Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; Fukatsu, Yuta
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.24(Energy & Fuels)Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Civil) Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.86(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-21-09, 204 Pages, 2021/11
 Cs
Cs , and
, and  I
I in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approaches
in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approachesFukatsu, Yuta; Yotsuji, Kenji*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 211, p.106176_1 - 106176_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:75.92(Chemistry, Physical)Okubo, Takahiro*; Yamazaki, Akio*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 313, p.110841_1 - 110841_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.65(Chemistry, Applied)Pore distributions in water-saturated Ca-montmorillonite were investigated using  H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm
H NMR measurements under various dry densities (0.8 - 1.6 g/cm ) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl
) and porewater salinity conditions (deionized water, 0.1 and 1 M CaCl ), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including
), at the temperature range of 233 - 303 K. The volume fractions of the interlayer pore including two and three hydrated layers and the non-interlayer pore in compacted Ca-montmorillonite were quantified by NMR relaxometry including 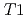 and
and 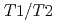 distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.
distribution analysis, and were compared with NMR cryoporometry and X-ray diffractometry. These analysis provided consistent pictures on the pore distributions in compacted Ca-montmorillonite, in contrast to Na-montmorillonite. The main factor affecting the pore distribution in compacted Ca- and Na-montmorillonite is the density, whereas the effect of porewater salinity is relatively smaller. The effect of interlayer cations is also relatively smaller at higher density, although the differences in the pore structures are significant at low density.
Fukatsu, Yuta; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishida, Keisuke*; Martin, A.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukatsu, Yuta; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishida, Keisuke*; Martin, A.*
no journal, ,
Martin, A.*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio; Ishida, Keisuke*; Muuri, E.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Havlov , V.*; Vokal, A.*
, V.*; Vokal, A.*
no journal, ,
Takei, Koyo*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta
no journal, ,
Cs adsorption sites on vermiculite clays were investigated by  Cs magic-angle-spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) and theoretical
Cs magic-angle-spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) and theoretical  Cs chemical shift calculations. A partially Cs exchanged vermiculite sample was prepared. Three peaks on
Cs chemical shift calculations. A partially Cs exchanged vermiculite sample was prepared. Three peaks on  Cs MAS NMR spectra were experimentally observed. However, Cs absorption sites were not assigned to these peaks. A molecular model of fully Cs exchanged vermiculite was built to obtain
Cs MAS NMR spectra were experimentally observed. However, Cs absorption sites were not assigned to these peaks. A molecular model of fully Cs exchanged vermiculite was built to obtain  Cs chemical shift theoretically by GIPAW method. Calculated
Cs chemical shift theoretically by GIPAW method. Calculated  Cs chemical shift ranged 23 to 47 ppm, which corresponds to the peak of the lowest field side. Detailed relationships between structure and
Cs chemical shift ranged 23 to 47 ppm, which corresponds to the peak of the lowest field side. Detailed relationships between structure and  Cs chemical shifts were investigated from Cs position and vermiculite layer structure.
Cs chemical shifts were investigated from Cs position and vermiculite layer structure.
 Cs
Cs ,
,  I
I and HTO in compacted Ca-montmorillonite by experimental and modelling approaches
and HTO in compacted Ca-montmorillonite by experimental and modelling approachesFukatsu, Yuta; Yotsuji, Kenji*; Okubo, Takahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta
no journal, ,
A low aqueous-phase diffusion in low-permeable clay barrier materials has been accepted as a critical process in the long-term performance evaluation of nuclear waste repository. Low-permeable clay materials whose pores are poorly interconnected are known to have anomalous diffusion properties that strongly impact long-term net diffusion. Related research works with mudrocks of Wakkanai formation of Horonobe URL in Japan, Opalinus clay of Mt. Terri URL in Switzerland, as well as various shale and clay mineral, utilizes a complementary suite of pore structure characterization approaches (e.g., mercury intrusion porosimetry, small angle neutron scattering) and tracer experiments followed with micro-scale mapping with laser ablation-ICP-MS. These results presents the relationship between pore connectivity and anomalous diffusion in clay materials. Pore size is not the major contributor to slow fluid flow and radionuclide transport, the anomalous behavior appears to be caused by low pore connectivity.
Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q.*; Oware, P.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Ilavsky, J.*; Almer, J.*
no journal, ,
Tachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Akagi, Yosuke*; Sato, Hisao*; Hu, Q.*; Martin, A. J.*
no journal, ,
Fukatsu, Yuta; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukatsu, Yuta; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Zhang, T.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta
no journal, ,
Tachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Akagi, Yosuke*; Sato, Hisao*; Martin, A. J.*
no journal, ,