Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Sawahata, Hiroaki; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Yamazaki, Kazunori; Yanagida, Yoshinori; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Takada, Shoji; Shinozaki, Masayuki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2016/06
In the HTTR,  Cf is loaded in the reactor core as a neutron startup source and changed at frequency. In this exchange work, there were two technical issues; slightly higher radiation exposure of workers by neutron leakage and reliability of neutron source transportation container in handling. To reduce the radiation dose by neutron leakage, detail numerical evaluations using PHITS code were carried out, the effective shielding method for fuel handling machine was proposed. Easily removable polyethylene blocks and particles were used as the neutron shielding, and installed in the cooling paths of the fuel handling machine. As a result, the collective effective dose by neutron was reduced from about 700 man-microSv to about 300 man-microSv. As to the neutron source transportation container, the handling performance was improved and the handling work was safety accomplished by downsizing.
Cf is loaded in the reactor core as a neutron startup source and changed at frequency. In this exchange work, there were two technical issues; slightly higher radiation exposure of workers by neutron leakage and reliability of neutron source transportation container in handling. To reduce the radiation dose by neutron leakage, detail numerical evaluations using PHITS code were carried out, the effective shielding method for fuel handling machine was proposed. Easily removable polyethylene blocks and particles were used as the neutron shielding, and installed in the cooling paths of the fuel handling machine. As a result, the collective effective dose by neutron was reduced from about 700 man-microSv to about 300 man-microSv. As to the neutron source transportation container, the handling performance was improved and the handling work was safety accomplished by downsizing.
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakatsuka, Shigehiro*; Nishimura, Kazuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Hori, Junichi*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Tagi, Kazuhiro*; Seki, Toshichika*; et al.
Reviews of Accelerator Science and Technology, 8, p.181 - 207, 2015/00
We choose nuclear data and nuclear material inspection for energy application and nondestructive testing of explosive and hidden nuclear materials for security application. 90 keV electrostatic accelerators of deuterium are commercially available for nondestructive testing. For nuclear data measurement, electrostatic ion accelerators and L-band and S-band electron linear accelerators (linac) are used for the neutron source. Compact or mobile X-band electron linac neutron sources are under development. Compact proton linac neutron source is used for nondestructive testing especially water in solids. Several efforts for more neutron intensity using proton and deuteron accelerators are also introduced.

Nakasone, Akari*; Fujiwara, Masayuki*; Fukao, Yoichiro*; Biswas, K.; Rahman, A.*; Yamada, Maki*; Narumi, Issei; Uchimiya, Hirofumi*; Ono, Yutaka
Plant Physiology, 160(1), p.93 - 105, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.62(Plant Sciences)Okuda, Takanari*; Fujiwara, Masayuki*; Nakai, Tatsuyoshi*; Shibata, Kenichi*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Inoue, Masaki; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Onuki, Somei*; Fujisawa, Toshiharu*; Abe, Fujio*
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), p.9229_1 - 9229_4, 2009/05
Oxygen content in ODS ferritic steel is the most important element to determine the mechanical properties. The oxygen contamination from the air is perfectly prevented by using new designed ball mill and the subsequent process control. Zr, Hf and Ti added ODS steels with three oxygen levels for the evaluation tests are fabricated.
Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ukai, Shigeharu; Nakai, Tatsuyoshi*; Fujiwara, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1213 - 1217, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Friction welding between oxide-dispersion-strengthened-steel (ODS) and ferritic-martensitic 11Cr-0.5Mo-2W, V, Nb steel (PNC-FMS) was examined to investigate the feasibility of the welding of this alloy combination. Forge pressure was varied in the welding test to investigate the effect on the soundness of the weld joint. Post weld heat treatment was necessary for the weld joint because the heat affected zone caused quench hardening in the as-welded condition. The welds were cross-sectioned and examined to determine their metallurgical structure, hardness and tensile strength. Since the heat treatment produced a softening zone near the weld interface, the furnace- cooling rate was investigated at which the softening did not occur. The weld joints were cold rolled and the soundness of the weld interface was determined by the tensile test with the cold rolled weld joints.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Sakasegawa, Hideo; Fujiwara, Masayuki; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.160 - 165, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:95.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper describes the effect on creep strength and microstructure of 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened martensitic steel (9Cr-ODS steel) brought by the differences in titanium concentration and consolidation temperature. The increase of titanium concentration to 0.30-0.35wt% was shown to provide remarkable improvement of creep strength accompanied by the increase of residual-alpha ferrite. The elevation of hot-extrusion temperature notably degraded the creep strength, however, appeared to increase the volume fraction of residual-alpha ferrite. Creep deformation process of 9Cr-ODS steel was discussed to explain these results based on microstructure observations.
