Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morita, Yoshimune*; Kamiya, Chiho*; Sasaki, Toshinori*; Miyagi, Toyohiko*; Sugai, Toshihiko; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Fujiwara, Osamu*
Kikan Chirigaku, 62(4), p.195 - 210, 2010/12
It is assumed that the variation of temperature and the precipitation with the climate change may affect geological environment such as the subsurface water flow. Therefore, as well as global climate change from the past to the present, investigation technology to grasp local climate change is indispensable. A palynological study was carried out using the sediment core taken from the Okute Basin, located in the northeast of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. As a result, it was appeared that in a interglacial epoch, there was much precipitation around this area, and that in a glacial epoch, became colder and more arid, compared with Kinki region in the same latitude. This shows that the modern analog method with pollen data from the sediment of the inland basin is effective technique to estimate a local climate change.
Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Sazaki, Gen*; Kikko, Tatsuhiko*; Fujiwara, Satoru; Ishikawa, Takuya*; Matsumoto, Osamu*; Morimoto, Yukio*
Crystal Growth & Design, 10(3), p.1090 - 1095, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We propose a technique for DNA crystallization using the thermal reversible process of DNA: a conversion between a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and two single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs) with temperatures. We investigated the solubility of the crystals of a DNA hexamer d(CGCGCG) and their melting temperature, at which the thermal conversion occurs. The results obtained suggest that the conversion from a dsDNA to ssDNAs results in an increase in solubility. It was shown that using this temperature-controlled technique, high-grade single crystals of the DNA hexamer could be obtained from a small amount of DNA samples. This easy-to-apply technique would be superior to the conventional vapor diffusion technique in that it allows the solubility of DNA crystals to be controlled with no need for expensive setups.
 C datings
C datingsOgami, Takashi*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Fujiwara, Osamu*; Yamaguchi, Masaaki*; Sasao, Eiji
Chigaku Zasshi, 118(4), p.665 - 685, 2009/00
The depositional process of the latest Pleistocene to Holocene shallow marine and fluvial sequences is investigated by using five drill cores from the Kiso river delta, central Japan. Based on facies analysis, the sediments were classified into 5 units; A: basal gravel, B: fluvial to intertidal sand and silt, C: transgressive lag deposit, prodelta mud or sandy silt, D: delta-front-slope sandy silt or sand, delta-front-platform sand, E: delta-plain to fluvial sand and silt. Detailed age-depth curves of each cores are reconstructed based on 107 AMS  C ages. The curves are divided into four sections; I: mainly consists of unit B with rapid accumulation (7.3-21.4 mm/yr), II: mainly consists of unit C with moderate accumulation (2.4-2.8 mm/yr), III: mainly consists of unit D with rapid accumulation (6.7-17.8 mm/yr), IV: consists of unit D and E with moderate accumulation (1.3-3.9 mm/yr). The section boundaries of I/II and II/III reflect inundation into the bay and achievement of progradational delta-front slope, respectively. The expanding rate of the bay is 10 m/yr during 10,200-7,900 cal yrs BP. The progradation rates of the delta are 3-4 m/yr (6.500-4,100 cal yrs BP), 5 m/yr (4,100-1,300 cal yrs BP), 10 m/yr (1,300 cal yrs BP to the present). These indicate the transition from transgression to regression occurred between 7,800 to 7,300 cal yrs BP. The geological cross section along the Kiso river coupled with isochrones indicates following history. (1) 10,000-7,280 cal yrs BP (K-Ah horizon): During the expansion of the bay, onlap of unit C on unit B is visible, and unit C overlapped all the core sites. (2) 7,280 cal yrs BP to present: Isochrones younger than 6,500 cal yrs BP are similar each other and cross unit boundaries of C/D and D/E. This demonstrates units C, D and E are contemporaneous heterotopic facies formed by progradational delta.
C ages. The curves are divided into four sections; I: mainly consists of unit B with rapid accumulation (7.3-21.4 mm/yr), II: mainly consists of unit C with moderate accumulation (2.4-2.8 mm/yr), III: mainly consists of unit D with rapid accumulation (6.7-17.8 mm/yr), IV: consists of unit D and E with moderate accumulation (1.3-3.9 mm/yr). The section boundaries of I/II and II/III reflect inundation into the bay and achievement of progradational delta-front slope, respectively. The expanding rate of the bay is 10 m/yr during 10,200-7,900 cal yrs BP. The progradation rates of the delta are 3-4 m/yr (6.500-4,100 cal yrs BP), 5 m/yr (4,100-1,300 cal yrs BP), 10 m/yr (1,300 cal yrs BP to the present). These indicate the transition from transgression to regression occurred between 7,800 to 7,300 cal yrs BP. The geological cross section along the Kiso river coupled with isochrones indicates following history. (1) 10,000-7,280 cal yrs BP (K-Ah horizon): During the expansion of the bay, onlap of unit C on unit B is visible, and unit C overlapped all the core sites. (2) 7,280 cal yrs BP to present: Isochrones younger than 6,500 cal yrs BP are similar each other and cross unit boundaries of C/D and D/E. This demonstrates units C, D and E are contemporaneous heterotopic facies formed by progradational delta.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Oe, Toshiaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Seichi*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Tanaka, Satoru*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Nagao, Seiya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2007-003, 120 Pages, 2007/03
The 1st information exchange meeting on Radioactive Waste Disposal Research Network was held in Nuclear Science Research Institute of Japan Atomic Energy Agency on August 4, 2006. Radioactive Waste Disposal Research Network was established by under Interorganization Atomic Energy Research Program of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, and the objective is to bring both research infrastructures and human expertise in Japan to an adequate performance level, thereby contributing to the development of the fundamental research area in the field of radioactive waste disposal. This lecture material is a collection of research presentations and discussions during the information exchange meeting.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Morita, Yoshimune*; Kamiya, Chiho*; Sasaki, Toshinori*; Miyagi, Toyohiko*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Yanagida, Makoto*; Furusawa, Akira*; Fujiwara, Osamu*; Moriya, Toshifumi*
Kikan Chirigaku, 58(3), p.123 - 139, 2006/00
A palynological study was carried out using the 25.3 m long sediment core taken from Okute basin, Mizunami city, central Japan. Sediments of this core were accumilated for more than ca. 300,000 years. From the results of pollen analysis, the sediments are devided into 15 pollen assemblages zones. These changes show a repetition of five warm and four cool stages. Each stage corresponds to MIS 9 to 1. Consequently, a temperature of MIS 5 was higher than those of MIS 7 and 9. A temperature of MIS 9 was not so high.
