Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Koide, Akihiro*; Otomo, Manabu; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Amemiya, Kenta*; Fujikawa, Takashi*; Sakai, Seiji
Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 1(35), p.5533 - 5537, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:76.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Proessdorf, A.*; Rodenbach, P.*; Grosse, F.*; Hanke, M.*; Braun, W.*; Riechert, H.*; Hu, W.; Fujikawa, Seiji*; Kozu, Miwa; Takahashi, Masamitsu
Surface Science, 606(17-18), p.1458 - 1461, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.47(Chemistry, Physical)Hojo, Ikuko*; Koide, Akihiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Maruyama, Takashi*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Entani, Shiro; Sakai, Seiji; Fujikawa, Takashi*
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 185(1-2), p.32 - 38, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.76(Spectroscopy)Sasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 323(1), p.13 - 16, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:82.36(Crystallography)Growth temperature dependence of strain relaxation during In![$$_{0.12}]$$](/search/images/ERPXWMBOGEZH0XJE.gif) Ga
Ga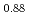 As/GaAs(001) molecular beam epitaxy was studied by in situ X-ray reciprocal space mapping. Evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality for the InGaAs film was obtained as a function of film thickness at growth temperatures of 420, 445 and 477
As/GaAs(001) molecular beam epitaxy was studied by in situ X-ray reciprocal space mapping. Evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality for the InGaAs film was obtained as a function of film thickness at growth temperatures of 420, 445 and 477  C. In the early stages of strain relaxation, it was found that evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality was dependent on the growth temperature. In order to discuss this observation quantitatively, the strain relaxation model was proposed based on the Dodson-Tsao kinetic model, and its validity was demonstrated by good agreement with the experimental residual strain. Additionally, rate coefficients reflecting dislocation motions during strain relaxation were obtained as a function of growth temperature and strain relaxation was discussed in terms of the thermally active dislocation motion.
C. In the early stages of strain relaxation, it was found that evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality was dependent on the growth temperature. In order to discuss this observation quantitatively, the strain relaxation model was proposed based on the Dodson-Tsao kinetic model, and its validity was demonstrated by good agreement with the experimental residual strain. Additionally, rate coefficients reflecting dislocation motions during strain relaxation were obtained as a function of growth temperature and strain relaxation was discussed in terms of the thermally active dislocation motion.
 films
filmsHojo, Ikuko*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Maruyama, Takashi*; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Entani, Shiro; Sakai, Seiji; Konishi, Takehisa*; Fujikawa, Takashi*
Photon Factory News, 29(1), p.20 - 25, 2011/05
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(4), p.04DH06_1 - 04DH06_5, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.53(Physics, Applied)Konishi, Tomoya*; Nishiwaki, Nagatoshi*; Tojo, Takashi*; Ishikawa, Takuma*; Teraoka, Teruki*; Ueta, Yukiko*; Kihara, Yoshifumi*; Moritoki, Hideji*; Tono, Tatsuo*; Musashi, Mio*; et al.
Physica Status Solidi (C), 8(2), p.405 - 407, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.77(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Kakuda, Naoki*; Kaizu, Toshiyuki*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Yamaguchi, Koichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 49(9), p.095602_1 - 095602_4, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.62(Physics, Applied)Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sasaki, Takuo*; Sai, Akihisa*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Kamiya, Itaru*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji
Applied Physics Letters, 97(4), p.041906_1 - 041906_3, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:73.85(Physics, Applied)Sasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1268, 6 Pages, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) real-time X-Ray reciprocal space mapping during InGaAs/GaAs growth for understanding strain relaxation mechanisms
real-time X-Ray reciprocal space mapping during InGaAs/GaAs growth for understanding strain relaxation mechanismsSasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Lee, J.-H.*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Arafune, Koji*; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Applied Physics Express, 2, p.085501_1 - 085501_3, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:75.65(Physics, Applied)Fujikawa, Seiji; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otomo, Manabu; Yamauchi, Yasushi*; Yamamura, Noyuri*; Avramov, P.; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Koide, Akihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Amemiya, Kenta*; Fujikawa, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Entani, Shiro; Koide, Akihiro*; Otomo, Manabu*; Avramov, P.*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Amemiya, Kenta*; Fujikawa, Takashi*; Sakai, Seiji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Seiji; Mitani, Seiji*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Otomo, Manabu; Entani, Shiro; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Fujikawa, Takashi*
no journal, ,
Otomo, Manabu; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Yamamura, Noyuri*; Entani, Shiro; Avramov, P.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Amemiya, Kenta*; Fujikawa, Takashi*; Sakai, Seiji
no journal, ,
Graphene has been intensively studied in the last few years for its long spin coherent length. The performance of graphene spintronic devices, however, are strongly influenced by poor spin injection efficiency at graphene/ferromagnetic metal (FM) interface. A promising solution for improving spin injection efficiency is to insert a tunnel barrier between graphene and FM. In this study, we propose hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) as a novel tunnel barrier for graphene spintronics. It was revealed that the N K-edge and B K-edge absorptions exhibit XMCD signals in response to the Ni magnetization. It was also found that the smaller incidence angle between the Ni magnetization and the X-ray propagation direction leads to larger XMCD signals. The nature of the spin polarization was discussed in connection with the energy and angle dependences of the XMCD signals, and contribution from magnetized Nickel atoms was proposed.
Fujikawa, Seiji; Kawamura, Tomoaki*; Bhunia, S.*; Watanabe, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
Growth mechanism of InP(001) of metalorganic chemical vapor deposition has been studied by X-ray reflectivity and grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD). The changes of reflectivity signal suggested that growth mode depended on substrate temperature, and particularly the step-flow growth mode was dominant at more than 550 C. Monitoring the fractional-order reflection of (2
C. Monitoring the fractional-order reflection of (2 1)-InP(001) using GIXD during the step-flow growth, the changes of fractional-order reflection suggested that indium atom migrate on the substrate surface more than 1 minute during the growth.
1)-InP(001) using GIXD during the step-flow growth, the changes of fractional-order reflection suggested that indium atom migrate on the substrate surface more than 1 minute during the growth.
Fujikawa, Seiji; Okane, Tetsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -Co compound affecting giant TMR effect, 2
-Co compound affecting giant TMR effect, 2Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Nagamatsu, Shinichi*; Hojo, Ikuko*; Fujikawa, Takashi*; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Maeda, Yoshihito; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English