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D. J.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Fujiwara, Masami*; Kirneva, N.*; Lackner, K.*; Nagami, Masayuki; Pustovitov, V. D.*; Uckan, N.*; Wesley, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S1 - S17, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:744 Percentile:99.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The Progress in the ITER Physics Basis document is an update of the ITER Physics Basis (IPB), which was published in 1999. The IPB provided methodologies for projecting the performance of burning plasmas, developed largely through coordinated experimental, modeling and theoretical activities carried out on today's tokamaks (ITER Physics R&D). In the IPB, projections for ITER (1998 Design) were also presented. The IPB also pointed out some outstanding issues. These issues have been addressed by the International Tokamak Physics Activities (ITPA), which were initiated by the European Union, Japan, Russia and the U.S.A.. The new methodologies of projection and control developed through the ITPA are applied to ITER, which was redesigned under revised technical objectives, but will nonetheless meet the programmatic objective of providing an integrated demonstration of the scientific and technological feasibility of fusion energy.
Narita, Takeshi*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
JAEA-Research 2006-050, 85 Pages, 2006/10
In 9Cr ODS martensitic steel, tungsten(W) is a solid solution strengthening element, whose addition increases high-temperature strength by the combined effect with oxide dispersion strengthening. However, its excessive addition results in the increase of ferrite phase causing precipitation of intermetallic compound (Laves phase) under high temperature irradiation condition and thus ductility degradation. The amount of W addition therefore should be as low as possible. In this report, the effects of W on microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of 9Cr ODS martensitic steels were examined for obtaining insights into optimum W concentration in terms of high-temperature strength and ductility. The results obtained are as follows: (1)In the 9CrODS martensitic steel, addition of W exceeding 2mass% is shown to cause precipitation of Laves phase which degrades the ductility and fracture toughness. It can be said that the current specification of W concentration, i.e. 2mass%W, is appropriate. (2)Hardness and tensile strength is shown to increase with W concentration. This increase is caused by the increase of solid solution strengthening and residual-alpha ferrite. The retainment of residual-alpha ferrite is enhanced by the addition of W (ferrite former element). The improvement of tensile strength at 973K provided by the solid solution strengthening is shown to be equivalent to that provided by the retainment of residual-alpha ferrite. (3)It would be open task to explorer an improved alloy design concept, i.e. decrease of W as low as possible and increase of residual-alpha ferrite. The degradation of high-temperature strength by decreasing W addition can be made up by the increasing fraction of residual-alpha phase that is provided by reduction of austenite former elements and increasing addition of ferrite former elements.
Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki*; Kobayashi, Toshimi*
Materia, 45(1), p.48 - 50, 2006/01
Development of 9Cr-ODS ferritic/martensitic steel cladding was introduced as a new technology applied onece a year by Japan Institute of Metal. This cladding was developed by JAEA, and manufacturing of cladding was originally attained by controlling microstructure. Its high temperature strength is the most superior in the world as a heat resistance ferritic steels.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Fujiwara, Masayuki; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi
JNC TN9400 2005-034, 197 Pages, 2005/08
Oxide dispersion strengthened(ODS) martensitic steel (9CrODS steel) has been identified as an attractive candidate for advanced fast reactor (FR) fuel cladding tube because of its superior high-temperature strength and radiation resistance. Our recent activities revealed that high-temperature strength of different lots of the cladding tubes is inconsistent each other, even though the same manufacturing process was applied to these tubes. This inconsistency means a critical problem that high-strength 9CrODS steel cladding tubes can not be manufactured reliably and consistently. In this report, a microstructure control technique for consistently and reliably manufacturing high-strength 9CrODS steel cladding tubes are examined based on a series of data concerning effect of excess oxygen concentration on high temperature strength and microstructure of 9CrODS steel.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
Materials Transactions, 46(3), 487 Pages, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:87.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)None
Narita, Takeshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
JNC TN9400 2004-011, 141 Pages, 2004/04
Mass production capability of ODS martensitic steel claddinghas been evaluated in the feasibility studies on commercialized fast reactor cycle system. In this study, Manufacturing the large scale mother tube which has a high degree of accuracy in size, has been successfully carried out using large scale hollow capsule. For reducing the manufacturing cost of the ODS steel claddings, manufacturing process of the mother tubes using a large scale hollow capsules is promising.
Narita, Takeshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
JNC TN9400 2003-103, 150 Pages, 2004/01
In order to apply to the real wrapper tube of "Joyo", PNC/FMS/SUS316 complex wrapper tube, which are welded at round tubes condition before cold drawing, were developped. In this study, the mechanical properties of complex tube were evaluated. As aresults, the mechanical properties of welded PNC-FMS/SUS316 is equivalent to base metal or more.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Fujiwara, Masayuki; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part A), p.372 - 376, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:99 Percentile:98.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of different percentages of excess oxygen and titanium on the mechanical property and microstructure of 9Cr-ODS steel were investigated in the wide range of excess oxygen from 0.03wt% to 0.18wt%. It was shown that the controlling of the atomic ratio between excess oxygen and titanium (x in TiOx) around 1.0 is indispensable for the high-temperature strength improvement.
