Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Urano, Hajime; Fujita, Takaaki*; Ide, Shunsuke; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Matsunaga, Go; Matsukawa, Makoto
Fusion Engineering and Design, 100, p.345 - 356, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:83.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)The operation scenarios for plasma breakdown and current ramp-up phases in JT-60SA tokamak have been developed. The induced current in the in-vessel conducting elements such as vacuum vessel and stabilizing plate increases to the comparable level of plasma current of  600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
Shimizu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Takaaki*; Arimoto, Hideki*; Nakano, Tomohide; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 10(Sp.2), p.3403062_1 - 3403062_4, 2015/07
Kurisaka, Kenichi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi*; Minagawa, Keisuke*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Takata, Takashi*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 269, p.268 - 280, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes a study to develop the level-1 probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) method that is applicable to the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR). This study aims to provide a new evaluation method of (1) passive safety architectures related to internal events and (2) an advanced seismic isolation system related to a seismic event as a representative external event in Japan. Regarding the internal events evaluation, a quantitative analysis on the frequency of the core damage caused by reactor shutdown failure was conducted. A failure in passive reactor shutdown was taken into account in the event tree model. The failure rate of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) specific components was evaluated based on the operating experience in existing SFRs by applying the Hierarchical Bayesian Method, which can consider a plant-to-plant variability. By conducting an uncertainty analysis, it was found that the assumption about the correlation of the probability parameters between the main and backup reactor shutdown systems is sensitive to the mean value of the frequency of the core damage caused by reactor shutdown failure. As for the seismic event evaluation, seismic response analysis and sensitivity analysis of a seismic isolation system were carried out. As a result, it was confirmed that nonlinear properties of rubber bearings have influence on response of the building and inner equipment.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 53(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:78.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of heat transport, edge pedestal and confinement on isotopic composition was investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas. Identical profiles for the electron density, electron temperature, and ion temperature were obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas, whereas the required power clearly increased for hydrogen, which resulted in reduction of heat diffusivity for deuterium. The inverse of the ion-temperature-gradient (ITG) scale length which is required for a given ion heat diffusivity increased by a factor of approximately 1.2 for deuterium compared with that for hydrogen.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8(Sp.1), p.2405109_1 - 2405109_6, 2013/08
The precise control of the plasma position is a key issue in safe and stable plasma operation. A plasma equilibrium control simulator has been developed in order to study the techniques of plasma equilibrium control for JT-60SA. The simulator consists of an equilibrium solver and controller. The equilibrium solver identifies the plasma equilibrium under the given coil current and unknown eddy current by iteration. The function which calculates the self-consistent 
 with magnetic flux consumption has been incorporated in order to simulate the
with magnetic flux consumption has been incorporated in order to simulate the 
 control. The waveforms of JT-60SA plasma operation scenario during the
control. The waveforms of JT-60SA plasma operation scenario during the 
 ramp-up and the controllability of the plasma equilibrium control using the equilibrium control simulator were reported.
ramp-up and the controllability of the plasma equilibrium control using the equilibrium control simulator were reported.
Honda, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Yoshida, Maiko; Yagi, Masatoshi; Fujita, Takaaki
Nuclear Fusion, 53(7), p.073050_1 - 073050_11, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:67.91(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Okano, Yasushi; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Topical Conference; In light of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Accident (PSAM 2013) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2013/04
Kurisaka, Kenichi; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Fujita, Satoshi*; Minagawa, Keisuke*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Takata, Takashi*
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Topical Conference; In light of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Accident (PSAM 2013) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2013/04
This study includes a level-1 PSA related to internal events and a seismic event as a representative external event for Japan sodium-cooled fast reactors with passive safety features and a seismic isolation system. For the internal events, it is necessary to evaluate the passive safety features, of which reliability depends on uncertainties of related physical phenomena. In order to consider the reliability of the passive natural circulation, accident sequences leading to core damage result from natural circulation failure were developed, and the annual frequency of the accident sequences was evaluated for the PSA method study. In respects of seismic event, we developed response analysis method considering the coupling effect of horizontal and vertical shaking on the horizontal seismic isolation characteristics, and developed a fragility evaluation model including the effect of seismic non-linearly for the seismic isolation system.
Honda, Mitsuru; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Yoshida, Maiko; Fujita, Takaaki
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Schneider, M.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Baruzzo, M.*; Bolzonella, T.*; Farina, D.*; Figini, L.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/01
Dependence of heat transport on isotopic composition is investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas for the application to ITER. The identical profiles of 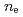 ,
, 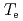 and
and 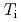 are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total
are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total 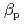 regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
Okano, Yasushi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Kubo, Shigenobu; Sakai, Takaaki; Nakai, Ryodai
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/12
General safety approaches are developed for next generation SFR based on the fundamental safety characteristics with incorporating lessons learned from the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi accidents. The fundamental characteristics are: reactivity, coolant pressure, sub-cool margin, ultimate heat sink, and sodium properties. These points are considered to derive general safety approach related to fundamental function. The key is to apply passive safety for prevention/mitigation of severe accident in design extension condition (DEC) with balancing active safety systems - passive mechanism should be built-in design for reactor shutdown and decay heat removal especially for DEC in order to enhance diversity to the engineered safety systems utilized for design basis accident. For containment integrity, the potentials of pressure/temperature increases via sodium leak and of significant mechanical energy release by re-criticality in the course of the CDA should be eliminated.
