decommissioning of those reactors, it is very important to obtain the density of carbon-14 in the graphite of which half-time is very long, and the development of the reduction technique for density of carbon-14 is one of the main technical issues as well. The reactor ceased the commercial operation on March 1998, and is in the process of the decommissioning. Technical developement on nuclear graphite disposal is one of the main issues, and it is pointed out that carbon-14 density is an impotant factor for the treatment on the disposal of the nuclear graphite. In order to resolve the problem, literatures survey was carried out for describing the status of technical development on resolving the problem. This report describes the outline of the literatures surveyed and the list of the related literatures is attached as well.
Fujii, Kimio
JAERI-Research 99-050, 99 Pages, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Reiji; Fujii, Kimio
Mater. Sci. Forum, 308-311, p.902 - 907, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio; Yamada, Reiji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.1953 - 1959, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakano, Junichi; Fujii, Kimio; Yamada, Reiji
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 80(11), p.2897 - 2902, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.37(Materials Science, Ceramics)no abstracts in English
Nakano, Junichi; Fujii, Kimio; Yamada, Reiji
Functionally Graded Materials 1996, 0, p.439 - 444, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Junichi; Fujii, Kimio; Shindo, Masami
JAERI-Research 94-016, 24 Pages, 1994/10
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio; Nakano, Junichi; Shindo, Masami
JAERI-M 94-001, 15 Pages, 1994/01
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Junichi; Fujii, Kimio; Shindo, Masami
JAERI-M 93-159, 20 Pages, 1993/08
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio; Nakano, Junichi; Shindo, Masami
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 203, p.10 - 16, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:80.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Imai, Hisashi; Fujii, Kimio; Nomura, Shinzo
High Temperature Corrosion of Advanced Materials and Protective Coatings, p.351 - 354, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio; ; Nomura, Shinzo; Shindo, Masami
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 187, p.204 - 208, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:74.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kimio; Nomura, Shinzo; ; Shindo, Masami
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 187, p.32 - 38, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:57.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English