Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Asamori, Koichi; Murakami, Osamu; Fukuda, Shoma; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Kagami, Saya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2024-013, 65 Pages, 2024/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 2nd fiscal year of the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakajima, Toru; Ogata, Manabu; Uchida, Mao; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Tanaka, Kiriha; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-035, 29 Pages, 2024/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2024. The objectives and contents of this research are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Fujita, Natsuko; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Kagami, Saya; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-017, 27 Pages, 2023/10
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2023. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2023 are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Ogawa, Hiroki; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2023-005, 78 Pages, 2023/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
 Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -rays of fuel debris
-rays of fuel debrisMatsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Fujita, Manabu*; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110298_1 - 110298_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.50(Chemistry, Physical)Matsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Fujita, Manabu*
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.144 - 149, 2022/03
We require reliable nuclear data that can appropriately evaluate the radiation characteristics of fuel debris for the purpose such as development of new sensors, non-destructive assay technologies and optimization of radiation shielding. In the past, even if different results were obtained depending on calculation codes, it was difficult to clarify what caused the differences. To overcome it, we have developed a new reliable code to calculate radiation decay and radioactive source spectra that can accurately treat with large amounts of nuclides and all decay modes in the decay data file. As the first step, we compared the photon spectra of fuel debris by using the recent decay data files: JENDL/DDF-2015, decay sub-libraries of ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3. In the presentation, we will report requests for the modifications on the decay scheme and branching ratio of decay mode for the next JENDL decay data file.
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Litaudon, X.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Tala, T.*; Angioni, C.*; Benkadda, S.*; Beurskens, M. N. A.*; Bourdelle, C.*; Brix, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073020_1 - 073020_13, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A variety of triggering mechanisms and structures of internal transport barrier (ITB) has been observed in various devices or depending on operation scenarios. Thus identity experiments on ITB in JT-60U and JET have been performed to shed light on the physics behind ITBs. Because of their similar size, the dimensionless parameters between both devices are the same. These experiments were performed with near identical magnetic configurations, heating waveforms and normalized quantities such as safety factor, magnetic shear, normalized Larmor radius, normalized collision frequency, beta, temperatures ratio. Similarities of the ITB triggering mechanism and the ITB strength have been observed when a proper match is achieved of the most relevant profiles of the normalized quantities. This paper will report on the detail comparison of transport properties of ITBs obtained in these JET/JT-60U identity experiments.
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 4, p.051_1 - 051_7, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095017_1 - 095017_8, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:76.57(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reports the recent development of reversed shear plasmas with a high bootstrap current fraction towards reactor relevant regime, especially lower 
 regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where
regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where 
 of 2.7,
of 2.7, 
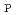 of 2.3 is achieved with reversed
of 2.3 is achieved with reversed  profile with
profile with 
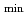 of 2.3, and then HH
of 2.3, and then HH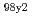 of 1.7,
of 1.7, 
 /
/
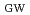 of 0.87 and
of 0.87 and 
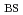 of 0.9 are also obtained at
of 0.9 are also obtained at 
 of 5.3.
of 5.3.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sato, Haruo; Tanai, Kenji; Inagaki, Manabu; Sawada, Atsushi; Niinuma, Hiroaki; Ishii, Eiichi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Tomura, Goji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-002, 156 Pages, 2009/05
The research and development plan for geological investigation, engineering technology and safety assessment during the drilling of a shaft down to intermediate depth are summarized according to the Midterm Plan till 2009 Fiscal year of JAEA. This report describes subject, current status and programme in the "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities). Furthermore regarding R&D plan in next Midterm Plan of JAEA, preliminary ideas are summarized.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasmas
plasmasMatsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takechi, Manabu; Kamada, Yutaka; Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1506 - 1511, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.97(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Controllability of plasmas with a large bootstrap current fraction (
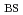 ) has been investigated in JT-60U. Dynamic change in current profile, especially
) has been investigated in JT-60U. Dynamic change in current profile, especially 
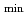 , which was induced by change in pressure profile at the internal transport barrier (ITB) through rotation control, was observed, indicating the strong linkage among the profiles. Response of pressure and current profiles to off-axis neutral beam injection is investigated and found that the alignment of peaks of total current profile and beam driven current profile affects to
, which was induced by change in pressure profile at the internal transport barrier (ITB) through rotation control, was observed, indicating the strong linkage among the profiles. Response of pressure and current profiles to off-axis neutral beam injection is investigated and found that the alignment of peaks of total current profile and beam driven current profile affects to 
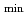 location, and the change in toroidal rotation induces the movement of ITB location. The current profile in strong reversed shear plasma without current hole is largely varied in the core region by electron cyclotron current drive, while the ITB structure is not affected.