Umeda, Koji; Osawa, Hideaki; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Sasao, Eiji; Fujiwara, Osamu; Asamori, Koichi; Nakatsuka, Noboru
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 11(2), p.97 - 112, 2005/03
This paper describes an overview of geotectonic events in Japan from the point of view of the long-term stability of geological environment. Moreover, the current status of research/prediction technologies developed by JNC is summarized.
Umeda, Koji; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Fujiwara, Osamu; Asamori, Koichi; Kinoshita, Hirohisa; Nakatsuka, Noboru
JNC TN7400 2004-004, 58 Pages, 2004/08
This report summarizes databases for the long-term stability of geological environment in Japan.
 C dating of marine shells
C dating of marine shellsFujiwara, Osamu; Kamataki, Takanobu*; Masuda, Fujio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 223-224, p.540 - 544, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiocarbon dating of sediments using marine shells involves uncertainties due to the mixed ages of the shells mainly attributed to depositional processes also known as sedimentological time-averaging. This stratigraphic disorder can be removed by selecting the well-preserved indigenous shells based on ecological and taphonomic criteria. These criteria on sample selection are recommended for accurate estimation of the depositional age of geologic strata from 14C dating of marine shells.
Nakatsuka, Noboru; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Umeda, Koji; Fujiwara, Osamu
JNC TN7440 2003-002, 19 Pages, 2003/04
None
Fujiwara, Osamu; Sanga, Tomoji*; Omori, Hiroo*
JNC TN7410 2001-015, 29 Pages, 2001/08
Regional distribution of erosion rates has been studied to clarify the long-term stability of the geological environment in Japan. The regional distribution of erosion rates should be estimated to predict long-term geomorphological changes. This research is to estimate the distribution of erosion rates over the Japanese Islands based on the relationship between the sediment delivery rates to reservoirs and the dispersion of altitude of the drainage basins. The relationship between erosion rate E(mm/y) and dispersion of altitude D(m) of drainage basins is expressed by E=0.000044 D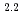 with a correlation coefficient of 0.94. This equation was used to calculate the denudation rate for each 6 km
with a correlation coefficient of 0.94. This equation was used to calculate the denudation rate for each 6 km  6 ㎞ area of the Japanese Islands using a "digital map 50 m grid". The denudation rates are, highest in the central Japanese mountains (
6 ㎞ area of the Japanese Islands using a "digital map 50 m grid". The denudation rates are, highest in the central Japanese mountains ( 3-5 mm/y), moderate in the outer belt of Southwest Japan, the inner belt of Northeast Japan and Hokkaido (
3-5 mm/y), moderate in the outer belt of Southwest Japan, the inner belt of Northeast Japan and Hokkaido ( 2-3 mm/y), and lowest in the inner belt of Southwest Japan, outer belt of Northeast Japan and central Hokkaido (
2-3 mm/y), and lowest in the inner belt of Southwest Japan, outer belt of Northeast Japan and central Hokkaido ( 1 mm/y). These regional characteristics are closely related to the distribution of Quaternary uplift rates, which caused the regional differences in surface topography.
1 mm/y). These regional characteristics are closely related to the distribution of Quaternary uplift rates, which caused the regional differences in surface topography.
Matsusue, Kazuyuki; Fujiwara, Osamu; Sueyoshi, Tetsuo*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (6), p.93 - 104, 2000/03
None
; Yanagida, Makoto*; Fujiwara, Osamu; Ozawa, Akio*
Chigaku Zasshi, 109(3), p.366 - 382, 2000/00
None
Fujiwara, Osamu; Sanga, Tomoji*; Omori, Hiroo*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (5), p.85 - 93, 1999/12
None
Fujiwara, Osamu; Masuda, Fujio; Sakai, Tetsuya*; Irizuki, Toshiaki*; Fuse, Keisuke*
Dai Yonki Kenkyu, 38(1), p.41 - 58, 1999/02
None
Irizuki, Toshiaki*; Fujiwara, Osamu; Fuse, Keisuke*; Masuda, Fujio*
Kaseki, (64), p.1 - 22, 1998/07
None
Machida, Hiroshi*; Yamazaki, Haruo*; Arai, Fusao*; Fujiwara, Osamu
Chigaku Zasshi, 106(3), p.432 - 439, 1997/00
None
Kamataki, Takanobu; Fujiwara, Osamu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English