Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
 Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.72(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
 F from
F from  O
O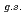 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 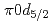 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O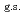 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Okane, Tetsuo; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Harii, Kazuya; Ieda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011192_1 - 011192_6, 2020/03
High energy X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements were carried out for the Spin Seebeck system Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe
(YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe
and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Wada, Michiharu*; Iimura, Hideki; Sonnenschein, V.*; Iimura, Shun*; Takamine, Aiko*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Kojima, Takao*; Ahn, D. S.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(11), p.113D02_1 - 113D02_12, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An in-flight separator, BigRIPS, at RIBF in RIKEN provides each experiment with specific nuclides separated from many nuclides produced by projectile fragmentation or in-flight fission. In this process, nuclides other than separated ones are discarded on the slits in BigRIPS, although they include many nuclides interested from the view point of nuclear structure. In order to extract these nuclides for parasitic experiments, we are developing a method using laser ion-source (PALIS). A test experiment with 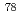 Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around
Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around  Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
 Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrier
B reaction in a lower-energy region below the Coulomb barrierDas, S. K.*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Jeong, S. C.*; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Makoto; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(5), p.055805_1 - 055805_4, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.61(Physics, Nuclear) As
As using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scattering
using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(2), p.020301_1 - 020301_5, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Faenov, A.*; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Yasuda, Ryo; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Sakai, Takuro; Shiozawa, Masahiro*; et al.
High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 3, p.e27_1 - e27_9, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:49.69(Optics)Amemiya, Kuniaki*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Maekawa, Yasunari; Shitomi, Hiroshi*; Numata, Takayuki*; Kinoshita, Kenichi*; Tanabe, Minoru*; Fukuda, Daiji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 356-357, p.154 - 159, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:67.3(Instruments & Instrumentation)Broadband low reflectance materials have various applications in the field of optical energy management; however, materials with ultra-low reflectance (below 0.1%) have been considered as mechanically delicate. We have developed a novel hard-surface optical absorber with microstructured, diamond-like carbon coated ion tracks on CR-39 plastic substrate. The spectral reflectance of the first prototype was below 2% for wavelengths ranging from 400 nm to 1400 nm; moreover, the optical absorber had mechanically hard surface and exhibited temporal durability. Choosing the appropriate design of the surface structure and coating layer is likely to reduce the reflectance to the order of 0.1%. This technique yields easy-to-handle broadband ultra-low reflectance absorbers.

Fukuda, Tatsuo; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Machida, Masahiko; Shamoto, Shinichi
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 3(2), p.290 - 293, 2015/07
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Yamazaki, Saishun; Hori, Toshihiko; Sawabe, Yuki; Chishiro, Etsuji; Fukuda, Shimpei; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Hirano, Koichiro; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 17(12), p.120101_1 - 120101_8, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.9(Physics, Nuclear)We performed a beam test of a new radio frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ III) for the beam current upgrade of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. First, the conditioning of RFQ III was conducted, and after 20 h of conditioning, RFQ III became very stable with a nominal peak power and duty factor of 400 kW and 1.5%, respectively. An off-line beam test was subsequently conducted before installation in the accelerator tunnel. The transmission, transverse emittance, and energy spread of the 50-mA negative hydrogen beam from RFQ III were measured and compared with simulation results. The experiment and simulation results showed good agreement; therefore, we conclude that the performance of RFQ III conforms to its design.
 Ca
CaSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Go, Shintaro*; Homma, Michio*; et al.
Nature, 502(7470), p.207 - 210, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:285 Percentile:99.78(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 and BaSO
and BaSO ; A Resonant X-ray emission study at the Ba-L
; A Resonant X-ray emission study at the Ba-L edge
edgeYoshii, Kenji; Jarrige, I.; Suzuki, Chikashi; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Ito, Yoshiaki*; Mukoyama, Takeshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 73(9), p.1106 - 1110, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:44.07(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have directly probed the Ba 5d states in the ferroelectric barium titanate BaTiO using resonant X-ray emission spectroscopy (RXES) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence mode (PFY-XAS) at the Ba-L
using resonant X-ray emission spectroscopy (RXES) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence mode (PFY-XAS) at the Ba-L edge. The results are compared with those of the non-ferroelectric BaSO
edge. The results are compared with those of the non-ferroelectric BaSO . While the RXES spectra point to a localized character for the Ba 5d states in both compounds, the main peak of the PFY-XAS spectrum, corresponding to the dipolar transitions from 2p to 5d, is found to be significantly broader for BaTiO
. While the RXES spectra point to a localized character for the Ba 5d states in both compounds, the main peak of the PFY-XAS spectrum, corresponding to the dipolar transitions from 2p to 5d, is found to be significantly broader for BaTiO than for BaSO
than for BaSO . On the basis of band structure calculations, this broadening is ascribed to strong hybridization between the unoccupied Ba 5d and O 2p states in the ferroelectric. This suggests that the hybridization between the conduction states of the Ba
. On the basis of band structure calculations, this broadening is ascribed to strong hybridization between the unoccupied Ba 5d and O 2p states in the ferroelectric. This suggests that the hybridization between the conduction states of the Ba and O
and O ions, and not only Ti
ions, and not only Ti and O
and O , plays a central role in determining the electronic structure of BaTiO
, plays a central role in determining the electronic structure of BaTiO .
