Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fukahori, Tokio
JAEA-Conf 2024-002, p.6 - 11, 2024/11
The author has been keeping relationship with Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library for around 38 years. During this period, he has been contributing code developments, for example, Preequilibrium Nuclear Reaction Calculation Code (ALICE-F) and Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System (PHITS). The author has also been assisting for EXFOR activities and promoting Evaluated Nuclear Data Processing Code (FRENDY) and Multiphase Multicomponent Detailed Thermal Fluid Analysis Code (JUPITER). In this paper, introduced are the outline of the author's works. Also reported are the author's perspective and challenge for the future form of nuclear data.
Fukahori, Tokio
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (137), p.1 - 10, 2024/02
At the request of the EC/Joint Research Center, the author attended on an EU-sponsored side event "Providing the best nuclear data for tomorrow's nuclear solutions: challenges and opportunities" held simultaneously at the IAEA 67th General Conference as a panelist. Presented were the prospects for nuclear data activities in Japan and discussed the sustainability and revitalization of nuclear data activities. In addition, based on the roundtable discussion at this side event, the Nuclear Data Section held a meeting consisting mainly of panelists to consider future responses. In this article, I would like to report on the side event and subsequent follow-up meetings and discuss the background of these meetings.
Fukahori, Tokio; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
, 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
The Investigative Committee on Nuclear Data investigates and observes global trends in nuclear research and development and conducts comprehensive examinations of Japanese nuclear data activities from a broader perspective, as well as cooperation with domestic and foreign academic institutions in a wide range of fields other than the Atomic Energy Society. We aim to establish a system for communication, information exchange, and interdisciplinary cooperation. In this report, we will report on three of the main activities for the 2021-2022 term: a request list site for nuclear data, human resource development, and roadmap production.
Fukahori, Tokio
INDC(JPN)-210 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
The  U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the
U(n,f) cross section values were not correctly compiled in the ENDF format, and wrong values are disseminated in the JENDL/HE-2007 file. The high energy part of the  U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct
U(n,f) cross section for the JENDL/HE-2007 library was evaluated by using the results of the FISCAL code. The correct  U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
U(n,f) cross section values of the JENDL/HE-2007 library above 200 MeV is given in this report.
Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kosako, Kazuaki*; Fukahori, Tokio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.911 - 922, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fukahori, Tokio
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (135), p.19 - 25, 2023/06
Initially, the Sigma Committee consisted of two sides of the same coin: the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) Sigma Special Committee and the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) Sigma Research Committee. It is original the Sigma Committee conducts actual work such as research, evaluation and evaluation of nuclear data (including measurement, called "nuclear data activity") rather than a "place for examination" that can be felt from the sense of the word "committee". At present, the AESJ's Investigation Committee of Nuclear Data and the JAEA's JENDL Committee are working independently, and the JENDL Committee has taken over the actual work of producing nuclear data files. On the occasion of the 60th anniversary of the Sigma Committee, we have reviewed its progress and historical description so far given in the references.
Fukahori, Tokio
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (134), p.34 - 45, 2023/02
On the occasion of the 60th anniversary of the founding of the Sigma Committee in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan, we will attempt to record and preserve its history as a reference for future activities.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Satoshi*
European Physical Journal A, 59(1), p.2_1 - 2_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Physics, Nuclear)Optical model or coupled-channels calculation serves as an entrance to sophisticated calculation of nuclear data. It was a great contribution of Dr. Efrem Sh. Soukhovitsukii who has developed an excellent computation scheme which takes account of the low-lying collective nuclear structure in terms of the soft-rotator + vibrational model, and integrated it into the coupled-channels calculation. In Japan, we had a fortuitous experience with him in parametrization of the optical model potential (OMP) and to employ this methodology in nuclear data evaluation for JENDL. Firstly, we summarize our collaborative works with him in this paper. Secondly, let us have a discussion on a new parameterization of OMP which we obtained for light nuclei within his framework, quite recently. It was found that values of the potential parameters themselves are rather similar among different nuclei while the nuclear deformation describes one of the main characteristics of each isotopes.