location, and the change in toroidal rotation induces the movement of ITB location. The current profile in strong reversed shear plasma without current hole is largely varied in the core region by electron cyclotron current drive, while the ITB structure is not affected.
Yamada, Hiroshi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1418 - 1424, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High densities exceeding the Greenwald limit by a factor of 1.7 have been obtained in discharges with high internal inductances of 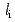 as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high
as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high 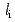 study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D
study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high
signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high 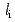 plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high
plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high 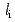 discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Hosoyama, Hiroki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 933, p.229 - 236, 2007/10
no abstracts in English
Sugita, Yutaka*; Takahashi, Yoshiaki*; Uragami, Manabu*; Kitayama, Kazumi*; Fujita, Tomoo; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2007-023, 70 Pages, 2007/03
The sealing performance of a repository is very important for the safety assessment of the geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste. NUMO and JAEA set up a technical commission to investigate sealing technology in a repository in 2004 following a cooperation agreement between these two organisations. The objectives of this commission were to present a concept of sealing performance required in the disposal system and to direct future R&D for design requirements of closure components (backfilling material, clay plug, etc.). Hydraulic analyses on tunnel intersections were carried out during the first year in 2004. This was expanded into a hydraulic analysis of a complete disposal panel with all tunnels during the second year in 2005. Since the model structure in 2005 was more complicated than the one used in 2004, the concept of equivalent permeability was adopted in and around each tunnel in the hydraulic analyses. Parameters used in the hydraulic analyses were installation positions of clay plugs, permeability of the backfilling material, permeability of disposal tunnel and directions of hydraulic gradient to estimate influences to the analytical results preliminary. Analytical results showed that flow rate in a disposal tunnel was influenced by directions of hydraulic gradient, installation of the clay plug at the both ends of each disposal tunnel and permeability of the main tunnel.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Ozeki, Takahisa; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Isayama, Akihiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
This is the first experimental result which demonstrates the dependence of critical RWM onset of plasma rotation and beta on initial plasma rotation with the variation of the angular momentum input and without magnetic braking. In the JT-60U with newly ferretic wall installed, it is possible to produce high beta plasma tightly coupled with the wall (b/a=1.2) above 



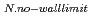 . In near-zero plasma rotation, the RWM started to grow at
. In near-zero plasma rotation, the RWM started to grow at 
 =
= 
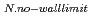 and with finite plasma rotation, the plasma pressure survives up to much higher
and with finite plasma rotation, the plasma pressure survives up to much higher 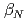 level than that with small rotation. The observed critical beta onset
level than that with small rotation. The observed critical beta onset 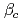 and the RWM growth rate
and the RWM growth rate 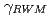 are discussed along with theoretical predictions using experimentally observed q-, pressure-, and rotation profiles. The critical rotation of RWM on JT-60U is less one-second times lower than previous report of other tokamaks.
are discussed along with theoretical predictions using experimentally observed q-, pressure-, and rotation profiles. The critical rotation of RWM on JT-60U is less one-second times lower than previous report of other tokamaks.
Yamada, Hiroshi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English