.
Saito, Yuji; Fukuda, Yoshihiro; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Sunao*; Asano, Yoshihiro*; Hara, Toru*; Shirasawa, Katsutoshi*; Takeuchi, Masao*; Tanaka, Takashi*; et al.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 19(3), p.388 - 393, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:101 Percentile:97.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)The soft X-ray beamline BL23SU at SPring-8 has undergone an upgrade with a twin-helical undulator of in-vacuum type to enhance the experimental capabilities of the end stations. The new light source with a fast helicity-switching operation allows not only the data throughput but also the sensitivity in X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) to be improved. The operational performance and potential are described by presenting XMCD results of paramagnetic  -US
-US measured with a 10 T superconducting magnet.
measured with a 10 T superconducting magnet.
 imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillator
imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillatorNakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Takeda, Kohei*; Nishi, Ryosuke*; Minami, Yuki*; Cadatal-Raduban, M.*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(12), p.122202_1 - 122202_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.03(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate the potential of a hydrothermal method-grown ZnO as a high-spatial resolution imaging device for in-situ soft X-ray laser diagnostics by characterizing the exciton emission patterns. By plotting the emission pattern radii at each position, we estimated the evolution of the beam radius around the focal point. The beam profile of the Ni-like Ag ion plasma laser was estimated from the waist radii as 29 and 21 m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6
m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6 m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
Naganawa, Hirochika; Kumazawa, Noriyuki*; Saito, Hiroshi*; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Nagano, Tetsushi; Kashima, Kaoru*; Fukuda, Tatsuya*; Yoshida, Zenko; Tanaka, Shunichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(4), p.227 - 234, 2011/12
no abstracts in English
 CuO
CuO
Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Akahama, Hiroshi*; Kano, Jun*; Kambe, Takashi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Physica C, 471(21-22), p.766 - 769, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.3(Physics, Applied)We have investigated the magnetic and dielectric properties of Bi CuO
CuO , which has the same chemical formula as that of the parent materials of high-Tc superconductors, R
, which has the same chemical formula as that of the parent materials of high-Tc superconductors, R CuO
CuO (R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that this oxide exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition at around 40 K, owing to the localized Cu
(R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that this oxide exhibits an antiferromagnetic transition at around 40 K, owing to the localized Cu spins. Dielectric constants were found to be about 100 at room temperature, which are smaller than those of R
spins. Dielectric constants were found to be about 100 at room temperature, which are smaller than those of R CuO
CuO (about 10000 at room temperature). The imaginary part of dielectric response showed the activation energy of about 0.1 eV, suggesting that the dielectric response is brought about by a transfer of Cu-3d electrons.
(about 10000 at room temperature). The imaginary part of dielectric response showed the activation energy of about 0.1 eV, suggesting that the dielectric response is brought about by a transfer of Cu-3d electrons.
Matsubayashi, Masahito; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Yasuda, Ryo; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Sakai, Takuro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 651(1), p.90 - 94, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron imaging by color center formation in LiF crystals was applied to standard samples such as a sensitivity indicator (SI) for neutron radiography. The SI was exposed to 5 mm pinhole collimated thermal neutron beam with a LiF crystal and a neutron imaging plate (NIP) for 120 min in JRR-3 thermal neutron radiography facility. The image in NIP was read out with a readout resolution of 50  m. The image of SI in LiF crystal was read out with pixel size of 1.38
m. The image of SI in LiF crystal was read out with pixel size of 1.38  m using a laser confocal microscope. All gaps were clearly observed in the images for both LiF crystal and NIP, but small holes were not recognized for NIP. The experiment showed that LiF crystals had excellent characteristics as neutron imaging detectors such as high sensitivity, high spatial resolution, wide dynamic range and so on. In the paper, detailed characteristics of LiF crystals are compared with those of other neutron imaging detectors: NIP, a combination of fluorescent converter and cooled CCD camera.
m using a laser confocal microscope. All gaps were clearly observed in the images for both LiF crystal and NIP, but small holes were not recognized for NIP. The experiment showed that LiF crystals had excellent characteristics as neutron imaging detectors such as high sensitivity, high spatial resolution, wide dynamic range and so on. In the paper, detailed characteristics of LiF crystals are compared with those of other neutron imaging detectors: NIP, a combination of fluorescent converter and cooled CCD camera.

Fukuda, Tatsuo; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Machida, Masahiko; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Iyo, Akira*; Kito, Hijiri*; Mizuki, Junichiro; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(6), p.064504_1 - 064504_13, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)