Fukahori, Tokio; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(7), p.413 - 414, 2022/07
, 64(7), p.413 - 414, 2022/07
The Investigation Advisory Committee on Nuclear Data monitors global nuclear research and development trends, and conducts collaborative nuclear data activities with domestic and foreign academic institutions in a wide range of fields. The aims are to contact, to exchange information, and to build an interdisciplinary cooperation system. Reported are the activities on the request list site, human resources development, and roadmap creation regarding nuclear data directly related to future nuclear data research activities, among the main activities in the 2019-2020 period.
Fukahori, Tokio
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, p.17 - 20, 2020/12
After 9 years from the accident at TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the "on-site" research and development (R&D) situation has been changed into new phase. It can be considered from understanding to predicting by many direct and indirect measurements and analyses. In this presentation, nuclear data needs for 1F decommissioning are revisited according to these situation. The needs for accident evolution characteristics, criticality management, debris storage, waste management, etc. are considered with the view point of R&D on prediction what is going on and will be happened in each stage of decommissioning.
Fukahori, Tokio
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (125), p.20 - 25, 2020/02
This report is review on one of the series presentations on "Work Reports on Nuclear Data of Sigma Special Advisory Committee in 2017-2018" at the Fall Meeting of Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ). In this report, the work plan of this Committee in the next two-years period is introduced. The AESJ Investigation Advisory Committee on Nuclear Data researches world-wide nuclear data activities, reports from the view point of wide range collaborative fields, contributes to Japanese nuclear data investigation activities with contacting many of related organizations.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Sato, Daiki*; Murakami, Nozomu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.206 - 216, 2019/09
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) started from 2015 in Japan. Since then, both experimental and analytical studies necessary for designing a new light water reactor (LWR) core with ATF candidate materials are being conducted within the Japanese ATF R&D Consortium for implementing ATF to the existing LWRs, accompanying with various technological developments required. Until now, we have accumulated experimental data of the candidate materials by out-of-pile tests, developed fuel evaluation codes to apply to the ATF candidate materials, and evaluated fuel behavior simulating operational and accidental conditions by the developed codes. In this paper, the R&D progresses of the ATF candidate materials considered in Japan are reviewed based on the information available such as proceedings of international conference and academic papers, providing an overview of ATF program in Japan.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:98.03(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Suyama, Kenya; Kunieda, Satoshi; Fukahori, Tokio; Chiba, Go*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(10), p.598 - 602, 2017/10
, 59(10), p.598 - 602, 2017/10
The nuclear data is the data on the reaction probability between the neutron and the nuclide in a narrow sense. However generally speaking, it is the data describing the physical change of the nuclide and the status of the nuclear ration. Since Japan had started the nuclear energy development, the nuclear data has been one of the most important technical development theme. Now, the nuclear data library of Japan, i.e., JENDL, is well recognized internationally because of the highest-accuracy and fully-furnished types of the included data. This serial lecture describes the significance and the status of the nuclear data development, the international trend, and the direction of the future development.
Tada, Kenichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kunieda, Satoshi; Suyama, Kenya; Fukahori, Tokio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02028_1 - 02028_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:88.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has started to develop new nuclear data processing system FRENDY (FRom Evaluated Nuclear Data libralY to any application). In this presentation, the outline of the development of FRENDY is presented. And functions and performances of FRENDY are demonstrated by generation and validation of the continuous energy cross section data libraries for MVP, PHITS and MCNP codes.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 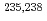 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Tada, Kenichi; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kunieda, Satoshi; Suyama, Kenya; Fukahori, Tokio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(7), p.806 - 817, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:98.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has developed an evaluated nuclear data library JENDL and several nuclear analysis codes such as MARBLE2, SRAC, MVP and PHITS. Though JENDL and these computer codes have been widely used in many countries, the nuclear data processing system to generate the data library for application programs had not been developed in Japan and foreign nuclear data processing systems, e.g., NJOY and PREPRO are used. To process the new library for JAEA's computer codes immediately and independently, JAEA started to develop the new nuclear data processing system FRENDY in 2013. In this paper, outline, function, and verification of FRENDY are described.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.41 - 46, 2016/09
Neutron- and proton-induced cross-section data are required in a wide energy range beyond 20 MeV, for the design of accelerator applications. New evaluations are performed with recent knowledge in the optical and pre-equilibrium model calculations. We also evaluated cross-sections for p+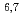 Li and p+
Li and p+ Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Fukahori, Tokio; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Yokoyama, Kenji
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (114), p.35 - 43, 2016/06
no abstracts in English