Narita, Takeshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
JNC TN9400 2003-076, 81 Pages, 2003/09
Mass production capability of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) ferritic claddings are evaluated in the PhaseII of Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System. The cost for manufacturing mother tube has a dominant factor in the total cost for manufacturing ODS ferritic cladding. In this study, the large scale 9Cr-ODS martensitic mother tube were produced by overseas supplier with mass production equipments for commercialized ODS steels. The process of manufacturing the ODS mother tube consists of production of raw material powder, mechanical alloying by high energy ball mill, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and hot extrusion. Following results were obtained in this study. (1) Micro structure of the ODS steels is equivalent to that of domestic products, and fine oxides are uniformly distributed. The mechanical alloying by large capacity (1 ton) ball mill can be satisfactorily carried out. (2) A large scale mother tube (65OD 48ID
48ID 10,000L), which can produce about 60pieces of 3m length ODS ferritic claddings by four times cold rolling, have been successfully manufactured through HIP and Hot Extrusion process.(3) Rough surface of the mother tubes produced in this study can be improved by selecting the reasonable hot extrusion condition. (4) Hardness and tensile strength of the manufactured ODS steels are lower than domestic products with same chemical composition. This is owing to the high aluminum content in the product, and those properties could be improved by decreasing the aluminum content in the raw material powder.
10,000L), which can produce about 60pieces of 3m length ODS ferritic claddings by four times cold rolling, have been successfully manufactured through HIP and Hot Extrusion process.(3) Rough surface of the mother tubes produced in this study can be improved by selecting the reasonable hot extrusion condition. (4) Hardness and tensile strength of the manufactured ODS steels are lower than domestic products with same chemical composition. This is owing to the high aluminum content in the product, and those properties could be improved by decreasing the aluminum content in the raw material powder.
 (
(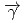 ,
,
 )
) and
and  (
(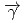 ,
,
 )
)
 reactions for
reactions for 
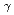 =1.5-2.4 GeV
=1.5-2.4 GeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Sumihama, Mizuki*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Dat , S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:94.9(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 = +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutron
= +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutronNakano, Takashi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Date, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(1), p.012002_1 - 012002_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:1006 Percentile:99.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Masayuki; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi; Ukai, Shigeharu
JNC TN9400 2003-008, 32 Pages, 2003/03
ODS martensitic steel is a prospective candidate cladding matenal for the advanced Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) core components. A previous result showed that the high temperature strengths were deteriorated by the oxide particle coarsening and the reduction of the residual-alpha grains as excess oxygen (EX.O) increased. In this study, the manufacturing conditions for reducing excess oxygen were examined in order to obtain the target strength. High excess oxygen steels with higher Y O
O addition were also manufactured with the intention of manufacturing the steel which has both fully martensitic microstructure and enough high temperature strength. The derived results can be summarized as follows. (1)It was shown that 0.04wt% excess oxygen was brought from the pre-alloyed raw powders, and 0.04-O.l wt% excess oxygen was mixed in the powders during the Mechanical Alloying(MA). (2)It was shown that excess oxygen could be reduced less than 0.1wt% by applying an ultra high purity Ar gas (99.9999wt%Ar) to MA atmosphere as well as reducing the agitating energy by using pin agitator with shorter length. (3)Residual alpha-grains and transformed alpha-grains were mixed in the furnace-cooled low excess oxygen steels (
addition were also manufactured with the intention of manufacturing the steel which has both fully martensitic microstructure and enough high temperature strength. The derived results can be summarized as follows. (1)It was shown that 0.04wt% excess oxygen was brought from the pre-alloyed raw powders, and 0.04-O.l wt% excess oxygen was mixed in the powders during the Mechanical Alloying(MA). (2)It was shown that excess oxygen could be reduced less than 0.1wt% by applying an ultra high purity Ar gas (99.9999wt%Ar) to MA atmosphere as well as reducing the agitating energy by using pin agitator with shorter length. (3)Residual alpha-grains and transformed alpha-grains were mixed in the furnace-cooled low excess oxygen steels ( 0.1wt%EX.O). These steels are expected to have the equal high temperature strength to Mm11 because their Vickers hardness is approximately the same Mm11. (3)Full martensitic microstructure was obtained in the higher Y
0.1wt%EX.O). These steels are expected to have the equal high temperature strength to Mm11 because their Vickers hardness is approximately the same Mm11. (3)Full martensitic microstructure was obtained in the higher Y O
O and excess oxygen-added steels (E1,E2). However enough high temperature strength are not expected in these steels because the Vickers hardness of these steels after the furnace-cooling(FC) or normalizing and tempering (NT) are apparently low.
and excess oxygen-added steels (E1,E2). However enough high temperature strength are not expected in these steels because the Vickers hardness of these steels after the furnace-cooling(FC) or normalizing and tempering (NT) are apparently low.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kaito, Takeji; Narita, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Masayuki
P121,2003, 121 Pages, 2003/00
None