Ohira, Shigeru; Fujita, Takaaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(12), p.768 - 770, 2012/12
This time, (1) the 11th BA Steering Committee (6 Nov.), (2) the 10th IFMIF/EVEDA Project Committee (PC, 18-19, Oct.), (3) the 11th IFERC PC (2-3 Oct.), (4) the 11th Satellite Tokamak (JT-60 SA) PC, latest activities in Rokkasho and progress of upgrade for JT-60SA are reported. At (1), the 2013 Annual Program and revised Project Plan, etc. were approved. At (2), the review of SRF Linac test, etc. were reported and discussed. At (3), the overall plan of REC, implementation of new four DEMO R&D items, etc. were presented and discussed. At (4), progress of upgrade for JT-60SA were reported from EU-IA and JA-IA and reviewed and discussed. The 3rd Platform Meeting for DEMO safety was held with participants from JAEA, Industry and universities. Technical meeting for installation and commissioning of the IFMIF Prototype Accelerator was held. Manufacturing of parts for JT-60SA are in progress in both EU and Japan, and disassemble of JT-60U main parts has been done in Oct. as scheduled.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 52(11), p.114021_1 - 114021_10, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:69.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energy confinement properties for hydrogen and deuterium H-mode plasmas are investigated. The stored energy for deuterium becomes larger approximately by a factor of 1.7-2.0 than that for hydrogen at a given heating power. When the stored energy is fixed for both cases, the required power differs roughly a factor of 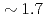 and the identical spatial profiles of electron density
and the identical spatial profiles of electron density 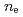 , electron temperature
, electron temperature 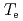 and ion temperature
and ion temperature 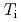 are obtained. Despite almost the same power crossing the separatrix, type-I ELM frequency for hydrogen becomes approximately in double from that for deuterium. The pedestal pressure differs approximately by a factor of
are obtained. Despite almost the same power crossing the separatrix, type-I ELM frequency for hydrogen becomes approximately in double from that for deuterium. The pedestal pressure differs approximately by a factor of 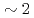 for the cases between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas at a given absorbed power. The relation between
for the cases between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas at a given absorbed power. The relation between 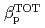 and
and 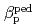 is almost identical regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
is almost identical regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 52(10), p.103012_1 - 103012_7, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The unified effect of counter toroidal rotation and heating power on type-I ELMs was investigated in JT-60U tokamak. ELM frequency 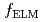 increased monotonically together with the power across the sepratrix
increased monotonically together with the power across the sepratrix 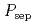 for all the cases of tangential NBs. However, dependence of
for all the cases of tangential NBs. However, dependence of 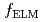 on
on 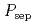 was explicitly stronger than a proportional relation when the perpendicular NBs were injected. The toroidal rotation velocity at the H-mode pedestal
was explicitly stronger than a proportional relation when the perpendicular NBs were injected. The toroidal rotation velocity at the H-mode pedestal 
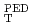 shifted continuously in counter direction when the perpendicular NBs were applied. At fixed values of
shifted continuously in counter direction when the perpendicular NBs were applied. At fixed values of 
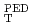 ,
, 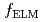 increased clearly in proportion to
increased clearly in proportion to 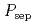 .
.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7, p.1405137_1 - 1405137_9, 2012/10
The plasma position and shape control is important issue in JT-60SA, ITER and future fusion reactor. In order to study the plasma position and shape control, we have developed a simulator which consists of an equilibrium solver and an "isoflux" controller. It is possible to simulate the position and shape control by using the "isoflux" technique and optimize the control logic of coil current in JT-60SA. It was demonstrated that the simulator can simulate the position and shape control in response to prescribed change in the configuration and internal parameters.
Ide, Shunsuke; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shiraishi, Junya; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403131_1 - 2403131_4, 2012/09
no abstracts in English

 /
/
 effect on confinement properties
effect on confinement propertiesNarita, Emi*; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Honda, Mitsuru; Isayama, Akihiko; Itami, Kiyoshi; Kamada, Yutaka; Tanaka, Yasuyuki*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403102_1 - 2403102_5, 2012/07
Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(2), p.188 - 194, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intermittent increase in background light induced by edge localized mode (ELM) in high confinement mode (H-mode) plasma gives disturbances to polarization angle of incident light measured by motional Stark effect (MSE) polarimeter using photo-elastic modulator (PEM), even if the background light is not polarized. The error in the polarization angle determined by the light intensity at the frequency modulated by the PEM originates in a broadband frequency spectrum of the intermittent background light. When the ELM frequency 
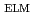 is sufficiently lower than a critical ELM frequency that is given by inverse of an apparent LPF time constant, the error has its peak, the height of which is independent of
is sufficiently lower than a critical ELM frequency that is given by inverse of an apparent LPF time constant, the error has its peak, the height of which is independent of 
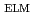 , soon after the ELM and vanishes between subsequent ELMs. However, when
, soon after the ELM and vanishes between subsequent ELMs. However, when 
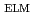 is higher than the critical ELM frequency, errors induced by subsequent ELMs pile up and the error increases with
is higher than the critical ELM frequency, errors induced by subsequent ELMs pile up and the error increases with 
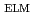 . Other dependences on background light height, LPF time constant, polarization angle of incident light are analyzed.
. Other dependences on background light height, LPF time constant, polarization angle of incident light are analyzed.